In some form or another, money has been part of human history for at least the past 5,000 years. The earliest known mints date to 650 and 600 B.C. in Asia Minor, where the elites of Lydia and Ionia used stamped silver and gold coins to pay armies.
Before that time, historians generally agree that a system of bartering was likely used. After thousands of years, something strange happened in 1983.
In 1983, the American cryptographer David Chaum conceived an anonymous cryptographic electronic money called ecash. But since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, many new currencies have come and been widely accepted by markets. So much so that some billionaires have been advocating the use of Crypto. Ethereum (ETH), Litecoin (LTC), Cardano (ADA)- the list is endless.
Barteringà Moneyà Crypto, we have come a long way. Be it any form of currency; traders need an exchange platform to make gains. The internet has unleashed multiple waves of innovation that are continuing to connect and transform many aspects of modern society across geographies.
To share a fact on the wide acceptability of Crypto, the overall market capitalization of crypto assets grew from less than $500 million to $782 billion between December 31, 2012, and December 31, 2020, representing a CAGR of over 150%.
Coinbase is one such cryptocurrency exchange platform that, as of Mar’22, enables approximately 89 million retail users, 11,000 institutions, and 210,000 ecosystem partners to engage with crypto assets. Such numbers made me curious to learn the business model of Coinbase and understand how it makes money. But let’s go step by step.
What is Coinbase?
Founded in 2012 by Brian Armstrong and Fred Ehrsam, Coinbase is an American company that operates a cryptocurrency exchange platform. It is the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the United States by trading volume. Coinbase operates as a remote-first company and has no physical headquarters.
Today’s financial system relies upon a patchwork of intermediaries that spans banks, brokers, clearinghouses, custodians, exchanges, payment processors, and their networks to facilitate money movement, safekeeping, lending, credit, and other capital markets activity.
Bound by legacy infrastructure and processes, trust and reliance on this complex web of intermediaries impose access, efficiency, and cost limitations.
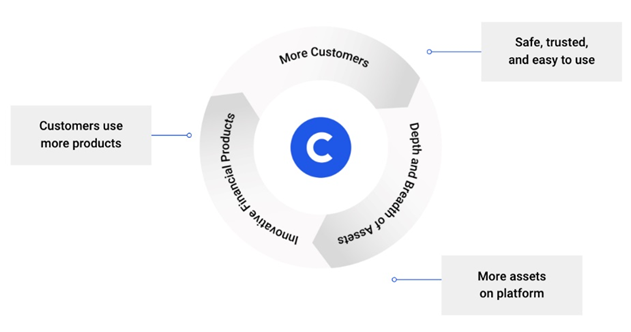
Understanding the challenges, Coinbase went on a mission to create an open financial system for the world. Coinbase is operating in a market with limitless opportunities as Crypto has the potential to be as revolutionary and widely adopted as the internet. So does the Coinbase.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are the highest traded currency on Coinbase, with 24% and 21% shares in trading volume. Coinbase went public in April 2021, valuing it at $85.8 billion.
Before we understand how Coinbase makes money, let’s go deep into the different components of Coinbase’s unique business model.
What makes Coinbase’s business model so unique?
Value Proposition
Coinbase has primarily three stakeholders: retail, institutions, and ecosystem partners, and has a unique value proposition for each of them.
Retail users: Coinbase offers the primary financial account for the crypto-economy – a safe, trusted, and easy-to-use platform to invest, store, spend, earn, and use crypto assets. As of Mar’22, 89 Million+ retail users who contributed 33% to the trading volume on Coinbase.
Institutions: Coinbase provides hedge funds, money managers, and corporations a one-stop-shop for accessing crypto markets through advanced trading and custody technology. As of Mar’22, there are 11,000 institutional users who contributed 66% of the trading volume on Coinbase.
Ecosystem partners: Coinbase provides developers, merchants, and asset issuers a platform with technology and services to build applications that leverage crypto protocols, actively participate in crypto networks, and securely accept cryptocurrencies as payment. As of Mar’22, Coinbase had 210,000 ecosystem partners.
Key Products
Coinbase creates products and services for its customers using its proprietary technology infrastructure that has been purpose-built to meet the needs of the crypto economy.
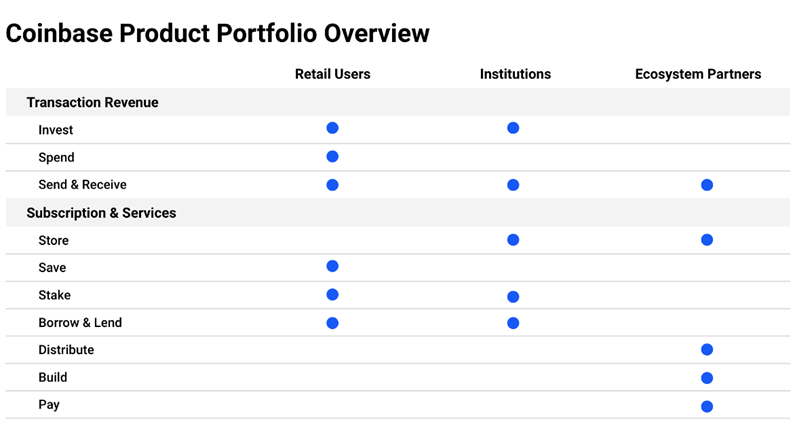
Coinbase enables its retail and institutional customers to safely and easily invest, spend, send and receive, store, save, stake, borrow, lend, distribute, build, pay, and access and transact with crypto assets.
Coinbase continues to grow its products and services to further its goal of becoming the primary financial account for all users to access the crypto-economy.
Coinbase has additional products that provide infrastructure and technology critical to support the growth of a vibrant ecosystem for its ecosystem partners. Coinbase has three products for its ecosystem partners:
- Distribute: Asset issuers engage with Coinbase customers through its learn and earn technology, where it distributes educational videos to its retail users to learn about new crypto assets and applications. This helps asset issuers to engage with the customer base and ultimately monetize that engagement.
- Build: Coinbase offers various infrastructure technology and services to empower current and future builders of the crypto economy. For example, Coinbase offers Coinbase analytics to law enforcement and financial institutions to monitor blockchain transactions. Its Rosetta tool makes it easier for developers to build applications that work across different blockchains.
- Pay: Coinbase Commerce helps merchants anywhere in the world accept cryptocurrency payments fully decentralized.
Competitive Advantages
The crypto-economy is highly fragmented, quickly evolving, and competitive. Coinbase faces significant competition from large, established financial incumbents to smaller, early-stage financial technology providers and companies native to the crypto-economy, such as decentralized exchanges.
Coinbase competes with traditional financial technology and brokerage firms like Square, Robinhood, and PayPal, which have recently introduced crypto products and services for retail users.
For institutions, Coinbase primarily competes with other crypto-focused companies and a few traditional financial incumbents that offer a point or siloed solutions.
But Coinbase has built certain competitive advantages to achieve its mission of creating an open financial system for the world:
- A cohesive ecosystem of products and services to address the distinct needs of customers
- A full-stack technology platform that is purpose-built for the crypto-economy
- Significant investments in regulatory compliance and licensure, advanced cryptography, and security expertise
- The market-leading brand exclusively focused on the crypto-economy
- Significant scale with over 11.5% of global crypto assets on its platform.
Key business metrics
Coinbase uses the following key business metrics to evaluate business and measure performance.
| Metric | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Verified Users (Mn) | 32 | 43 | 89 |
| Monthly Transacting Users (Mn) | 1 | 2.8 | 11.4 |
| Assets on platform ($ bn) | 17 | 90 | 278 |
| Trading Volume ($ bn) | 80 | 193 | 1671 |
| Net Income ($ Mn) | -30 | 322 | 3624 |
[icon name=”lightbulb”] N26 wants to transform the way individuals manage money and change banking for the better. How?
How does Coinbase make money?
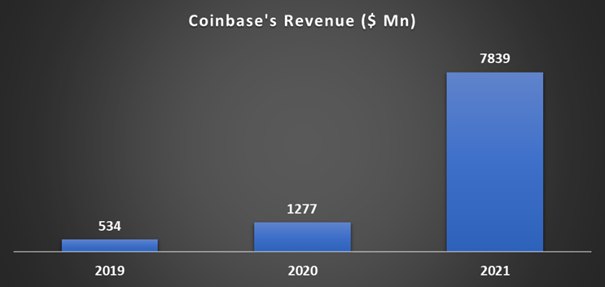
Coinbase made $7.8 billion in 2021, an astonishing growth of 524% over 2020. Coinbase is adopting the right strategies to make money.
Coinbase makes money through two revenue streams: Net Revenue (which forms 94% of revenue and includes Transaction and Subscription revenue) and Other Revenue.
Net revenue
Transaction revenue: The transaction fee earned is based on the price and quantity of the crypto asset bought, sold, or withdrawn. Transaction revenue makes up 87% of the total revenue of Coinbase.
Subscription and services revenue: Subscription and services revenue primarily consists of Blockchain rewards (Crypto assets it earns for its staking validation), Custodial fee revenue (fee to hold Crypto in its dedicated cold storage solution), Campaign revenue (campaigns by asset issuers to engage with users), Interest income and others. Subscription and service revenue make up 7% of the total revenue of Coinbase.
Other revenue
Other revenue includes selling crypto assets when Coinbase is the principal (when Coinbase is itself a trader) in the transaction.
Coinbase keeps custody of a few crypto assets if user orders do not meet the minimum trade size for execution on its platform or maintain customers’ trade execution and processing times during unanticipated system disruptions.
Coinbase records the total value of the sale as revenue. Other revenue includes interest income earned on its corporate cash and cash equivalents.
[icon name=”lightbulb”] Why did Goldman Sachs decide to become a full-service bank?
What does the future hold for Coinbase?
Although Coinbase has lost 75% in market value since its IPO, Coinbase has become the first crypto firm to enter the prestigious Fortune 500 list after posting revenue of over $7.8 billion in 2021.
Crypto has the potential to be as revolutionary and widely adopted as the internet. The unique properties of crypto assets naturally position them as digital alternatives to the store of value analogs such as gold, enable the creation of an internet-based financial system, and provide a development platform for applications that are unimaginable today.
With the increasing acceptability of Crypto by large companies like Microsoft, Burger King, and Starbucks, among many more, the sky is the limit for Coinbase- the largest cryptocurrency platform in the USA.
Coinbase would undoubtedly grow as the crypto-economy grows.