Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of Uber. Uber Technologies Inc. is a multinational ride-hailing company based in San Francisco, California. It develops and operates various businesses across more than 70 countries worldwide.
As of 2022, here are the core components of Uber’s business:
- Ride-hailing: Uber’s ride-hailing service allows customers to request rides from registered drivers through a mobile app. It offers different service levels ranging from budget options like UberX and UberPool to luxury options like UberBlack and UberLux.
- Uber Eats: This is Uber’s food delivery service. Customers can order from various restaurants and deliver their food by Uber Eats drivers.
- Uber Freight: This service connects shippers with truckers, much like the ride-hailing service does with drivers and riders, but for large-scale freight instead.
- Advanced Technologies Group (ATG): Uber’s team is working on self-driving technology to build autonomous cars and trucks for the Uber network. The goal is to increase safety and efficiency while reducing costs. However, this part of the business has faced numerous challenges and controversies.
- Uber Health: This service provides patient transportation for healthcare providers. It is HIPAA-compliant and is meant to assist those who may not have easy transportation access to their medical appointments.
- Uber Business: This service caters to businesses by providing a platform for employee travel, customer rides, and food delivery for employees. It offers tools for managers to set rules for employees, customers, and clients to use Uber and Uber Eats.
- Bike and Scooter Rentals: In certain cities, Uber offers electric bike and scooter rentals for short trips.
Uber operates on a gig economy model, with drivers and couriers working as independent contractors, not employees. This has been a point of contention and legal dispute in several jurisdictions.
Uber’s business model is a multi-sided platform that connects drivers and passengers, restaurants and customers, and shippers and carriers, creating value for all participants. However, Uber has faced criticism and legal challenges regarding worker rights, safety, competitive practices, and other issues.
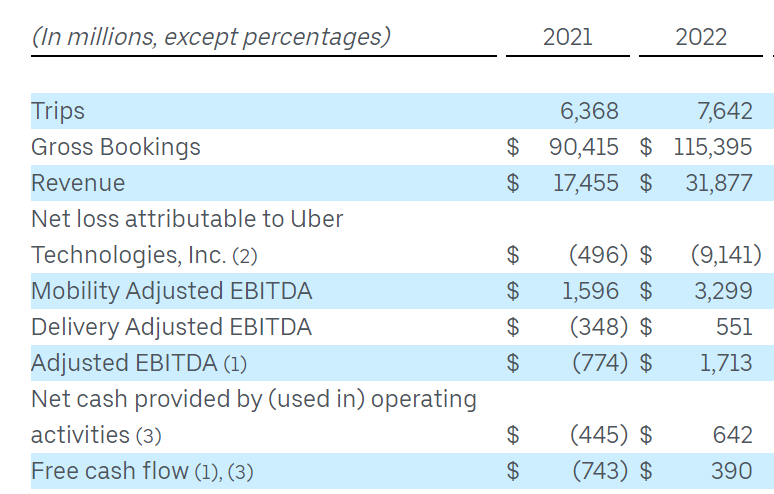
Uber drivers completed 7.6 billion trips in 2022, and Uber has a 68% market share in the US.
Financial Performance: In 2022, Uber generated a revenue of $31.9 bn with a net loss of $9.1 bn. More details are presented below:
How does Uber work & make money | Business Model
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Uber
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Uber.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Regulation and Legal Challenges: Uber operates in various countries, and each country or city has its own rules and regulations. These regulations related to ride-sharing services vary widely and can have a significant impact on Uber’s operations. For example, in some places, Uber has faced legal battles and has even been banned due to local regulations, such as in London, where the service was temporarily banned due to safety concerns.
- Labor Laws: One of the significant political issues Uber has faced is related to its drivers. Uber categorizes its drivers as independent contractors rather than employees. This has led to legal disputes in multiple regions, with drivers demanding more rights and benefits. In California, for instance, a law was passed (Proposition 22) to redefine the status of gig economy workers, directly affecting Uber.
- Public Safety and Security Regulations: Political factors also include public safety and security rules. Uber has faced scrutiny from politicians and regulatory authorities over its safety protocols. For instance, questions have been raised about Uber’s background check processes for drivers and its procedures for handling customer complaints.
- International Relations and Trade Policies: Since Uber operates in many different countries, international trade agreements and relations can impact its business. Political tensions or changes in trade policies can pose risks.
- Tax Policies: Uber has faced issues regarding tax policies in various countries. Different jurisdictions have different rules about how to tax ride-sharing services, and changes in these policies can impact Uber’s revenue.
- Infrastructure Policy: Infrastructure quality and availability, often a matter of political policy, can affect Uber’s business. For example, regions with poor road infrastructure or limited internet access may present operational challenges.
Economic
- Market Conditions: The state of the economy in any given region impacts consumers’ spending habits, affecting Uber. In a strong economy, people are more likely to use services like Uber for convenience. In contrast, consumers might reduce such services during economic downturns to save money.
- Fuel Prices: While Uber drivers are responsible for fuel costs, fluctuating fuel prices can indirectly impact Uber. High fuel costs can discourage drivers from working for Uber or lead to demands for higher pay. These costs can also impact consumers’ behavior if they’re passed along in the form of higher prices.
- Unemployment Rates: Higher unemployment rates can have a dual impact on Uber. On the one hand, they might increase the pool of potential drivers. On the other hand, they could decrease the number of people who can afford to use Uber’s services.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation affects both the cost and price of goods and services. As inflation rises, Uber may need to raise its prices to maintain profitability, potentially leading to a decrease in demand for its services.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates can affect the cost of capital for Uber if it wants to invest in new technologies or expand its operations. Higher interest rates mean higher borrowing costs.
- Exchange Rates: Since Uber operates globally, fluctuations in exchange rates can impact its revenues and profitability. For instance, if a foreign currency weakens against the US dollar, then Uber’s income from that country decreases in dollar terms.
Sociocultural
- Changing Lifestyles: With the increase in urbanization and hectic lifestyles, the demand for quick, easy, and convenient services is rising. Uber’s business model leverages this societal shift towards instant gratification and convenience.
- Attitudes Towards Gig Economy: Society’s perception of gig-based work affects Uber significantly. If people view gig work positively, as flexible and liberating, this can increase the pool of potential drivers. However, if it’s viewed negatively, as unstable or exploitative, this could lead to challenges in finding drivers and possible regulatory backlash.
- Environmental Consciousness: As society becomes more environmentally aware, people may choose to use ride-sharing services like Uber over owning a personal vehicle to reduce their carbon footprint. However, there could also be a backlash if rideshare proliferation increases congestion or if Uber’s fleet is not seen as green enough.
- Attitudes Towards Technology and Privacy: Trust in technology is crucial for Uber. If society is generally accepting of or enthusiastic about technological innovation, Uber is more likely to succeed. However, data privacy and security concerns can negatively impact Uber’s reputation and usage.
- Cultural Differences: Uber operates globally, so it must adapt to different cultural norms, behaviors, and expectations. For instance, tipping customs, communication styles, and expectations about punctuality can vary from place to place.
- Demographics: The demographic composition of a region, including factors like age distribution, income levels, and population density, can significantly impact Uber’s business. For example, Uber might be more prevalent in dense urban areas with a large population of young, tech-savvy professionals.
Technological
- Ride-sharing Technology: Uber’s entire business model is built on mobile technology. Advances in GPS tracking, app development, and mobile payment technology all play a crucial role in Uber’s business. The speed of technology adoption by society can affect the rate of Uber’s growth.
- Data Analysis: Uber generates a massive amount of data from its users. Advanced data analytics and machine learning technologies allow Uber to analyze this data to improve its services, predict demand, adjust pricing, and maintain a competitive edge.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation: Uber has invested heavily in self-driving technology to increase efficiency and reduce costs. The progress and acceptance of autonomous vehicles can significantly impact Uber’s future.
- Cybersecurity: Uber is vulnerable to cyber threats, including data breaches, as a digital platform. Technological advances in cybersecurity are crucial to protect the company and its users’ data.
- Connectivity: The quality of network infrastructure and internet connectivity in a given market can influence the feasibility and quality of Uber’s service.
- Digital Payment Systems: The rise of digital wallets and online payment systems has facilitated transactions on platforms like Uber. Developments in financial technology can influence how easy it is for customers to pay for rides.
- Technological Regulations: Laws and regulations related to technology can affect Uber, such as rules around data privacy, self-driving cars, or gig economy platforms.
Environmental
- Carbon Emissions: Ride-sharing services like Uber contribute to CO2 emissions. Increasing awareness and concern about climate change can affect public perception and regulation. For instance, Uber may face pressure to incorporate more electric or hybrid cars.
- Waste Management: The life cycle of cars used in Uber’s service, from production to disposal, has environmental implications. Waste and pollution from old cars that are no longer used can be a concern.
- Sustainable Energy: As the world moves towards renewable energy, companies that don’t comply may face backlash. For Uber, using non-renewable fuel sources could be a point of contention. Transitioning to electric or hybrid fleets where possible may be beneficial.
- Urban Planning and Congestion: Ride-sharing services can impact traffic congestion in urban areas, which can have environmental consequences in increased pollution. Cities might implement policies to combat this, which could affect Uber’s business.
- Climate Change: Extreme weather events related to climate change can impact the demand for Uber’s services. For example, harsh weather conditions might increase ride demand and make it more difficult for drivers to operate.
- Regulatory Changes: New environmental regulations could impact Uber’s business model, such as laws promoting public transportation or cycling over private car use or regulations aimed at reducing vehicle emissions.
Legal
- Employment Laws: Uber classifies its drivers as independent contractors rather than employees. This classification has been challenged in several jurisdictions worldwide, leading to significant legal battles. Laws regarding worker classification and rights are key legal factors for Uber.
- Regulatory Compliance: Uber has faced regulatory issues in various cities and countries. The company has even been banned or suspended in some places due to non-compliance with local transportation laws. Regulatory laws can significantly impact Uber’s operations.
- Data Protection Laws: Uber collects and stores a substantial amount of data from its users as a digital platform. Data privacy and protection laws, such as GDPR in the European Union, can affect how Uber handles its data.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Uber, like many tech companies, has to protect its proprietary technology and manage intellectual property rights. This can include issues related to patents, trademarks, copyrights, etc.
- Competition Laws: Uber has faced scrutiny in several markets over concerns of anti-competitive behavior, such as predatory pricing to drive out competitors.
- Safety and Liability Laws: Passenger safety and driver liability laws can impact Uber. The company has to ensure that it complies with local safety regulations and manages the risk of accidents or incidents involving its drivers.
- Tax Laws: Uber faces different tax obligations in countries, states, or cities. Changing tax laws can impact Uber’s revenues and profitability.











