Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Mastercard. Mastercard is a technology company in the global electronic payment industry, facilitating electronic payments across a network that connects various transaction participants, including businesses, financial institutions, merchants, and consumers.
The company’s services are centered around its range of payment programs and services, utilizing credit, debit, or prepaid cards as core payment instruments. Mastercard’s revenue model is based on assessing customers through Gross Dollar Volume (GDV) fees, derived from the aggregate dollar amount of transactions made using Mastercard-branded cards.
Mastercard’s business model does not include issuing cards or extending credit directly to consumers. Instead, it provides the technological infrastructure and network—MasterNet—enabling electronic payment transactions. The company works in partnership with financial institutions that issue Mastercard-branded cards and determine the terms and conditions for cardholders. Mastercard’s vast offerings encompass traditional payment processing and various co-branded collaboration arrangements, extending its reach into new markets and customer segments.
The company’s operations are extensive, with a presence in numerous countries. It serves many clients, including individuals, financial institutions, governments, and businesses, thereby shaping the digital economy to allow all participants to realize their ambitions.
Mastercard also offers business prepaid cards, providing a solution for managing expenses and protecting business finances, showcasing the company’s commitment to delivering flexible and secure payment options for businesses of all sizes.
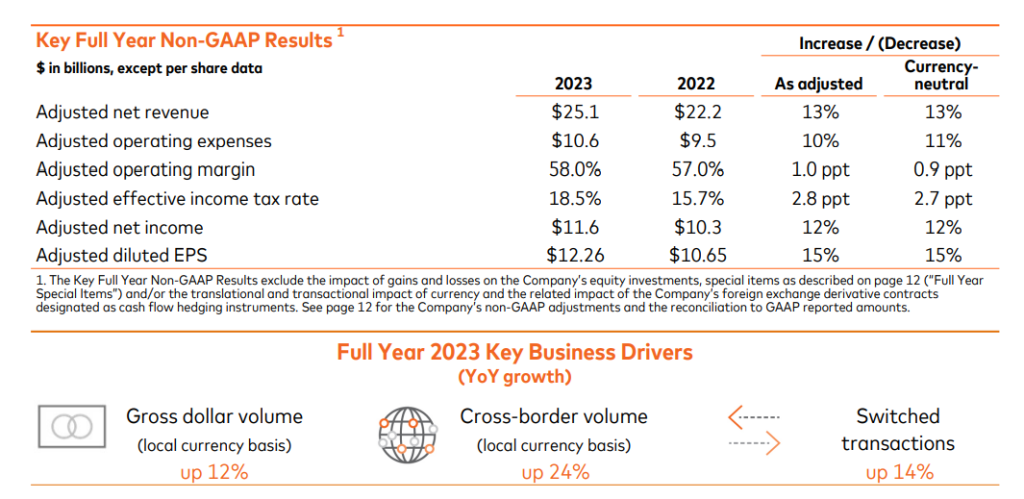
Financial Performance 2023: Mastercard generated $25.1 Billion in revenue and $11.2 billion in net income.
How does Mastercard work & make money: Business Model & Strategy
Here is the SWOT analysis for Mastercard
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Mastercard.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Global Brand Recognition: Mastercard is one of the most recognized brands in the global payments sector, known for its reliability and widespread acceptance.
- Extensive Network: The company operates a comprehensive payment network that connects consumers, merchants, financial institutions, and businesses across various transactions, facilitating electronic payments worldwide.
- Innovative Payment Solutions: Mastercard is at the forefront of payment technology innovation, offering a broad range of services, including credit, debit, and prepaid card programs, as well as advanced digital payment solutions.
- Strong Partnerships: The company has established strategic partnerships with financial institutions, governments, and businesses, enabling it to expand its services and access new markets.
- Revenue Diversification: Unlike traditional banking institutions, Mastercard’s revenue model is based on processing fees rather than interest, providing a stable income stream less affected by interest rate fluctuations.
- Advanced Security Features: Mastercard invests heavily in security technologies to ensure the safety and integrity of transactions on its network, enhancing consumer and merchant trust.
- Commitment to Financial Inclusion: The company is actively involved in initiatives aimed at promoting financial inclusion providing accessible payment solutions to underbanked and unbanked populations around the world.
Weaknesses
- Regulatory Compliance and Legal Risks: Operating in a highly regulated financial industry, Mastercard must navigate complex legal landscapes across different countries. Compliance with these regulations can be costly and challenging; any failure could result in fines or restrictions.
- Dependence on Economic Conditions: Mastercard’s performance is closely tied to global economic conditions like that of other financial services companies. Economic downturns can reduce consumer spending and transaction volumes, potentially affecting the company’s revenue.
- Intense Competition: The payments industry is highly competitive, with traditional competitors like Visa and emerging fintech and payment solutions posing a constant challenge. This competition can pressure fees and market share.
- Cybersecurity Threats: In an era where digital transactions are prevalent, cybersecurity remains a critical concern. Despite advanced security measures, Mastercard is susceptible to potential breaches that could undermine consumer trust and lead to financial losses.
- Technological Disruptions: Rapid technological advancements in the payment industry, including blockchain and cryptocurrencies, could disrupt traditional card-based payment models, necessitating continuous innovation and adaptation.
- Market Saturation in Developed Countries: In mature markets, high levels of penetration for card payments may limit growth opportunities, pushing Mastercard to seek expansion in emerging markets, which come with its own set of challenges.
Opportunities
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: There’s significant potential for growth in emerging markets where digital payment adoption is still evolving. Mastercard can leverage its global network to increase its presence in these regions, capitalizing on the growing middle class and rising smartphone penetration.
- Digital Payment Innovations: The rapid pace of technological advancement offers Mastercard opportunities to innovate in contactless payments, mobile wallets, and blockchain. Developing new payment solutions can help the company stay ahead of industry trends and meet evolving consumer demands.
- Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with fintech companies, tech giants, and other non-traditional financial players can provide Mastercard access to new technologies and business models, enhancing its product offerings and market reach.
- Financial Inclusion Initiatives: There’s a significant opportunity for Mastercard to drive financial inclusion by providing accessible financial services to unbanked and underbanked populations, especially in developing countries. This expands Mastercard’s customer base and contributes to societal benefits.
- Value-Added Services: Mastercard can further diversify its revenue streams by expanding its value-added services, such as data analytics, cybersecurity solutions, and loyalty programs, to deepen its relationships with existing clients and attract new ones.
- Cross-Border Payments: As global commerce grows, there is an increasing demand for efficient and secure cross-border payment solutions. Mastercard can leverage its global network to enhance cross-border payment capabilities, offering faster and more transparent transactions.
Threats
- Regulatory Changes: The payments industry is subject to stringent and diverse regulations across different countries. Changes in regulatory landscapes, such as increased scrutiny on transaction fees or data privacy laws, could impose additional costs or restrictions on Mastercard’s operations.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As digital transactions continue to rise, so do the threats of cyberattacks. A significant security breach could lead to substantial financial losses, damage Mastercard’s reputation, and erode consumer trust in its network.
- Technological Disruption: The financial services industry is rapidly evolving with the introduction of new technologies like blockchain, cryptocurrencies, and peer-to-peer payment platforms. These innovations could disrupt traditional payment networks and reduce the reliance on card-based transactions.
- Competition: Mastercard faces intense competition from traditional rivals like Visa and fintech startups and technology companies venturing into the payments space with innovative solutions. This could potentially erode Mastercard’s market share and pressure its fee structures.
- Global Economic Fluctuations: Mastercard’s performance is closely linked to global economic conditions. Economic downturns or financial market instability can lead to decreased consumer spending and lower transaction volumes, adversely affecting Mastercard’s revenues.
- Exchange Rate Volatility: Being a global company, Mastercard is exposed to currency exchange rate fluctuations, which can impact its financial performance, especially when repatriating profits from foreign operations.











