Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Barclays Bank.
- History and Origin: Barclays has its roots in the goldsmith banking business established in the City of London in 1690. James Barclay became a partner in the business in 1736, and the company name “Barclays” became associated with it.
- Business Structure: Barclays operates through two primary business divisions:
- Barclays UK: This division provides retail banking, local business banking, and wealth management services within the UK.
- Barclays International: This covers corporate banking, investment banking, and wealth management operations outside the UK.
- Products and Services: Barclays offers a wide array of services, including:
- Retail Banking: Current accounts, savings accounts, mortgages, personal loans, and other retail banking services.
- Credit Cards: Under the Barclaycard brand, they offer credit card services in many countries.
- Wealth Management: Investment management, wealth planning, and private banking services.
- Corporate Banking: Business loans, treasury solutions, commercial mortgages, and other corporate finance services.
- Investment Banking: Financial advisory, underwriting, and brokerage services.
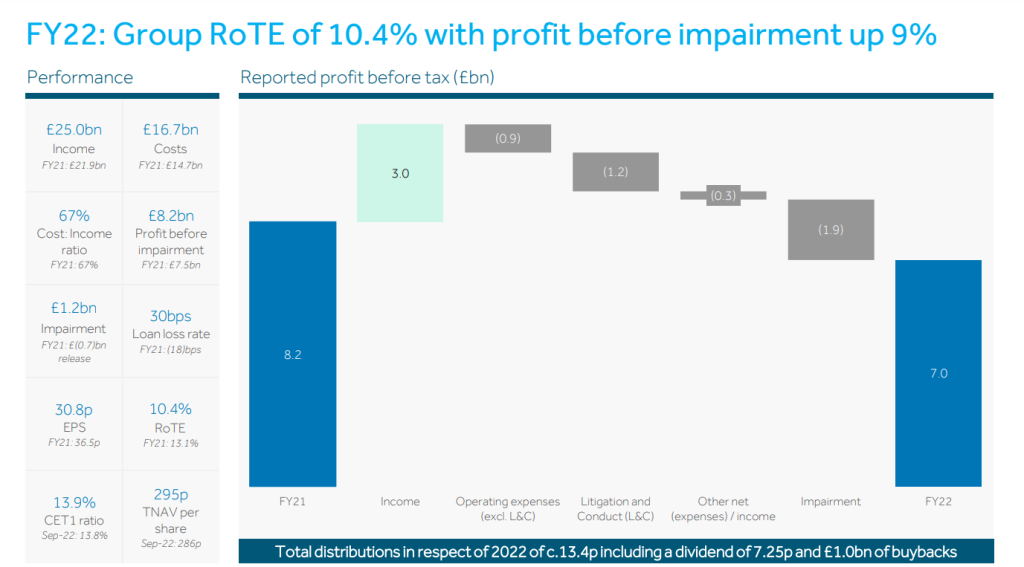
- Financial Performance 2022: Refer to the image below
Here is the SWOT analysis for Barclays Bank
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Barclays Bank.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong Brand Reputation: Barclays is one of the oldest and most established banks in the world, with a brand recognized for its reliability and history.
- Diverse Product Portfolio: The bank offers a comprehensive range of financial services, including retail banking, wealth management, investment banking, and corporate banking, which cater to a broad customer base.
- Global Presence: With operations in over 40 countries, Barclays has a significant global footprint, providing diverse market access and an international customer base.
- Innovative Banking Solutions: Barclays has been at the forefront of introducing innovative banking services, such as the first credit card in the UK, and continues to invest in digital banking technologies.
- Investment in Technology: Barclays has significantly invested in technology to improve customer experience and operational efficiency, such as online banking and mobile apps.
- Risk Management: Barclays has robust risk management frameworks to identify, assess, and mitigate risks, which is crucial in the banking industry.
- Strong Capital and Liquidity Ratios: Barclays often maintains strong capital adequacy and liquidity ratios, which are important indicators of financial health and stability.
- Customer Base: A large and diversified customer base provides stable revenue streams and reduces dependence on any single market segment.
Weaknesses
- Past Controversies and Scandals: Barclays has faced several controversies, such as the LIBOR scandal and issues related to fraudulent sales practices, which have tarnished its reputation and could affect customer trust and loyalty.
- Restructuring Costs: Over the years, Barclays has undergone numerous restructurings, which can be costly and may distract from its core operations.
- Dependence on the UK Market: Despite its international presence, Barclays still has a significant dependence on the UK market, making it vulnerable to regional economic and political uncertainties, particularly in the context of Brexit.
- Low-Interest Rate Environment: Like many banks, Barclays is affected by the global low-interest-rate environment, which can compress net interest margins and reduce profitability.
- Operational Issues: Operational issues, such as system outages or service interruptions, can impact customer satisfaction and lead to financial losses.
- Competition from Fintech: The rise of fintech companies offering agile and innovative financial solutions can erode the market share of traditional banks like Barclays, especially among tech-savvy younger consumers.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Barclays, like all central banks, is exposed to the risk of cyber attacks, which can lead to financial loss, data breaches, and damage to reputation.
- Performance of Investment Banking Division: Volatility in the performance of its investment banking division can lead to uncertainty in overall business performance.
- Asset Quality: The quality of the bank’s asset portfolio can be a concern, especially during economic downturns when the risk of loan defaults is higher.
- Cost Efficiency: There may be issues around cost efficiency and the need to reduce costs to maintain competitiveness against leaner, more cost-effective rivals.
Opportunities
- Digital Banking Expansion: There is a growing trend towards digital and mobile banking. Barclays can capitalize on this by further developing its digital banking platforms to attract tech-savvy customers and reduce operational costs.
- Emerging Markets: Expanding into emerging markets could provide new revenue streams and diversification of assets, reducing reliance on mature markets.
- Fintech Partnerships: Collaborating with fintech companies could enable Barclays to innovate more quickly and offer cutting-edge services to its customers.
- Sustainable Finance: As there is increasing interest in sustainability, Barclays could increase its offering of green finance products and services, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses.
- Diversification of Services: Offering new financial products or entering into new economic sectors (like insurance, asset management, etc.) could provide new sources of income.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Improving customer service through personalization and better responsiveness can increase customer loyalty and attract new clients.
- Regulatory Changes: Sometimes regulatory changes can open up new markets or allow for new products that were previously not possible or viable.
- Operational Efficiency: Investing in new technologies such as AI and blockchain could improve operational efficiency and reduce costs through automation.
- Acquisitions and Mergers: There could be opportunities for mergers or acquisitions that could expand Barclays’ market share or capabilities in certain areas.
- Banking as a Service (BaaS): Barclays could leverage its banking infrastructure to offer BaaS to non-banking companies looking to integrate financial services into their offerings.
- Wealth Management: With the growing number of high-net-worth individuals globally, there is an opportunity to expand wealth management and private banking services.
- Global Trade Finance: Barclays can leverage its international presence to enhance its role in global trade finance, especially post-Brexit, by facilitating trade across borders.
- Cybersecurity Services: By developing robust cybersecurity services, Barclays can differentiate itself and offer these services to other businesses as a value proposition.
- Financial Literacy and Inclusion: Engaging in initiatives that promote financial literacy and inclusion can improve the bank’s public image and open up untapped customer bases.
Threats
- Economic Fluctuations: Global economic volatility, including the risk of recession, can lead to decreased consumer spending and increased loan default rates.
- Brexit Consequences: As a UK-based bank, Barclays faces specific threats from the economic and regulatory uncertainties resulting from Brexit.
- Regulatory Pressure: Banks are subject to intense regulatory scrutiny. New regulations can increase compliance costs or limit certain profitable activities.
- Competitive Market: The banking industry is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share, including traditional banks, online banks, and fintech startups.
- Interest Rate Risks: Changes in interest rates can affect the bank’s margins. A low-interest-rate environment can be exceptionally challenging for profitability.
- Technology Disruption: Technological advances by fintech and big tech companies threaten traditional banking models, potentially displacing established players like Barclays.
- Cybersecurity Threats: The risk of cyber attacks is a constant threat to the banking industry, potentially leading to financial loss and damage to reputation.
- Consumer Behavior Changes: As customers become more digitally savvy, they might favor banks that offer the most advanced digital services, putting pressure on Barclays to keep up with digital transformations.
- Political Instability: Political events and instability can affect market confidence and economic conditions, impacting the bank’s operations, especially in countries with higher political risks.
- Currency Fluctuations: Since Barclays operates internationally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact profits repatriated from foreign operations.
- Credit Risk: In times of economic downturn, there is an increased risk of loan defaults which can affect the bank’s asset quality.











