Apple is a brand that needs no introduction or context. As of Jan’22, Apple CEO Tim Cook revealed that Apple now has 1.8 billion active devices. On average, 1 in every four is touched by Apple. In this strategy story, we will look at the business model of Apple and understand how does Apple make money.
In simple terms, Apple designs, manufactures, and markets smartphones, personal computers, tablets, wearables, and accessories and sells a variety of related services. Apple designs and develops nearly the entire solution for its products, including the hardware, operating system, numerous software applications, and related services.
What are the components of the business model of Apple?
Products
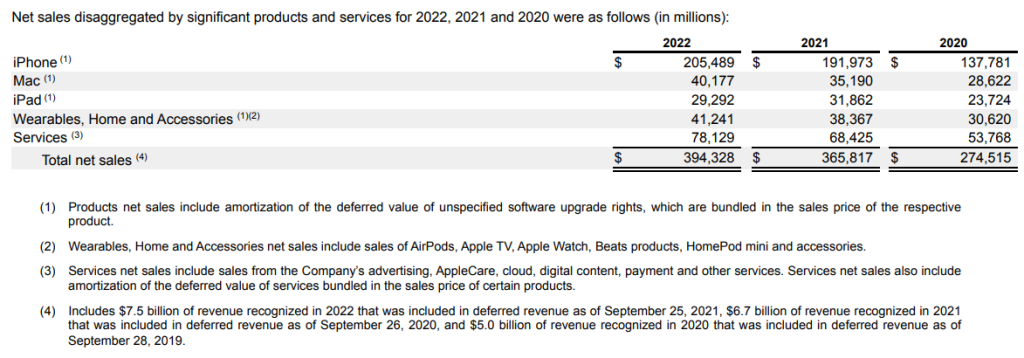
iPhone: iPhone is Apple’s line of smartphones based on its iOS operating system. The iPhone line includes iPhone 14 Pro, iPhone 14, iPhone 13, iPhone SE, iPhone 12, and iPhone 11.
Mac: Mac is Apple’s line of personal computers based on its macOS operating system. The Mac line includes laptops, MacBook Air and MacBook Pro, as well as desktops iMac, Mac mini, Mac Studio, and Mac Pro.
iPad: iPad is Apple’s line of multipurpose tablets based on its iPad operating system. The iPad line includes iPad Pro, iPad Air, iPad, and iPad mini.
Wearables, Home, and Accessories:
- AirPods, Apple’s wireless headphones, including AirPods, AirPods Pro, and AirPods Max
- Apple TV, Apple’s media streaming and gaming device based on its tvOS operating system, including Apple TV 4K and Apple TV HD;
- Apple Watch, Apple’s line of smartwatches based on its watchOS operating system, including the Apple Watch Ultra,
- Apple Watch Series 8 and Apple Watch SE, and
- Beats products, HomePod mini, and accessories
Services
Advertising: Apple’s advertising services include various third-party licensing arrangements and Apple’s own advertising platforms.
AppleCare: Apple offers a portfolio of fee-based service and support products under the AppleCare brand. The offerings provide priority access to Apple technical support, access to the global Apple authorized service network for repair and replacement services, and in many cases, additional coverage for instances of accidental damage and/or theft and loss, depending on the country and type of product.
Cloud Services: Apple’s cloud services store and keep customers’ content up-to-date and available across multiple Apple devices and Windows personal computers.
Digital Content: Apple operates various platforms, including the App Store, that allow customers to discover and download applications and digital content, such as books, music, video, games, and podcasts. Apple also offers digital content through subscription-based services, including:
- Apple Arcade, a game subscription service;
- Apple Fitness+, a personalized fitness service;
- Apple Music, which offers users a curated listening experience with on-demand radio stations,
- Apple News+, a subscription news and magazine service; and
- Apple TV+, which offers exclusive original content and live sports.
Payment Services: Apple offers payment services, including Apple Card, a co-branded credit card, and Apple Pay, a cashless payment service.
Apple’s services compete with business models that provide content to users for free and use illegitimate means to obtain third-party digital content and applications.
Markets and Distribution
Apple’s customers are primarily in the consumer, small and mid-sized business, education, enterprise, and government markets. Apple sells its products and resells third-party products in most of its major markets directly to consumers, small and mid-sized businesses, education, enterprise, and government customers through its retail and online stores and direct sales force.
Apple also employs a variety of indirect distribution channels, such as third-party cellular network carriers, wholesalers, retailers, and resellers. In 2022, Apple’s net sales through its direct and indirect distribution channels accounted for 38% and 62% of total net sales.
Marketing & Advertising Strategy of Apple: A critical lens
Supply Chain
Apple’s global supply chain is large and complex, and a majority of the Company’s supplier facilities, including manufacturing and assembly sites, are located outside the U.S. As a result, Apple’s operations and performance depend significantly on global and regional economic conditions.
Apple relies on single-source outsourcing partners in the U.S., Asia, and Europe to supply and manufacture many components and on outsourcing partners primarily located in Asia for the final assembly of substantially all of Apple’s hardware products.
Although most components essential to Apple’s business are generally available from multiple sources, certain components are currently obtained from single or limited sources. Apple also competes for various components with other market participants for smartphones, personal computers, tablets, wearables, and accessories.
Therefore, many components used by Apple, including those available from multiple sources, are subject to industry-wide shortages and significant commodity pricing fluctuations.
Apple uses some custom components that its competitors do not commonly use, and new products introduced by Apple often utilize custom components available from only one source. When a component or product uses new technologies, initial capacity constraints may exist until the suppliers’ yields have matured or their manufacturing capacities have increased.
Substantially all of Apple’s manufacturing is performed in whole or in part by outsourcing partners located primarily in Asia, including mainland China, India, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and Vietnam.
Why you never see any social media post from Apple
How does Apple make money?
Apple made $394 billion in FY22. Total net sales in FY22 increased 8% or $28.5 billion, compared to 2021, driven primarily by higher net sales of iPhone, Services, and Mac. Business model of Apple makes money from selling iPhones, Mac, iPad, Services, and other products. Apple manages its business primarily on a geographic basis. Apple’s reportable segments consist of the Americas, Europe, Greater China, Japan, and the Rest of Asia Pacific.
The Economics of Apple One: Pricing Strategy
Although each region provides similar hardware and software products and similar services, each one is managed separately to better align with the location of Apple’s customers and distribution partners and the unique market dynamics of each geographic region.