The traditional used-car retailing model is costly, operationally challenging, and difficult to scale. Providing an end-to-end solution requires inspection, repair, reconditioning, showroom facilities, and inventory sourcing and financing capabilities, all of which are traditionally done at each dealership location.
Customer acquisition is expensive and inefficient for traditional automotive retailers as they are typically confined to local advertising channels and must drive foot traffic to their physical locations, where they offer an often undifferentiated service and limited inventory.
Conventionally used car retailers are limited by staging capacity and anticipated local demand at each dealership; they generally lack the logistical capabilities to source vehicles from other locations quickly and cost-effectively.
Additionally, consumer needs are changing and have distinct expectations challenging for traditionally used car retailers to address. Consumers want a wide selection and a fair process at a reasonable price.
Carvana was built to provide a no-pressure, no-haggle experience with flexible and fast transactions in response to these evolving consumer needs. Consumers can research and identify a vehicle, inspect it using interactive high-definition photography, obtain financing and warranty coverage, value their current vehicle, complete their purchase, and schedule delivery or pick up, all from its online platform.
Just by selling used cars, Carvana makes $12 billion a year. As strategy enthusiasts, we asked ourselves how Carvana works and makes money. What are the different components of Carvana’s business model? Who are Carvana’s significant competitors?
Carvana’s business overview
Carvana, founded in 2012, is an e-commerce platform for buying and selling used cars. Carvana aims to transform the used car buying and selling experience by giving consumers what they want—a wide selection, great value and quality, transparent pricing, and a simple, no-pressure transaction.
Carvana works on a platform on which consumers can research and identify a vehicle, inspect it using 360-degree vehicle imaging technology, obtain financing and warranty coverage, purchase the car, and schedule delivery or pick-up. (Buying process)
Alternatively, a customer can obtain a firm offer online for their vehicle by answering a few questions without needing to provide photos or service records. (Selling process)
The operations of Carvana work on advanced algorithms to optimize its nationally pooled inventory of over 71,000 total website units, inspect and recondition the vehicles based on its 150-point inspection process, and operate its logistics network to deliver cars directly to customers.
Customers in specific markets also can pick up their vehicles at one of Carvana’s vending machines, which provides an exciting pick-up experience for the customer while decreasing Carvana’s variable costs, increasing scalability, and building brand awareness.
The automotive retail industry’s large size, fragmentation, and lack of differentiated offerings present an opportunity for disruption. Carvana is capitalizing on this opportunity.
Since its inception, Carvana has purchased, reconditioned, sold, and delivered approximately 1 million vehicles to customers through our website, cumulatively generating roughly $25.7 billion in revenue. (As of 2021)
Carvana has become one of the youngest companies to be included in Fortune 500.
How does Carvana make money? What is the business model of Carvana?
Value Proposition
Carvana’s business model is disrupting the traditional used vehicle sales model by focusing on delivering an unparalleled customer experience. Let’s analyze the value proposition of Carvana’s business model for buyers and sellers.
For Buyers
- Carvana’s vertically integrated platform offers a lower and differentiated cost structure critical to providing a seamless car buying and selling experience. Carvana’s end-to-end business model allows it to provide a solution while reducing the cost of operations.
- Carvana offers its customers preapproved financing options. Due to low car prices, Carvana’s customers generally have lower PTI (Payment to Income) and LTV (Loan to Value) ratios.
- In-house delivery network
For Sellers
- Carvana eliminates the need to visit a dealership or negotiate a private sale. Sellers can receive a firm offer for their vehicle from Carvana’s website simply by answering a few questions about its condition and features.
- Carvana offers fewer days to a sale than the industry average, resulting in higher selling prices.
How does Turo work and make money: Business Model
Marketing Strategy
Carvana’s customers are usually on the younger side. The marketing strategy of Carvana utilizes a multi-channel approach. Carvana combines brand building and direct response channels to seed and scale local markets efficiently.
Carvana’s paid advertising and marketing strategy includes advertisements through national and local television, search engine marketing, inventory site listing, retargeting, organic referral, display, out-of-home, digital video, digital radio, direct mail, and branded pay-per-click channels.
In addition to our paid channels, Carvana intends to attract new customers and drive repeat purchases by enhancing its earned media and public relations efforts and investing in its patented vending machines.
The network effect of Carvana’s business model
The business model of Carvana benefits from powerful network effects. Carvana’s logistics capabilities allow it to offer every car in its inventory to customers across its markets. As Carvana adds markets, the demand for its products and inventory increases.
A broader vehicle inventory would further improve its offering across markets, enabling it to increase market share. Furthermore, increased brand awareness, driven by national advertising, will allow Carvana to expand its nationwide inventory and further these network effects.
Supply Chain of Carvana
Vehicle sourcing and acquisition: Carvana acquires most of its used vehicle inventory from wholesale auctions. To a lesser extent, Carvana acquires vehicles from consumers and directly from used vehicle suppliers, including franchise and independent dealers, leasing companies, and car rental companies.
Inspection and reconditioning: After acquiring a vehicle, Carvana transports it to one of its inspection and reconditioning centers, where it undergoes a 150-point inspection and is reconditioned to meet “Carvana Certified” standards.
Photography and merchandising: Carvana photographs vehicles to display interactive, 360-degree images of each car on its website, along with a list of features and imperfections to assist customers in evaluating each vehicle.
Logistics and fulfillment: Carvana finally transports purchased vehicles to their local market for home delivery or pick-up from vending machines. These vending machines are multi-story glass towers where our customers deposit a token into a coin slot. An automated platform delivers the purchased vehicle to a garage bay where the customer is waiting.
How does Carvana make money: revenue model
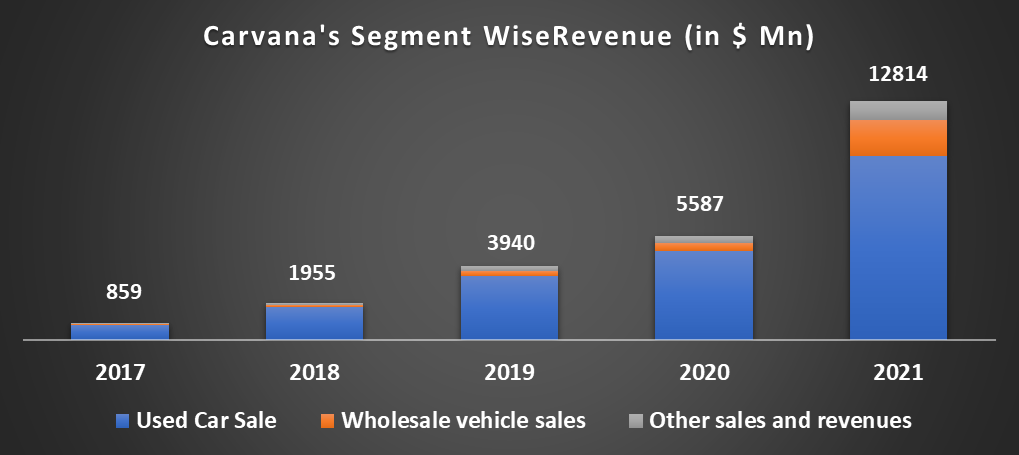
Carvana made $12.8 billion in 2021. Carvana makes money primarily from three segments: Used vehicle Sales (retail customers), Wholesale vehicle sales (wholesalers), and Others (loans and commissions).
Used Vehicle Sales
In this segment, Carvana makes money by selling used vehicles directly to its customers through its website. This is Carvana’s most significant revenue segment, with a ~77% contribution to overall revenue in 2021.
Factors affecting used vehicle sales revenue include the number of retail units sold and the average selling price of these vehicles. Changes in retail units sold are a much more significant driver of changes in revenue than the change in average selling price.
Wholesale Vehicle Sales
In this segment, Carvana makes money by selling vehicles to wholesalers. The vehicles Carvana sells to wholesalers are primarily acquired from customers who sell a car to Carvana without purchasing a retail vehicle and from customers who trade in their existing cars when buying from Carvana.
The average selling price of wholesale units is primarily driven by the mix of vehicles Carvana sells to wholesalers and general supply and demand conditions in the applicable wholesale vehicle market. The segment contributed ~15% to overall revenue in 2021.
Other Sales and Revenues
In this segment, Carvana makes money through the sales of loans and commissions on VSCs and sales of GAP waiver coverage. This segment contributed ~8% to overall revenue in 2021.
Who are Carvana’s biggest competitors?
The U.S. used car marketplace is highly fragmented. There are approximately 43,000 used car dealerships in the United States, including 27,000 independent dealerships.
The largest dealer brand commands approximately 2.2% of the U.S. market, and the top 100 used car retailers collectively hold about 10.2% market share.
The top 10 Carvana competitors for Carvana are Uxin, carwow, Cazoo, Cars24, TRED, CarTrade, Rodo, Roadster. These competitors of Carvana can be primarily classified into the following segments:
- franchised dealerships – 37% of establishments;
- independent dealerships – 63% of establishments; and
- online dealerships/marketplaces. \
How CARS24 is leveraging technology to encourage online buying of cars
Carvana believes its vertically integrated business model provides a significant and sustainable competitive advantage in transparency, convenience, price, selection, and vehicle quality.
















