Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Visa. Visa Inc. is a leading global digital payment technology company that facilitates electronic funds transfers worldwide, mainly through Visa-branded credit, debit, and prepaid cards.
The company does not issue cards or set consumer rates and fees; instead, it provides Visa-branded payment products to financial institutions, offering customers credit, debit, prepaid, and cash access programs. Visa’s global network, VisaNet, processes billions of transactions, supporting various payment solutions and services.
Founded in 1958 as BankAmericard, Visa has evolved into one of the world’s most valuable payment card services corporations, with operations across more than 200 countries and territories.
The company’s headquarters are in San Francisco, California. Visa’s key offerings include authorization, clearing, and settlement of transactions, routing payment information and related data, contactless payments, and various digital services. Visa’s transaction processing network, VisaNet, plays a crucial role in the clearing, authorization, and settlement of payment transactions.
How does Visa work & make money: Business Model
Visa’s business strategy encompasses consumer payments, new flows, value-added services, and foundational business model elements. The company focuses on transitioning consumer spending from cash and checks to cards and digital accounts, leveraging its extensive network. Visa Direct, part of Visa’s broader strategy, facilitates the delivery of funds to cards, deposit accounts, and digital wallets in over 190 countries and territories.
Visa also offers a portfolio of commercial payment solutions, including small business and corporate cards, purchasing and virtual cards, non-card cross-border B2B payment options, and disbursement accounts, catering to significant industry segments worldwide. Furthermore, Visa’s cross-border solutions aim to build infrastructure that enables clients of all sizes to deliver cross-border products with visibility, speed, and security.
Here is the SWOT analysis for Visa
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Visa.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Global Brand Recognition: Visa is one of the most recognized and trusted brands in the financial services sector, with widespread acceptance by merchants and consumers worldwide.
- Extensive Network and Reach: Visa’s payment network, VisaNet, processes transactions in over 200 countries and territories, supporting various payment methods and facilitating global commerce.
- Innovative Payment Solutions: Visa is at the forefront of payment technology, offering products and services, including contactless payments, digital wallets, and Visa Direct for fast money transfers.
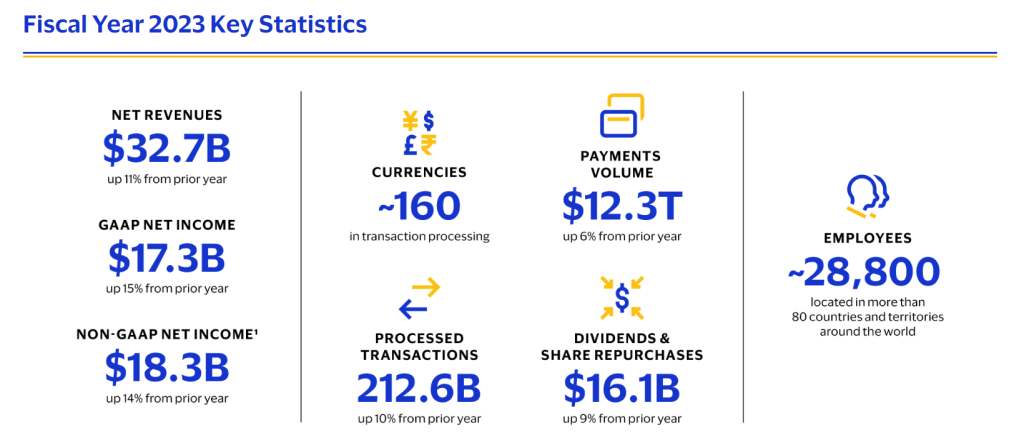
- Strong Financial Performance: Visa has demonstrated robust financial health, with significant revenue, operating income, and net income figures, showcasing its ability to generate and grow wealth.
- Advanced Security Measures: The company invests heavily in security and fraud prevention technologies, ensuring the safety and integrity of transactions processed on its network.
- Diverse Product Portfolio: Visa’s offerings extend beyond consumer credit and debit cards to include prepaid solutions, commercial payment services, and value-added services tailored to various market segments.
- Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions: Visa continuously expands its capabilities and market presence through strategic partnerships and acquisitions, enhancing its product offerings and entering new markets.
- Commitment to Innovation: Visa is committed to innovation, investing in new technologies and platforms to enhance the payment ecosystem and improve customer experiences.
Weaknesses
- Regulatory Challenges: Visa operates in a highly regulated environment globally, and any changes in regulations or non-compliance could result in significant legal costs and impact its operations.
- Dependence on Banking and Financial Institutions: Visa’s business model relies heavily on relationships with banks and other financial institutions. Changes in these relationships or the financial industry’s structure could affect Visa’s revenue streams.
- Competition and Market Saturation: The payments industry is intensely competitive, with traditional players like Mastercard and emerging fintech companies offering innovative payment solutions. This competition could limit Visa’s growth opportunities, particularly in mature markets.
- Cybersecurity Risks: While Visa invests heavily in security, the increasing sophistication of cyber threats poses a constant risk to its systems and the financial data it processes, potentially leading to financial and reputational damage.
- Technological Disruptions: Rapid technological change in the payments sector requires continuous innovation and adaptation. Visa may face challenges in adapting to new technologies and consumer demands for payment methods.
- Economic Dependency: Visa’s performance is closely tied to the overall health of the global economy. Economic downturns can reduce consumer spending and transaction volumes, impacting Visa’s revenues.
- Market Diversification: While Visa has a global presence, its performance in emerging markets may be affected by local competitors, regulatory environments, and economic factors, limiting its growth potential in these regions.
Opportunities
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Visa can leverage its global brand and technology to penetrate emerging markets further, where digital payment adoption is proliferating due to increasing internet and smartphone penetration.
- Innovations in Payment Technology: The continuous evolution of payment technologies, such as blockchain and cryptocurrency, gives Visa opportunities to innovate and offer new payment solutions that meet changing consumer preferences and needs.
- Partnerships with Fintech Companies: Collaborating with Fintech startups can provide Visa access to innovative technologies and business models, enabling it to enhance its product offerings and enter new segments of the payments market.
- Growth in E-commerce: The rapid growth of online shopping globally allows Visa to expand its digital payment services and solutions, catering to businesses and consumers in the e-commerce ecosystem.
- Contactless and Mobile Payments: With the increasing adoption of contactless and mobile payments, Visa can capitalize on this trend by promoting its contactless solutions and mobile payment platforms to facilitate convenient and secure transactions.
- Value-Added Services: Visa can further develop and offer value-added services, such as fraud management, data analytics, and loyalty programs, to enhance its offerings to merchants and financial institutions, thereby generating additional revenue streams.
- Financial Inclusion Initiatives: Visa can leverage its technology and network to drive financial inclusion initiatives, particularly in underbanked regions, by providing accessible and affordable digital financial services.
Threats
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Changes in global regulatory landscapes, including increased regulation of payment fees and data protection laws, pose significant challenges to Visa’s operations and profitability.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As a financial services corporation, Visa is a prime target for cyberattacks. Breaches in security could lead to significant financial losses and damage to the company’s reputation.
- Technological Disruptions: Rapid advancements in payment technologies and the rise of alternative payment methods, such as cryptocurrencies and mobile wallets, could disrupt traditional card-based payment systems and reduce Visa’s market share.
- Intense Competition: The payments industry is highly competitive, with traditional competitors like Mastercard and emerging fintech companies offering innovative payment solutions that could erode Visa’s market dominance.
- Economic Fluctuations: Visa’s business is sensitive to global economic conditions. Economic downturns can lead to reduced consumer spending and lower transaction volumes, adversely affecting revenues.
- Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Disputes: Visa’s global operations could be affected by geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and sanctions, which might restrict its activities in specific regions or increase operational costs.
- Market Saturation in Developed Economies: In mature markets, high market saturation for card payments may limit Visa’s growth potential, pushing the company to seek expansion in less familiar and potentially more volatile emerging markets.











