Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of Barclays Bank.
- History and Origin: Barclays has its roots in the goldsmith banking business established in the City of London in 1690. James Barclay became a partner in the business in 1736, and the company name “Barclays” became associated with it.
- Business Structure: Barclays operates through two primary business divisions:
- Barclays UK: This division provides retail banking, local business banking, and wealth management services within the UK.
- Barclays International: This covers corporate banking, investment banking, and wealth management operations outside the UK.
- Products and Services: Barclays offers a wide array of services, including:
- Retail Banking: Current accounts, savings accounts, mortgages, personal loans, and other retail banking services.
- Credit Cards: Under the Barclaycard brand, they offer credit card services in many countries.
- Wealth Management: Investment management, wealth planning, and private banking services.
- Corporate Banking: Business loans, treasury solutions, commercial mortgages, and other corporate finance services.
- Investment Banking: Financial advisory, underwriting, and brokerage services.
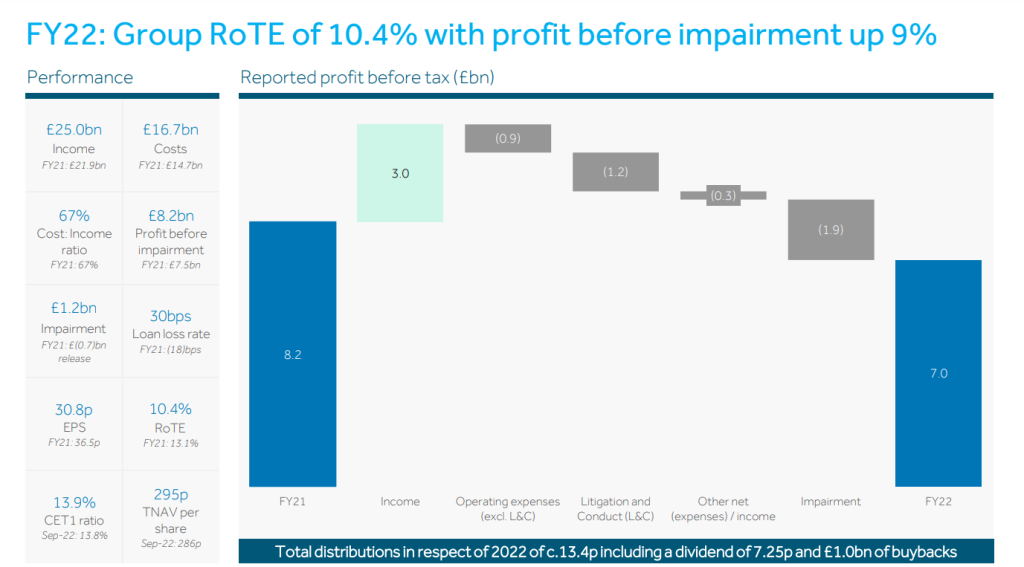
- Financial Performance 2022: Refer to the image below
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Barclays Bank
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Barclays Bank.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Regulatory Environment: The banking sector is highly regulated, and any changes in banking laws and financial regulations can impact Barclays’ operations. These regulations include capital requirements, liquidity standards, and customer protection measures.
- Brexit: Barclays, being a UK-based bank, has been affected by the political implications of Brexit. Uncertainties surrounding Brexit negotiations, potential economic implications, and changes in trade relationships have posed challenges for the bank.
- Global Political Relations: Barclays has a global presence, and hence, its operations in different countries are susceptible to the political relationships between the UK and those countries. Bilateral and multilateral relations can influence the bank’s business in particular regions.
- Public Perception and Trust: The banking industry has been under scrutiny, especially after the 2008 financial crisis. Political narratives focusing on banking accountability, transparency, and ethical conduct can shape public opinion and influence the bank’s reputation.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) Policies: Stringent AML and CTF regulations require banks like Barclays to invest significantly in compliance measures, monitoring, and reporting.
Economic
- Interest Rates: The central banks’ decisions on interest rates directly impact Barclays’ lending and borrowing rates. Higher interest rates can increase the cost of borrowing, potentially reducing loan demand, but can also lead to higher interest income for the bank.
- Economic Growth: The overall economic growth rate of countries where Barclays operates influences the demand for banking services. In thriving economies, businesses and individuals are more likely to borrow, invest, and save.
- Exchange Rates: Being a global bank, Barclays engages in significant foreign currency transactions. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the bank’s foreign investments, assets, and revenue from international operations.
- Inflation: Inflation rates affect the purchasing power of consumers and businesses. High inflation can erode the real value of savings, affecting the bank’s deposit base and influencing interest rates.
- Property Market Dynamics: The property market’s health is crucial for Barclays, given its exposure to mortgages. A buoyant property market can increase mortgage demand, while a downturn can raise the risk of defaults.
- Consumer Spending and Confidence: Economic factors influencing consumer confidence can determine spending behaviors, affecting demand for various banking products like credit cards and personal loans.
- Public and Private Debt Levels: High public or private debt levels in economies where Barclays operates can influence the bank’s lending practices and risk assessments.
Sociocultural
- Changing Customer Expectations: With the advent of technology, customers’ expectations from banking services have evolved. They expect seamless online banking, instant services, and personalized experiences. Barclays needs to cater to these changing expectations to remain relevant and competitive.
- Financial Literacy: The level of financial literacy among the population impacts how customers interact with banking services. Educating customers can increase financial product use and reduce the risk of defaults.
- Cultural Attitudes Towards Debt: Different cultures have varying views on borrowing and debt. In some cultures, taking on debt might be seen negatively, while others view it as a standard financial strategy.
- Ethical Banking: There’s a growing trend towards ethical banking, where customers prefer banks that follow ethical practices, invest in sustainable ventures, and avoid sectors like fossil fuels.
- Urbanization: As more people move to urban areas, there’s a change in banking needs, with possibly a higher demand for digital banking services and lesser dependency on physical branches.
- Attitude Towards Savings: Societal attitudes towards savings vs. spending can significantly impact a bank’s deposit base and the demand for investment products.
- Globalization and Mobility: As people become more globally mobile, there’s a need for banking services that cater to international clients, expatriates, and frequent travelers.
Technological
- Digital Banking: The rise of online banking platforms and apps has shifted how customers interact with banks. Barclays must continually innovate its digital offerings to enhance customer experience and meet the increasing demand for online services.
- Cybersecurity: With the increase in digital transactions and online banking, the threat of cyber-attacks is more prevalent. Barclays must invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect its assets and customer data.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: The advent of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies can potentially revolutionize the banking sector. Barclays can explore blockchain applications in cross-border transactions, fraud prevention, and smart contracts.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: These technologies can be employed in various banking functions, including customer service (chatbots), fraud detection, credit scoring, and personalized banking recommendations.
- Automated Financial Advisors and Robo-Advisors: With AI’s aid, automated platforms can provide financial advice, investment strategies, and portfolio management at lower costs.
- Cloud Computing: Leveraging cloud technology can help Barclays streamline operations, enhance data storage capacities, and improve service delivery efficiency.
- Payment Technologies: The emergence of new payment technologies, like contactless payments, mobile wallets, and peer-to-peer payment systems, requires Barclays to adapt and integrate these methods.
- RegTech: Regulatory Technology (RegTech) uses technology to help financial institutions comply with regulations efficiently and at a lower cost. Given the heavily regulated nature of the banking sector, adopting RegTech can benefit Barclays.
- Biometric Verification: Using biometrics, like fingerprint and facial recognition, adds a layer of security to banking operations and can enhance the user experience in mobile and online banking.
- Infrastructure Modernization: Continuous updating and modernizing IT infrastructure is crucial to ensure smooth operations, integrate new technologies, and prevent system downtimes.
- Open Banking: With regulations like PSD2 in Europe, open banking, which allows third-party developers to create applications and services around a financial institution, is on the rise. This can lead to increased competition and innovation in banking services.
Environmental
- Sustainable Banking: As global attention focuses on sustainability, there’s a growing demand for green banking solutions. Barclays can offer financial products and services that support eco-friendly initiatives, such as green bonds and sustainable investment portfolios.
- Investment in Renewable Energy: There’s increasing scrutiny on banks’ investment portfolios. Barclays may need to increase its investments in renewable energy projects and decrease financing for fossil fuel ventures to align with global sustainability goals.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Barclays’ CSR initiatives, which address environmental concerns, can significantly enhance its corporate image. Activities could include tree planting, waste reduction campaigns, or community clean-up projects.
- Regulatory Compliance: With stricter environmental regulations, Barclays must ensure that its operations, investments, and partnerships comply with local and global environmental standards and regulations.
- Green Technology: The bank can invest in and adopt green technologies. This might include energy-efficient systems, green building certifications for its properties, or supporting green tech startups.
- Eco-friendly Products and Services: Introducing services like eco-loans for green home improvements or electric vehicle purchases can attract environmentally conscious customers.
- Transition to a Circular Economy: This involves minimizing waste and maximizing resources. Barclays can play a role by financing businesses that promote circularity or by implementing circular practices in its operations, like recycling and reusing resources.
Legal
- Regulatory Compliance: Banks like Barclays operate under stringent regulatory frameworks set by central banks and other regulatory bodies. These include capital adequacy requirements, liquidity standards, and other operational criteria that banks must meet to ensure financial stability.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) & Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations: Barclays must adhere to AML and KYC protocols, which mandate comprehensive background checks for customers, monitoring suspicious transactions, and reporting to authorities.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws aim to protect consumers from unfair banking practices, requiring transparency in the provision of financial services, clarity in terms and conditions, and fairness in charging fees and interest rates.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Barclays must comply with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, which mandates strict protocols for collecting, storing, and sharing personal data.
- Taxation: Barclays, like all multinational banks, must navigate complex global tax environments, ensuring compliance with tax laws in every jurisdiction they operate.
- Financial Product Regulations: Various products and services offered by Barclays, from mortgages to insurance, are subject to their regulations. This ensures that customers are treated fairly and fully informed about their purchasing products.
- Post-Brexit Regulations: With the UK’s exit from the European Union, Barclays, like other UK-based banks, has to navigate the new regulatory landscape, which might necessitate structural changes to serve European clients.
- Digital Banking and Fintech Regulations: As Barclays continues its digital transformation and engages with more FinTech solutions, it must adhere to regulations specific to digital banking, online transactions, and electronic data handling.











