Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Porsche. Porsche AG is a German multinational automobile manufacturer specializing in high-performance sports cars, SUVs, and sedans. The company was founded in 1931 by Ferdinand Porsche, an Austrian engineer. Since its inception, Porsche has earned a reputation for producing high-performing and luxurious vehicles.
Porsche is a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group, one of the world’s leading automobile manufacturers. Porsche and Volkswagen merged in 2011. At that time, Porsche was designated a subsidiary of Volkswagen AG (interestingly, besides being the Porsche parent company, VW also owns Audi, Bugatti, and Lamborghini). So, from that standpoint, Volkswagen AG is the company that owns Porsche. However, Porsche also owns a majority share in Volkswagen AG.
The company’s headquarters are located in Stuttgart, Germany. In addition to manufacturing automobiles, Porsche also offers engineering, design, and consulting services. Other car manufacturers worldwide have adopted many of the innovations created by Porsche.
Porsche’s product line includes renowned models such as the 911, Boxster, Cayman, Panamera, Cayenne, Macan, and the Taycan, the company’s first fully electric car, introduced in 2019. Each model carries the distinctive design language and performance characteristics Porsche is known for.
Porsche also has a long history in motorsport, with many successes in races like the 24 Hours of Le Mans. Motorsport boosts the brand’s image and serves as a testing ground for technologies that eventually become Porsche’s production cars.
In Sep’22, Porsche was the largest IPO ever carried out in Europe, with a market capitalization of around 78 billion euros. With the IPO, Porsche is shifting up a gear and setting itself ambitious goals: economically, ecologically, and socially.
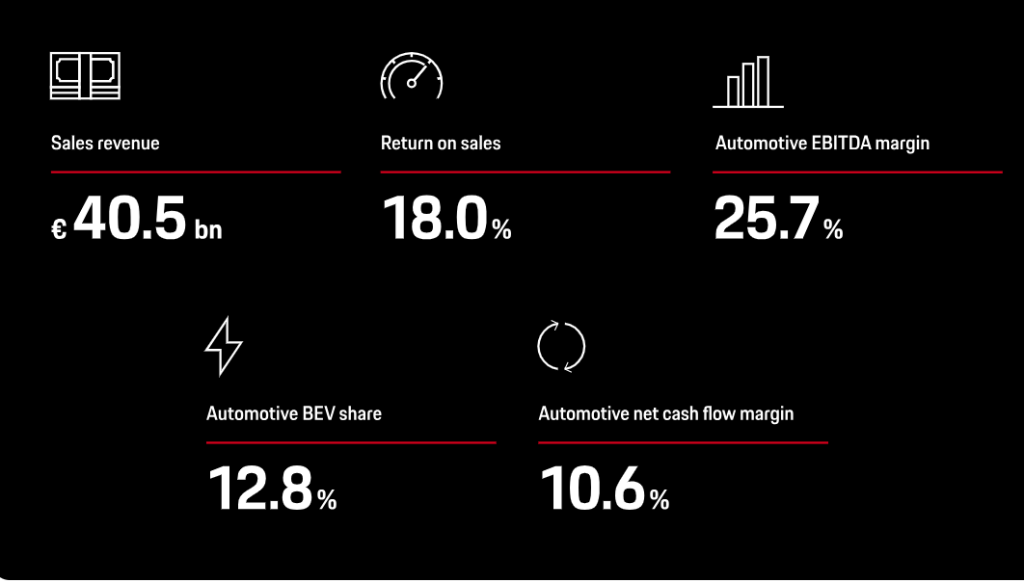
Financial Performance 2023:
Here is the SWOT analysis of Porsche
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Porsche.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong Brand Recognition: Porsche has an iconic brand image known for luxury, performance, and reliability. The brand is associated with status and prestige, which helps drive sales in the luxury car market.
- High-Quality and Innovative Products: Porsche’s cars are renowned for their design, quality, and performance. The company continually invests in R&D to maintain its products’ superior quality and stay at the forefront of automotive technology. The launch of the Taycan, their first electric car, exemplifies this innovative spirit.
- Diverse Product Range: While Porsche is most famous for its 911 series, it offers a wide range of high-performance sports cars, SUVs, and sedans. This diversity allows Porsche to cater to a broader customer base, ranging from sports car enthusiasts to consumers looking for luxury family vehicles.
- Success in Motorsports: Porsche’s impressive track record in motorsports, particularly its numerous victories at the 24 Hours of Le Mans, not only boosts the company’s image but also validates the performance of its vehicles.
- Strong Financial Performance: Porsche consistently shows strong sales and profitability. This financial stability allows the company to invest in future-focused strategies like electric vehicle technology and autonomous driving.
- Global Presence: Porsche has a strong global presence with sales in over 100 countries. Its largest single market is China, followed by the United States and Germany. This geographical diversification helps mitigate the impact of regional economic downturns.
- Support from Volkswagen Group: Being part of the Volkswagen Group, one of the world’s leading automotive conglomerates, provides Porsche with numerous benefits, such as shared R&D, access to resources, and economies of scale.
- Commitment to Sustainability: Porsche increasingly focuses on sustainability, a growing concern for modern consumers. The launch of the Taycan is a part of this commitment, as is Porsche’s dedication to reducing its environmental footprint through more sustainable production methods.
Weaknesses
- High Pricing: While the premium pricing of Porsche vehicles underscores their luxury and quality, it also limits their market to high-income individuals. This pricing strategy could limit the brand’s customer base compared to competitors with a wider range of price points.
- Dependence on a Few Models: Porsche’s 911 model is a cornerstone of the brand. While this has solidified the 911’s iconic status, an overreliance on a single model could pose risks, especially if consumer preferences shift away from sports cars.
- Dependence on Specific Markets: As of 2021, a significant portion of Porsche’s sales comes from China, the United States, and Germany. Any economic or political instability in these markets could negatively affect Porsche’s revenue.
- Limited Electric Vehicle (EV) Range: As of 2021, Porsche had only one fully electric model, the Taycan. While the Taycan is an impressive vehicle, the limited variety of EVs could put Porsche at a disadvantage compared to competitors with more extensive electric offerings.
- Brand Damage from Volkswagen Emissions Scandal: As a part of the Volkswagen Group, Porsche’s reputation suffered indirect damage from the emissions scandal in 2015, also known as “Dieselgate.” Although Porsche vehicles were not directly implicated, trust in the entire Volkswagen Group, including Porsche, took a hit.
- Environmental Impact: Like other traditional automobile manufacturers, Porsche’s manufacturing processes and the use of its vehicles contribute to environmental pollution. Although Porsche has taken steps to reduce its environmental footprint and transition to electric vehicles, it still faces criticism and regulatory pressures related to environmental sustainability.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Like many car manufacturers, Porsche’s supply chain is complex and spans multiple countries. This exposes the company to risks such as fluctuating exchange rates, trade wars, or disruptions due to pandemics or natural disasters.
Opportunities
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Market: A global shift towards electric vehicles is driven by growing consumer awareness of environmental issues and increasingly stringent emissions regulations. Porsche entered the EV market with the Taycan, and there is a significant opportunity to expand its electric lineup to meet rising consumer demand and regulatory requirements.
- Autonomous Vehicles: The self-driving car market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. Porsche can capitalize on this trend by investing in autonomous driving technology through in-house development or partnerships with technology companies.
- Sustainability Initiatives: There is a growing demand for businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. Porsche can leverage this trend by investing in sustainable manufacturing processes, using more eco-friendly materials, and promoting its electric vehicles as a green alternative to traditional cars.
- Emerging Markets: Porsche has an opportunity to expand its presence in emerging markets like India, Southeast Asia, and Africa. These markets have growing middle and upper classes that could form a new customer base for luxury car brands like Porsche.
- Digitalization and Connectivity: Integrating digital technology into vehicles is becoming increasingly important. This allows Porsche to develop more advanced infotainment systems, connected car services, and other digital features to enhance the driving experience and provide new revenue streams.
- Expansion of Services: Porsche could expand its offerings in car sharing, financing, and other mobility services. These services can provide additional revenue streams and deepen customer relationships.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming strategic alliances with other companies can provide Porsche access to new technologies, markets, or customer segments. For example, partnerships with tech companies could accelerate Porsche’s development of autonomous driving technology or connected car services.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The automotive industry is intensely competitive, particularly in the luxury and high-performance segment. Competitors like Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Audi, Ferrari, and Tesla constantly introduce new products and innovations that could outperform Porsche’s offerings.
- Regulatory Environment: Increasingly stringent emissions standards worldwide, particularly in Europe and China, pose a significant challenge to automakers. While Porsche has initiated its transition to electric vehicles with the Taycan, a failure to keep pace with regulations could result in fines or restrictions on selling its vehicles in certain markets.
- Economic Fluctuations: Porsche, being a luxury carmaker, can be significantly impacted by global economic conditions. Economic downturns can reduce the demand for luxury goods, including high-end vehicles, negatively affecting Porsche’s sales and profitability.
- Technological Disruption: The automotive industry is undergoing a massive transformation with trends like electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and connected cars. Porsche’s future success depends on its ability to adapt to these technological changes and meet new consumer expectations.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events such as pandemics, trade wars, or natural disasters can disrupt Porsche’s supply chain, leading to production delays and increased costs.
- Reputation Risk: Any negative incidents, such as safety issues, recalls, or scandals, could harm Porsche’s reputation and affect customer trust. As a part of the Volkswagen Group, Porsche’s reputation can also be impacted by incidents related to other brands, as was the case with the Dieselgate scandal.
- Transition to EVs: While the shift to electric vehicles represents an opportunity for Porsche, it’s also a significant threat. The transition requires substantial investment, and there are risks related to technological development, charging infrastructure, and consumer acceptance of EVs.











