Undoubtedly the United States has been the pioneer in technology startups, but Southeast Asia was quick to learn and implement. Moreover, global investors are looking to invest in diverse markets. Many are keeping an eye on Southeast Asian countries (ASEAN).
As per Invest ASEAN, ASEAN’s market of more than 600 million people is 9% of the world’s total population. The combined income per capita in the region for the past six years has been rising and reached an average of US$3,600 as of 2011. Singapore has the highest GDP per capita at over US$50,000, followed by Brunei at US$39,000.
According to Jungle Ventures, Southeast Asia’s technology startups had a combined valuation of $340 billion in 2020, and they anticipate this will triple by 2025. Factors such as growing middle class, high literacy, and exponentially rising startup ecosystem have attracted the interest of founders and investors.
One such technology startup Grab, founded in 2012 by Anthony Tan (while he was in Harvard Business School) and Tan Hooi Ling, is the developer of the Grab super-app, which provides users with transportation, food delivery, and digital payments services via a mobile app.
Grab currently operates in Singapore, Malaysia, Cambodia, Indonesia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam. It is Southeast Asia’s first decacorn and the biggest technology startup in the region. In April 2021, Grab went public at a valuation of $40 bn through a SPAC deal but had so far failed to deliver to shareholders (down 80% since then).
Nevertheless, it’s interesting to know how ASEAN’s biggest technology startup, Grab, started and its business model.
What is Grab, and How did it all start?
Grab was founded in 2012 when transportation in most Southeast Asian cities was generally neither accessible nor safe for many. Hooi Ling, one of the co-founders, used to take taxis home after a late night of work.
She would often call her family and friends for a sense of security. Anthony Tan and Hooi Ling set out to create a mobility solution that would make it safe and easy for anyone to commute in the ASEAN region.
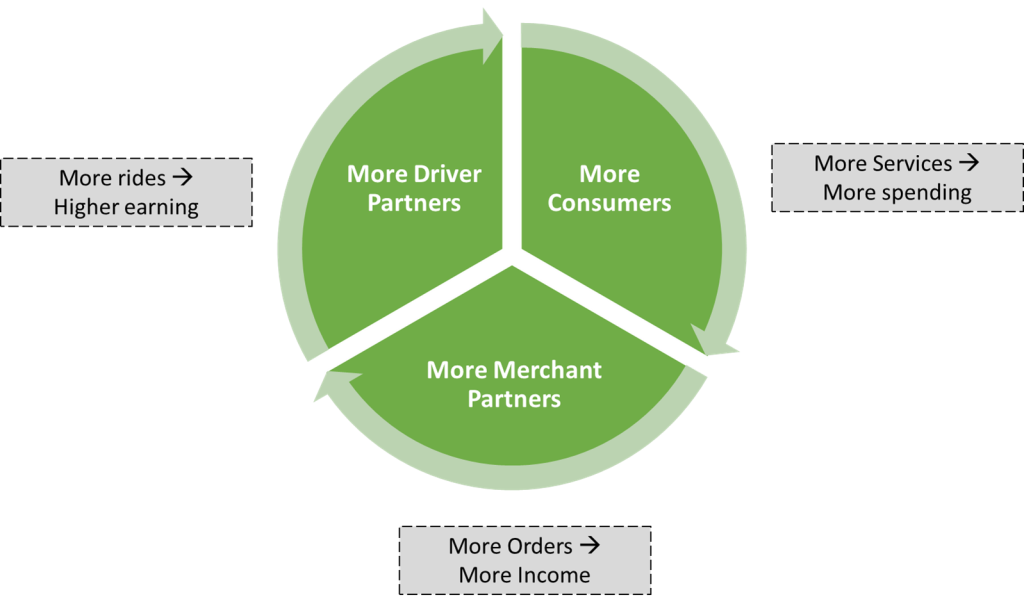
Starting with the taxi business, Grab’s business model has now become a Super App concept that enables millions of people each day to access driver- and merchant-partners to order food or groceries, send packages, hail a ride or taxi, pay for online purchases, or access services such as lending, insurance, wealth management, and telemedicine.
The following graphic summarizes the scale of Grab’s business model.

Key Thematic Drivers for Grab’s Industry in Southeast Asia
- Rapid urbanization is driven by macroeconomic and demographic growth.
- Mobile-first population with increasing digital engagement.
- The increasing digitalization of services and consumption.
- Regulatory landscape supportive of technology and digital advancement.
- Large unbanked and underserved population.
[icon name=”lightbulb”] How does Uber work & make money | Business Model
What is the business model of Grab?
Value Proposition
Customers: More offerings and partners on Grab drive more incredible selection, better value, more bookings, and faster delivery times. Focus on providing a broad range of key offerings contributes to the resilience of Grab’s business model.
Driver Partners: Ability to earn a sustainable living, flexibility to work, access to Grab’s financial services, and ability to manage workflows are some of the key value propositions of Grab for its 5 Million (as of 2020) driver community.
Merchant Partners: Grab has 4 million (as of 2020) merchant partners, ranging from small restaurants, convenience, and grocery stores, to multinational franchises and lifestyle service providers. These merchants can access Millions of Grab’s users to sell their services while being empowered to manage their advertisements and track performance.
Offerings
Deliveries: Grab’s delivery platform connects drivers and merchant partners with consumers to create a local logistics platform, facilitating on-demand and scheduled delivery of a wide variety of daily necessities, including in selected markets, ready-to-eat meals, and groceries, as well as point-to-point package delivery.
Mobility: Grab offers to connect driver-partners with consumers seeking rides across a wide variety of multi-modal mobility options, including private cars, taxis, motorcycles in certain countries, and shared mobility options such as carpooling in selected markets.
Financial Services: Grab’s financial services offerings include digital solutions to address the financial needs of the driver- and merchant-partners and consumers, including digital payments, lending, receivables factoring, insurance distribution, and wealth management in selected markets.
Enterprise and New Initiatives: Grab has a suite of enterprise offerings, including advertising and marketing offerings, GrabAds, and anti-fraud offerings, GrabDefence.
In addition, Grab’s partners offer other lifestyle services to consumers through its super app, including domestic and home services, flights, hotel bookings, subscriptions, and more in certain countries.
Revenue
Grab generated $675 Mn in FY2021, 44% higher than FY2020. Grab primarily generates revenue through 4 streams.
- Mobility: Grab makes money from driver-partners and consumers by connecting consumers with transportation rides provided by driver-partners across various multi-modal mobility options. In FY21, the mobility segment contributed 22% to the revenue.
- Deliveries: Grab makes money from driver-partners, merchant-partners, and consumers by connecting driver-partners and merchant-partners with consumers to facilitate deliveries, including prepared meals and groceries, as well as point-to-point parcel delivery. In FY21, the deliveries segment contributed 68% to the revenue.
- Financial Services: Grab earns fees from digital payment processing services charged to merchant partners primarily based on the total payments volume (“TPV”) processed through its platform. TPV is the value of payments, net of payment reversals, successfully completed through Grab’s platform. . In FY21, the financial services segment contributed 4% to the revenue.
- Enterprise & New initiatives: Grab earns fees from enterprise offerings predominantly from digital advertising and marketing services. In FY21, the enterprise segment contributed 6% to the revenue.
[icon name=”lightbulb”] How does Shopify make money | Business Model
Conclusion
Grab started by providing a platform addressing the mobility opportunity in Southeast Asia. Grab has since expanded its platform to manage food and other deliveries and e-wallet opportunities.
As Grab continues to expand its business model and increase the breadth of its offerings over time, it increases its addressable market. Grab believes there is an enormous opportunity to help millions of small businesses in ASEAN that are operating in an informal economy to navigate an increasingly digital world.
Grab wishes to leverage its existing reach with its driver- and merchant partners to provide digital tools and train critical to thriving in the increasingly digital economy, helping lay the foundations for more inclusive growth across the region.
With Grab’s scale, ecosystem, and platform advantages, it seems well-positioned to navigate the complexity of Southeast Asia and address certain vital challenges in the region.