Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Tata Motors. Tata Motors Limited, part of the larger Tata Group conglomerate, is a leading global automobile manufacturer based in India.
Established in 1945, Tata Motors primarily focuses on designing, manufacturing, and selling a wide range of vehicles, including passenger cars, trucks, buses, and other commercial vehicles. The US$ 37-billion* Tata Motors Group is a leading global automobile manufacturer with many commercial, passenger, and electric vehicle offerings.
The Company focuses on engineering and tech-enabled automotive solutions to bring the future of mobility closer. The Company is pioneering India’s Electric Vehicle transition and enjoys a considerable advantage in one of the fastest-growing automotive markets in the world.
Tata Motors is India’s largest-selling commercial vehicle manufacturer and is amongst the top three in the passenger vehicles market. Tata Motors’ operations span India, the UK, South Korea, and South Africa with a network of 86 subsidiaries, 10 associate companies, 4 joint ventures, and 2 joint operations as of March 31, 2022.
The Company operates through several key business divisions and subsidiaries to cater to market segments.
- Passenger Vehicles: Tata Motors’ passenger vehicle division includes a diverse lineup of cars, SUVs, and electric vehicles. Some popular models include the Tata Tiago, Tigor, Nexon, Harrier, and Altroz. Tata Motors is known for its focus on safety, innovation, and affordability.
- Commercial Vehicles: As one of the largest commercial vehicle manufacturers in India, Tata Motors produces a broad range of trucks, buses, pickups, and other specialized vehicles for various industries. These vehicles are designed to meet the transportation needs of businesses and government organizations.
- Electric Vehicles: Tata Motors is committed to sustainable mobility and has invested significantly in developing electric vehicles (EVs). The Company has introduced electric versions of some of its popular passenger car models, such as the Nexon EV and Tigor EV. It continues to develop new EV technologies and charging infrastructure.
- Global Operations: Tata Motors has a strong international presence, with manufacturing facilities in several countries, including India, the United Kingdom, and South Africa. The Company also exports its vehicles to numerous markets worldwide, particularly in Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia.
- Subsidiaries and Joint Ventures: Tata Motors has several subsidiaries and joint ventures to expand its product offerings and strengthen its presence in the automotive industry. Some notable examples include Jaguar Land Rover (a British luxury automobile brand acquired by Tata Motors in 2008), Tata Marcopolo Motors (a joint venture with Brazil’s Marcopolo S.A. to produce buses), and Tata Daewoo (a South Korean truck manufacturer).
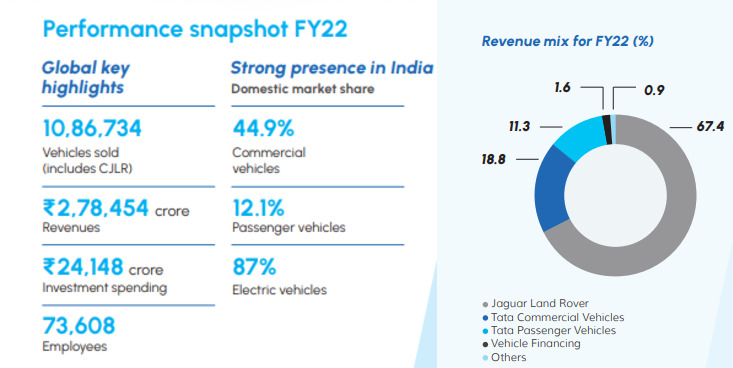
Financial Performance: Refer to the numbers below (Source: Tata Motors annual report)
Here is the SWOT analysis for Tata Motors
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Tata Motors.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong Brand Reputation: As part of the prestigious Tata Group, Tata Motors enjoys a solid reputation for quality, reliability, and value for money. This strong brand recognition has helped the Company attract a loyal customer base and maintain its position as one of the leading automakers in India.
- Diverse Product Portfolio: Tata Motors offers a wide range of vehicles catering to different customer needs and preferences. Its product lineup includes passenger cars, SUVs, commercial vehicles, buses, and electric vehicles, ensuring the Company remains relevant across various market segments.
- Focus on Innovation: Tata Motors is committed to developing and adopting new technologies to improve its vehicles’ performance, safety, and efficiency. The Company’s investment in electric vehicles, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and connected car technologies demonstrate its commitment to innovation.
- Global Presence: Tata Motors has established a solid global footprint, with manufacturing facilities in several countries and exports to numerous markets worldwide. This international presence helps the Company to diversify its revenue streams and minimize the impact of economic downturns in specific regions.
- Acquisition of Jaguar Land Rover (JLR): The acquisition of JLR in 2008 provided Tata Motors with access to luxury vehicle segments, cutting-edge technologies, and a strong global brand. This has helped the Company expand its product offerings and improve its competitiveness.
- Vertical Integration: Tata Motors benefits from vertical integration within the Tata Group, which includes businesses in sectors such as steel, automotive components, and information technology. This integration allows the Company to achieve cost efficiencies, maintain quality control, and streamline its supply chain.
- Skilled Workforce: Tata Motors has a skilled workforce capable of designing, manufacturing, and marketing a wide range of vehicles. The Company’s commitment to employee development, training, and retention helps maintain expertise and competitiveness.
Weaknesses
- Dependence on the Indian Market: A significant portion of Tata Motors’ revenue comes from the domestic Indian market, making the Company vulnerable to fluctuations in the country’s economy and regulatory environment. This reliance on a single market exposes Tata Motors to risks associated with economic downturns, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory changes in India.
- Limited Presence in Luxury Car Segment: Although acquiring Jaguar Land Rover has provided Tata Motors access to the luxury vehicle market, the Company’s presence remains limited compared to some of its global competitors. As a result, Tata Motors may miss out on growth opportunities in the luxury car segment, which tends to have higher profit margins.
- Challenges with Jaguar Land Rover (JLR): JLR has faced several challenges in recent years, including declining sales in key markets, Brexit-related uncertainties, and the need to invest heavily in electric vehicles and advanced technologies. These issues have weighed Tata Motors’ financial performance and required significant management attention.
- Competition: The automotive industry is highly competitive, and Tata Motors faces intense competition from both domestic and international players. Competitors such as Maruti Suzuki, Hyundai, and Mahindra & Mahindra are continually innovating and launching new products, putting pressure on Tata Motors to keep up and maintain its market share.
- Quality and After-Sales Service Concerns: In the past, Tata Motors has faced criticism for the quality of some of its vehicles and the after-sales service provided by its dealer network. While the Company has made efforts to improve in these areas, any perceived shortcomings in quality or service can harm its brand reputation and customer loyalty.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Like other automakers, Tata Motors is susceptible to disruptions in its supply chain due to factors such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and global pandemics. Such disturbances can lead to production delays and increased costs, ultimately impacting the Company’s bottom line.
Opportunities
- Electric Vehicle Market: The global demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and supportive government policies. Tata Motors can capitalize on this trend by expanding its EV product lineup, investing in advanced battery technology, and improving charging infrastructure.
- Growing Demand for SUVs: The SUV segment has been experiencing robust growth worldwide, particularly in emerging markets like India. Tata Motors can leverage this opportunity by introducing new and competitive SUV models across various price points to attract a broader customer base.
- Emerging Markets Expansion: Tata Motors can explore opportunities for expansion in emerging markets such as Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia, where the demand for affordable and reliable vehicles is growing. Establishing local manufacturing facilities, strategic partnerships, and developing vehicles tailored to local preferences can help the Company gain a foothold in these markets.
- Connected and Autonomous Vehicle Technologies: The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the advent of connected and autonomous vehicle technologies. Tata Motors can invest in research and development to integrate these technologies into its vehicles, providing customers with advanced features and setting the Company apart from its competitors.
- Strengthening After-Sales Services: Improving after-sales services, such as maintenance, repairs, and customer support, can enhance customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. Tata Motors can invest in strengthening its dealer network, offering value-added services, and leveraging digital platforms to improve the overall customer experience.
- Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions: Tata Motors can explore strategic partnerships and acquisitions to gain access to new technologies, expand its product portfolio, and strengthen its presence in the global automotive market. Collaborating with technology companies, battery manufacturers, or other automakers can help accelerate innovation and drive growth.
- Focus on Sustainability: As environmental concerns gain prominence, Tata Motors can emphasize its commitment to sustainability by adopting greener manufacturing processes, increasing recycled materials, and working towards carbon neutrality. This focus on sustainability can enhance the Company’s brand image and attract environmentally conscious customers.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The automotive industry is highly competitive, with global and domestic players constantly introducing new products and technologies. Tata Motors must continually innovate and improve its product offerings to maintain its market share and remain competitive.
- Economic Downturns: Economic slowdowns, particularly in key markets like India, can negatively affect consumer demand for vehicles and impact Tata Motors’ sales and profitability. The Company must be prepared to respond to such downturns by adjusting production levels, optimizing costs, and focusing on high-margin segments.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in government policies, regulations, and emission standards can impact Tata Motors’ operations and product development. For example, stricter emission norms, electric vehicle incentives, and import/export duties changes can all affect the Company’s growth and profitability.
- Fluctuating Raw Material Prices: Tata Motors, like other automotive manufacturers, is vulnerable to fluctuations in the prices of raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and rubber. Volatile prices can increase production costs and negatively impact the Company’s profit margins.
- Technological Disruption: Rapid advancements in automotive technology, such as electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and connected cars, can disrupt the industry and render traditional products obsolete. Tata Motors must continually invest in research and development to keep pace with these changes and remain competitive.
- Exchange Rate Fluctuations: As a global company with operations in various countries, Tata Motors is exposed to fluctuations in currency exchange rates. These fluctuations can impact the Company’s revenue, profitability, and competitiveness, particularly in international markets.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events like natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics can disrupt Tata Motors’ supply chain, leading to production delays and increased costs. Ensuring a resilient and diversified supply chain is crucial to mitigate these risks.