Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Ford. Ford Motor Company is one of the oldest automobile companies in the world. Henry Ford founded it on June 16, 1903. The company introduced revolutionary methods of mass production, such as the assembly line, which played a crucial role in the industrialization of many countries.
The core business of Ford revolves around the design, manufacture, marketing, and servicing of a full line of cars, trucks, SUVs, and electrified vehicles.
Ford operates globally with a significant presence in North America, Europe, South America, Asia Pacific, and Africa. Its headquarters is located in Dearborn, Michigan, USA.
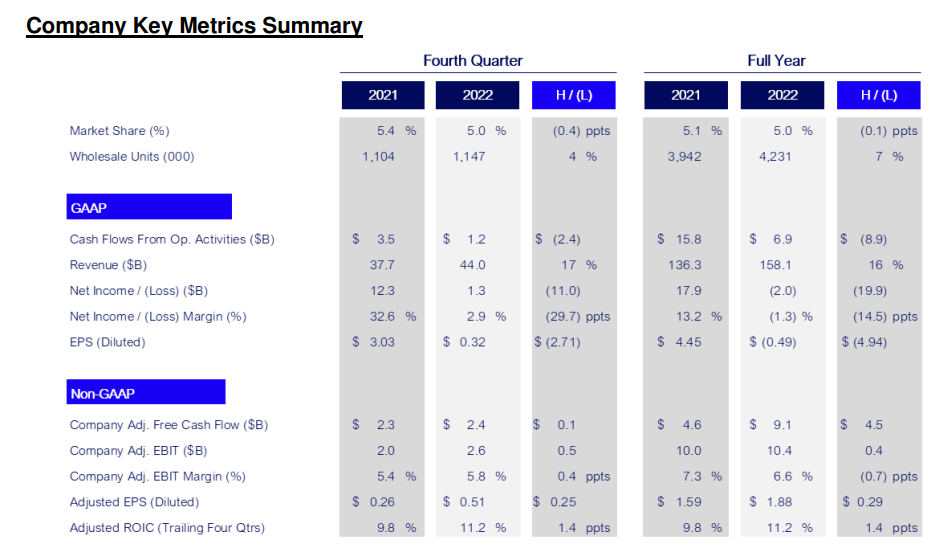
Financial Performance 2022: Ford generated $158 bn in revenue in 2022 at a loss of $2 bn. Details are as follows:
Here is the SWOT analysis for Ford
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Ford..
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong Brand Image: Ford has been around for over a century and is recognized globally. Its logo and brand are synonymous with American automotive history.
- Diverse Product Portfolio: Ford offers a variety of vehicles ranging from cars to trucks to SUVs. This helps them cater to a wide range of customer needs and preferences.
- Innovative Technology: Ford has been proactive in investing in advanced technologies. They’ve focused on electric and hybrid vehicles, autonomous driving technologies, and advanced infotainment systems.
- Global Reach: Ford operates in many countries worldwide. This global presence allows them to tap into various markets and cater to regional needs.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Over the years, Ford has honed its manufacturing processes, resulting in efficient production lines and practices, such as the famous assembly line introduced by Henry Ford.
- Strong Dealer Network: Ford has a robust dealer network that ensures customers can access their vehicles, parts, and services almost everywhere.
- Research and Development: Ford invests significantly in R&D to stay ahead of technological trends and meet evolving consumer demands.
- Strong Financial Position: Although the company has seen ups and downs, Ford generally has a good credit rating and access to capital. This financial stability allows them to invest in new ventures and weather economic downturns.
- Loyalty Programs: Ford’s customer loyalty programs and financing solutions make it easier for customers to remain with the brand and repurchase in the future.
- Strong Leadership and Culture: Ford has benefited from stable leadership and a company culture emphasizing innovation, teamwork, and customer satisfaction.
- Focus on Sustainability: The company has shown commitment to sustainability with endeavors in electric vehicle development, sustainable manufacturing processes, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
- Noteworthy Partnerships: Ford has cultivated partnerships with various companies and tech firms to bolster its capabilities in autonomous driving, electric vehicle infrastructure, and more.
Weaknesses
- Declining Market Share in Key Segments: Ford has experienced declining market shares in certain key segments and regions despite its strong brand. Competitors, especially from Asia, have been gaining ground. As per its annual report, Ford’s market share in the global market has declined from 5.4% in 2021 to 5% in 2022.
- Reliance on the North American Market: Historically, a significant portion of Ford’s profits have come from the North American market, especially from selling trucks and SUVs. This heavy reliance on one region makes them vulnerable to economic downturns in that specific area.
- Recalls and Quality Issues: Over the years, Ford has had to deal with vehicle recalls due to various issues, from software glitches to hardware failures. These recalls can hurt the brand’s image and result in significant financial burdens.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Ford has occasionally struggled with operational inefficiencies, leading to higher production costs than some of its competitors.
- Delayed Entry in Electric Vehicle Segment: Although Ford has moved towards electric vehicles (EVs), they were slower to enter and invest in the EV market than competitors like Tesla or Nissan.
- Labor Relations: Ford, like other U.S. automakers, has sometimes faced challenges with labor relations, strikes, and the associated costs of union agreements.
- High Debt Levels: At various points in its history, Ford has carried a high level of debt, which can limit its ability to invest in new technologies or ventures. Ford Motor had US$138.4b in debt in December 2022.
- Global Restructuring Costs: Ford’s moves to restructure its global operations, such as exiting certain markets or closing plants, come with high costs.
- Ageing Facilities: Some of Ford’s production facilities, particularly in older markets, are aged and may not be as efficient as newer plants. This can lead to increased production costs and reduced flexibility in manufacturing.
Opportunities
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): As the world is shifting towards sustainable energy solutions, there’s a growing demand for electric vehicles. Ford can expand its footprint in this area, given the expected growth of the EV market in the coming years.
- BlueOval City: Ford to bring electric zero-emission vehicles at scale to American customers with the largest, most advanced, most efficient auto production complex in its 118-year history. Ford and SK Innovation plan to invest $11.4 billion and create nearly 11,000 new jobs – close to 6,000 in Stanton, Tennessee, and 5,000 in Glendale, Kentucky; production of the new electric vehicles and advanced lithium-ion batteries will begin in 2025.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The development and eventual commercialization of autonomous vehicles present a significant opportunity for major automakers, including Ford.
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Regions such as Asia, Africa, and South America have rapidly growing middle-class populations. Ford can focus on increasing its presence in these markets to tap into the potential growth.
- Hybrid Technologies: Beyond full electric vehicles, there’s also a market for hybrid cars that combine traditional fuel with electric power. This transition technology can be a significant avenue for Ford.
- Digital Services and Connectivity: With the increasing integration of digital tech in vehicles, there are opportunities for Ford to offer advanced connectivity features, infotainment systems, and even subscription-based services.
- Shared Mobility: As urbanization increases and cities become more congested, many consumers prefer car-sharing and ride-hailing services instead of owning a car. Collaborating or investing in such platforms can be an opportunity for Ford.
- Strengthening Online Sales Channels: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of digital sales channels. Enhancing online sales and virtual showrooms can provide Ford with a competitive edge.
- Sustainable Practices and Circular Economy: There’s an increasing demand from consumers for environmentally friendly and sustainable products. Ford can invest in more sustainable manufacturing processes, recycling, and circular economy initiatives.
- Diversification into Related Mobility Solutions: This includes opportunities like e-bikes, e-scooters, or even urban public transport solutions, broadening Ford’s scope beyond just cars.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Strategic alliances with tech companies, battery manufacturers, and other stakeholders can help Ford quickly adapt to the evolving landscape of the auto industry.
- Enhanced After-Sales Services: Offering premium after-sales services, maintenance packages, and loyalty programs can boost customer retention and brand loyalty.
- Research and Development: Continued investment in R&D can lead to discovering new technologies, materials, and designs, keeping Ford ahead in the innovation curve.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The automotive industry is highly competitive, with global giants like Toyota, General Motors, Volkswagen and newer entrants like Tesla. These competitors constantly challenge Ford’s market share and profit margins.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns, recessions, or financial crises can drastically reduce consumer spending on big-ticket items like vehicles, affecting Ford’s sales and profitability.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Events such as natural disasters, trade wars, global pandemics, or geopolitical tensions can disrupt Ford’s extensive global supply chain.
- Regulatory Pressures: Stricter emission regulations, especially in Europe and parts of Asia, mandate automakers to invest heavily in cleaner technologies and adapt their product line-up, which could lead to increased costs for Ford.
- Rapid Technological Changes: The auto industry is witnessing rapid technological advancements. Companies slow to adapt can quickly become obsolete or lose market share.
- Shifts in Consumer Preferences: As seen in recent years, there’s a growing preference for SUVs and trucks over sedans in markets like the U.S. Ford needs to anticipate and adapt to such shifts to stay relevant.
- Global Political and Trade Uncertainties: Events like Brexit or U.S.-China trade tensions can impact global trade dynamics, potentially affecting Ford’s operations and profitability.
- Rising Raw Material Costs: Increases in the prices of steel, aluminum, or other raw materials would elevate production costs for Ford.
- Labor Issues: Strikes, union negotiations, and labor disputes can halt production and increase operational costs.
- Electric and Autonomous Vehicle Competition: Companies like Tesla in the EV segment and various tech companies in the autonomous driving space could outpace Ford if they don’t innovate quickly.











