Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of NVIDIA. NVIDIA Corporation is an American multinational technology company. It’s known for its work in artificial intelligence (AI) computing, as well as its graphics processing units (GPUs) and system-on-a-chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive markets.
Here’s an overview of its main business segments:
- GPU Business: This is NVIDIA’s core business, where it designs and sells GPUs for gaming and professional markets. These chips are popular among PC gamers for rendering high-quality visuals. Professionals also use them for tasks like computer-aided design and video editing.
- Tegra Processor Business: This segment includes NVIDIA’s SoCs, used in devices like smartphones, tablets, and automotive infotainment systems. For example, the company’s Drive platform uses this technology to provide AI capabilities for autonomous vehicles.
- Data Center Business: NVIDIA has made significant inroads into the data center market, selling high-powered GPUs that can handle AI computations and data processing tasks. In addition, the company provides a suite of software libraries and frameworks, collectively known as CUDA, that allow developers to use these GPUs for general-purpose computing.
- Professional Visualization: This segment includes GPUs for workstations professionals use for visual effects, design, and other similar applications.
- Automotive: NVIDIA offers infotainment solutions and autonomous driving technology in this segment. It has partnerships with numerous car manufacturers and tech companies working on self-driving cars.
- Software and Services: NVIDIA offers a range of software, including its Game Ready Drivers for optimizing gaming performance, GeForce Experience for game setting optimization, and its suite of deep learning and AI tools.
In recent years, NVIDIA has been moving beyond hardware into providing comprehensive solutions that include both hardware and software. It’s also increasingly focusing on AI applications, as seen with its development of AI software, its powerful AI-oriented GPUs, and its efforts in the autonomous vehicle space.
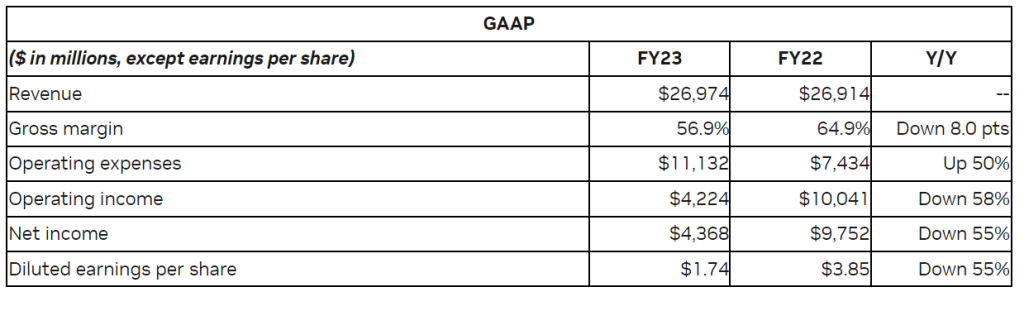
Financial Performance: For fiscal 2023, revenue was $26.97 billion, flat from a year ago. GAAP earnings per diluted share were $1.74, down 55% from a year ago. Non-GAAP earnings per diluted share were $3.34, down 25% from a year ago.
On 19th June’24, Nvidia beats Microsoft and Apple to become the world’s most valuable company with a valuation of $3 trillion.
What does Nvidia do: Business model analysis
Here is the SWOT analysis of NVIDIA
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of NVIDIA.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Technological Innovation: NVIDIA has been at the forefront of several major technological innovations. They introduced the world’s first Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) in 1999 and have continued to innovate in this space. NVIDIA’s GPUs are considered state-of-the-art, allowing the company to maintain a competitive advantage.
- Leadership in AI: NVIDIA’s GPUs have proven extremely useful for AI applications, especially deep learning, where they can dramatically speed up computations. NVIDIA has capitalized on this by creating specialized hardware, like the Tesla and Volta lines of GPUs, and software for AI applications.
- Strong Brand and Market Position: NVIDIA is a leading player in the world of graphics cards. Due to their performance and reliability, their GeForce line of GPUs is very popular among gamers and professionals. NVIDIA is a well-known and respected brand in its market.
- Diversification: NVIDIA has diversified its business across several high-growth markets, including gaming, professional visualization, data centers, and automotive. This diversification reduces risk and opens up multiple avenues for growth.
- Strategic Partnerships: NVIDIA has formed numerous strategic partnerships with other tech companies, car manufacturers, and research institutions, helping to solidify its place in various markets.
- Robust Ecosystem: NVIDIA has built a strong ecosystem around its products, including software development kits, APIs, and a large developer community. This ecosystem reinforces NVIDIA’s products’ appeal and helps lock in users.
- Proposed Acquisition of ARM: The proposed acquisition of ARM Holdings, if completed, would significantly expand NVIDIA’s product portfolio and market reach, particularly in mobile and IoT devices.
Weaknesses
- Dependency on Few Markets: NVIDIA’s business largely depends on a few key markets, such as gaming and data centers. Any downturn in these markets could significantly affect NVIDIA’s revenues.
- Regulatory Approval for ARM Acquisition: The proposed acquisition of ARM Holdings is subject to regulatory approval, and there has been significant opposition from several quarters. If the deal falls through, it could impact NVIDIA’s strategic plans.
- Competitive Market: The market for GPUs is intensely competitive. While NVIDIA is a leading player, it faces significant competition from companies like AMD and Intel. Increased competition can put pressure on prices and margins.
- Supply Chain Risks: The semiconductor industry has a complex global supply chain, which can be disrupted by various factors, from trade tensions to global pandemics. Disruptions in the supply chain could impact NVIDIA’s manufacturing and delivery ability.
- Technological Disruptions: The tech industry is characterized by rapid change and innovation. New technologies or architectural shifts (for example, the rise of quantum computing) could disrupt NVIDIA’s business if the company cannot adapt quickly enough.
- Intellectual Property Disputes: NVIDIA, like other tech companies, has been involved in various intellectual property disputes. Such disputes can lead to financial costs and business uncertainties.
Opportunities
- Growth in AI and Machine Learning: NVIDIA’s GPUs are well-suited for AI and machine learning workloads. NVIDIA will have more opportunities to sell its high-powered GPUs and AI solutions as these technologies continue to evolve and proliferate across different industries.
- Expansion in Data Centers: Data centers’ demand for accelerated computing has grown, and NVIDIA’s GPUs have become a staple. Expanding cloud services, increasing computational workloads, and AI applications in data centers provide significant opportunities for growth.
- Autonomous Vehicles: NVIDIA has been investing in technology for autonomous vehicles. As this market matures, there are considerable opportunities for the company. This includes the hardware, software, and platforms that power autonomous driving systems.
- Edge Computing: With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the rollout of 5G, more computing is moving to the network’s edge. This transition represents a significant opportunity for NVIDIA, as GPUs and AI technology can help power these edge devices.
- Acquisition of ARM Holdings: If NVIDIA’s proposed acquisition of ARM Holdings is approved, it would give NVIDIA access to ARM’s extensive ecosystem and allow NVIDIA to extend its reach into areas like mobile computing, IoT, and more.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR are still emerging fields with significant growth potential. NVIDIA’s powerful GPUs could be critical for rendering the complex visuals needed for immersive VR and AR experiences.
- Growth in Gaming: The gaming market continues to grow, with increasing demand for high-quality graphics and real-time performance. This is a market where NVIDIA has traditionally been very strong.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): There’s a growing demand for HPC in scientific research, engineering, and data analysis. NVIDIA’s GPUs and AI platforms can address these needs.
Threats
- Intense Competition: NVIDIA operates in a highly competitive environment with key rivals, including AMD and Intel. These companies continually work on new products that could outperform NVIDIA’s offerings or undercut them on price.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: The proposed acquisition of ARM Holdings is under regulatory scrutiny from different parts of the world. It could affect NVIDIA’s expansion strategy and reputation if it doesn’t go through.
- Economic Conditions: NVIDIA’s business, particularly its gaming segment, can be affected by broader economic conditions. Economic downturns, for example, can lead to reduced consumer and enterprise spending on high-end GPUs.
- Technological Shifts: Rapid technological shifts are commonplace in the tech industry. The emergence of new computing paradigms like quantum computing or the decline in Moore’s Law could pose significant threats to NVIDIA’s business model.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The semiconductor industry is subject to various supply chain disruptions, such as those caused by trade wars, geopolitical tensions, pandemics, or natural disasters. Any disruption in the supply chain could lead to an inability to meet product demand.
- Dependence on Manufacturing Partners: NVIDIA does not manufacture its chips but relies on third-party foundries. Any problems at these foundries could affect NVIDIA’s ability to produce its products.
- Intellectual Property Disputes: NVIDIA, like many technology companies, faces the risk of intellectual property disputes, which could result in costly litigation and potential disruptions to certain aspects of its business.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As a tech company, NVIDIA faces threats related to cybersecurity. A significant breach could lead to financial and reputational damage.











