Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Intel. Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. The company was founded in 1968 by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce and has been a cornerstone in developing semiconductor technology. It is a leader in the manufacture of microprocessors, the central unit of many types of computers.
Core Business Segments: Intel’s business can be categorized into several key segments:
- Client Computing Group (CCG): This is typically the largest revenue generator for Intel and focuses on processors and platforms for laptops, desktops, and tablets.
- Data Center Group (DCG): This segment deals with hardware and software solutions for data centers, which include powerful processors and chips that are optimized for enterprise-level tasks, cloud computing, and network infrastructure.
- Internet of Things (IoT): This unit works on making processors and platforms that will power connected devices.
- Non-Volatile Memory Solutions Group: This segment produces memory and storage products, including NAND flash memory and 3D XPoint memory.
- Programmable Solutions Group: This unit specializes in field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), which are chips that can be programmed for specific tasks after they’ve been manufactured.
- Intel Labs: This is the research arm of Intel, responsible for exploring cutting-edge technologies that may be commercially viable.
- Other technologies: Includes various other smaller segments, including software products and other initiatives like autonomous driving through its Mobileye subsidiary.
Manufacturing: Intel has been one of the few semiconductor companies designing and manufacturing their own chips. However, it has been increasingly exploring external foundries for some of its products.
Financial Performance 2022: Full-year revenue was $63.1 billion, down 20% YoY. Net income was $7.6 bn, down 65%.
Here is the SWOT analysis for Intel
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Intel.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
Intel Corporation has several strengths that have contributed to its success as a leading technology company:
- Technological innovation: Intel has a long history of developing and delivering cutting-edge technologies that have driven the evolution of the computer industry. The company invests heavily in research and development to continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with computer hardware.
- Strong brand reputation: Intel is a globally recognized brand with high-quality, high-performance computer products. Its processors are widely used and trusted by consumers and businesses alike.
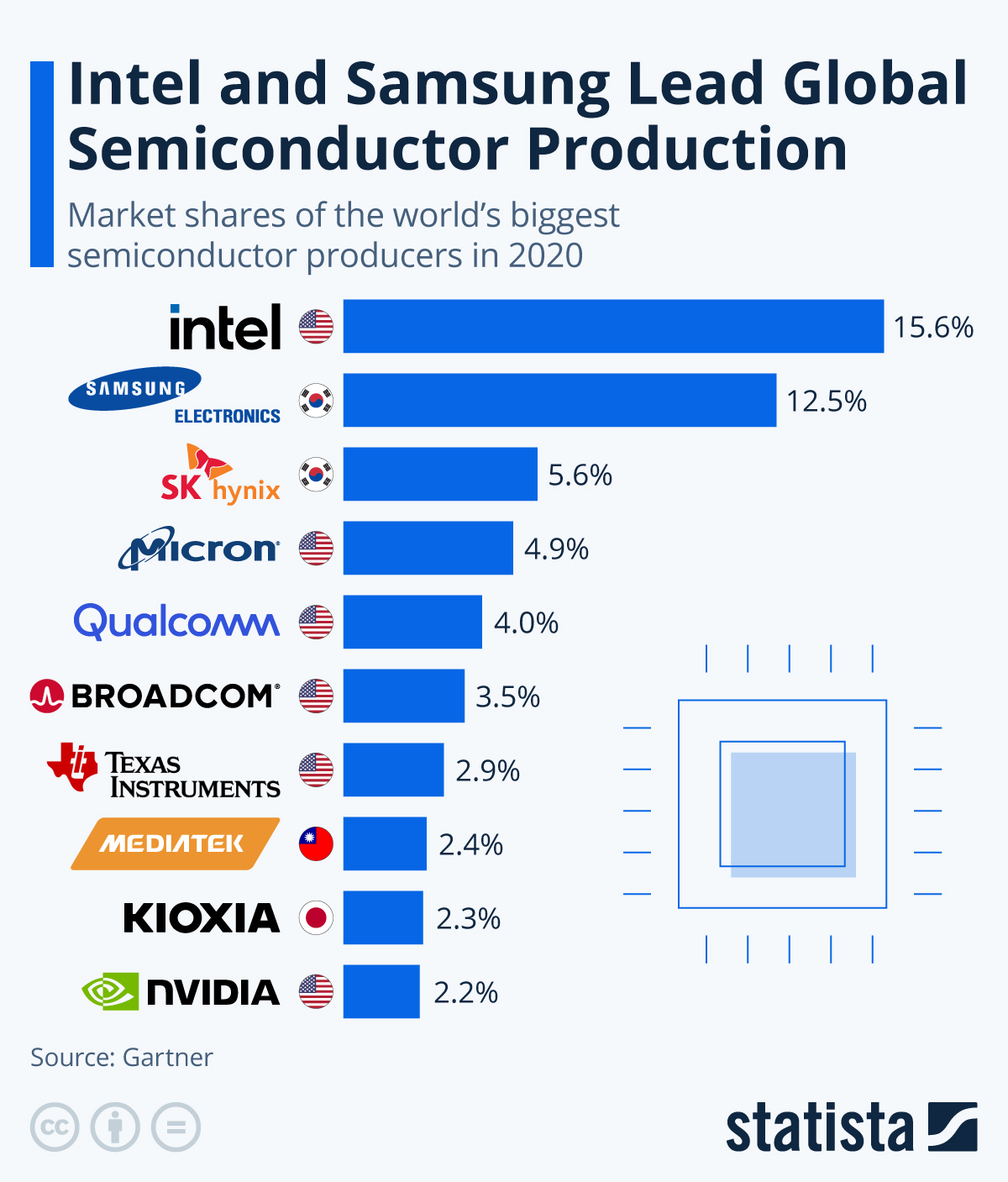
- Strong market position: Intel is dominant in the computer processors market, with a market share of over 75%. This gives the company significant pricing power and allows it to invest in new technologies and products.
- Diversified product portfolio: Intel has a broad range of products beyond processors, including network interface controllers, memory chips, and graphics processors. This diversification helps the company mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations in any product category.
- Strong financial performance: Intel has a solid financial position, with consistently high revenue and profit margins. This allows the company to invest in research and development, make strategic acquisitions, and reward shareholders with dividends and stock buybacks.
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
Weaknesses
Intel Corporation also has a few weaknesses that can impact its performance and competitive position:
- Dependence on the PC market: Despite diversifying its product portfolio, Intel still heavily depends on the PC market, which has declined in recent years as consumers shift towards mobile devices. This dependence can make the company vulnerable to changes in the market.
- Manufacturing delays: Intel has faced manufacturing delays and quality issues in recent years, which have impacted its ability to bring new products to market on time. This has allowed competitors to gain ground and erode Intel’s market share.
- Competition from rivals: Intel faces intense competition from other companies, including AMD and Nvidia, which have gained market share in recent years. These competitors offer alternative processor and graphics solutions that can be more attractive to consumers in terms of price and performance.
- Limited presence in the mobile market: While Intel has made efforts to enter the mobile market, it has yet to have much success. This limits the company’s growth potential in this rapidly growing market segment.
- High research and development costs: While Intel’s investment in research and development is a strength, it is also a high cost for the company. High R&D costs can impact profitability and make competing on price more difficult with rivals with lower R&D expenses. As per Intel’s annual report, Intel spent ~$17 billion on R&D.
Opportunities
Intel Corporation has several opportunities to capitalize on in the technology industry:
- Expansion into new markets: Intel can expand into new markets such as artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These markets are overgrowing and offer significant potential for revenue and profit growth.
- Development of new technologies: Intel can continue to invest in developing new technologies, such as advanced manufacturing processes, 5G wireless technology, and quantum computing. These technologies can potentially create entirely new markets and disrupt existing industries.
- Acquisitions and partnerships: Intel can leverage its financial strength to acquire or partner with companies that complement its existing product portfolio or help it enter new markets. For example, Intel recently acquired Mobileye, a leading developer of autonomous vehicle technology.
- Focus on sustainability: With increasing global concern about environmental sustainability, there is an opportunity for Intel to develop products and technologies that are more energy-efficient and have a lower environmental impact. This can help the company to differentiate itself from competitors and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
- Expansion into emerging markets: As emerging markets continue to grow and develop, there is an opportunity for Intel to expand its presence in these markets. This can help the company to diversify its revenue streams and reduce its dependence on mature markets such as the United States and Europe.
Threats
Intel Corporation faces several threats that can impact its performance and competitive position:
- Increasing competition: Intel faces intense competition from other companies, including AMD, Nvidia, and Qualcomm, which are all aggressively pursuing the development of new technologies and products.
- Rapidly changing technology landscape: The technology industry is constantly evolving, and new technologies are emerging rapidly. This can make it difficult for Intel to keep up with changing market trends and consumer preferences.
- Dependence on key customers: Intel depends heavily on key customers, such as PC and server manufacturers, for a significant portion of its revenue. Any change in the demand or preferences of these customers can impact the company’s financial performance.
- Geopolitical risks: Intel operates in many different countries, and geopolitical risks such as trade disputes, sanctions, and political instability can impact its operations and revenue.
- Intellectual property infringement: As a leading technology company, Intel is vulnerable to intellectual property infringement by competitors or other third parties. This can result in legal disputes, reputational damage, and financial losses.