Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let us get the business overview of Volkswagen. Volkswagen AG is a German multinational automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Wolfsburg, Germany.
It is one of the largest automakers globally in terms of production volume and sales. The company designs, manufactures and distributes passenger and commercial vehicles, motorcycles, engines, and turbomachinery. It also provides related services, including financing, leasing, and fleet management.
Volkswagen operates through multiple brands, including:
- Volkswagen Passenger Cars: The brand produces vehicles ranging from small cars and luxury vehicles.
- Audi: This luxury brand produces high-end cars and sport utility vehicles.
- SEAT: A Spanish automaker producing cars and sport utility vehicles.
- Škoda: This Czech automaker produces a range of vehicles, including small cars, sedans, and sport utility vehicles.
- Bentley: A British brand producing luxury cars and SUVs.
- Bugatti: A manufacturer of hyper sports cars.
- Lamborghini: An Italian brand producing super sports cars and SUVs.
- Porsche: This German automaker specializes in high-performance sports cars, SUVs, and sedans.
- Ducati: An Italian company producing motorcycles.
- Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles: Produces light commercial vehicles, including vans, pick-up trucks, and camper vans.
- Scania and MAN: These brands produce trucks and buses for heavy transport applications.
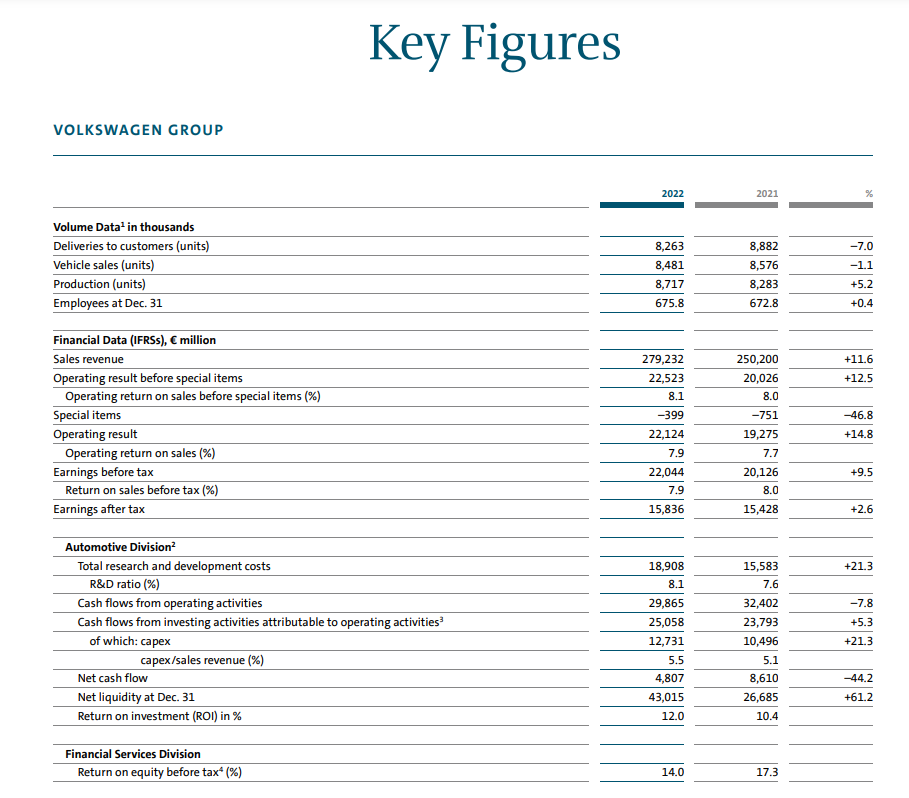
In recent years, Volkswagen has invested heavily in electric mobility and digital transformation as part of its “TOGETHER – Strategy 2025”. The company aims to become a world-leading provider of sustainable mobility.
Volkswagen’s business model includes sales through a network of dealerships and distributors across the globe. The company also has numerous production facilities in Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Volkswagen
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Volkswagen.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Government Stability: The political stability of the countries where Volkswagen operates significantly influences the business. Unstable political environments can lead to supply chain disruptions and sales and may increase operational risks. Volkswagen has a global presence, so it needs to account for political conditions in various regions of the world.
- Regulations and Policies: Government policies on emissions, vehicle safety, and fuel efficiency significantly affect Volkswagen. After the Dieselgate scandal, these regulations have had an even stronger impact on the company. Strict regulations in many developed countries force the company to invest heavily in research and development to adhere to these policies.
- International Trade Policies: Trade policies such as tariffs, duties, import/export restrictions, and Brexit implications play a role in shaping Volkswagen’s political landscape. Any changes in these policies directly affect Volkswagen’s cost of operations and profitability.
- Political Relations: The relationship between Germany (where Volkswagen is based) and other countries is also crucial. Good relationships mean more straightforward trade and fewer restrictions. However, strained relationships could result in trade sanctions or restrictions.
- Government Initiatives: Government initiatives promoting electric vehicles and other alternative energy sources offer opportunities for Volkswagen, which is working to become a leader in electric vehicles. Governments worldwide are providing subsidies to promote the use of electric vehicles, which Volkswagen can capitalize on.
- Infrastructure Quality: Government investment in infrastructure quality can also impact Volkswagen. Better roads lead to higher demand for cars, while good transportation infrastructure can facilitate supply chains.
Economic
- Global Economic Conditions: The economic health of the regions Volkswagen operates in significantly impacts its performance. During economic downturns or recessions, people have less disposable income and are less likely to purchase new vehicles, reducing sales for the company.
- Exchange Rates: Volkswagen operates globally, and changes in exchange rates can affect its profits, especially in countries outside of the Eurozone. A weaker Euro might make Volkswagen’s products more competitive in international markets but could increase the costs of imported inputs.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates influence the cost of capital for Volkswagen. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive and hamper infrastructure investments or research and development. Interest rates also affect consumers’ willingness to finance vehicle purchases.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation affects both the cost of production (raw materials, labor, etc.) and consumer purchasing power. High inflation could lead to increased costs for Volkswagen while reducing demand if consumers’ purchasing power decreases.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment rates generally lead to lower demand for vehicles, as fewer people have the income necessary to afford them. Conversely, low unemployment rates usually correlate with stronger vehicle sales.
- Fuel Prices: Fluctuating fuel prices can also influence consumer preference for vehicle types. Rising fuel prices may lead consumers to prefer more fuel-efficient or electric vehicles, impacting the types of cars Volkswagen should focus on producing.
- Tax Policies: Various tax policies, including taxes on luxury goods or vehicles, import-export taxes, and corporate taxes, can affect the net profitability of Volkswagen.
Sociocultural
- Changing Consumer Attitudes: As societal attitudes towards sustainability and the environment evolve, consumers increasingly prefer eco-friendly, electric, and hybrid vehicles. Volkswagen needs to cater to this change and accelerate its efforts in sustainable vehicle technology.
- Consumer Trust: Following the Dieselgate scandal, Volkswagen may have to work to rebuild trust among consumers. Trust plays a significant role in customers’ purchasing decisions, especially in industries like automotive, where safety and reliability are crucial.
- Cultural Preferences: Cultural preferences can vary significantly by region. For instance, in some markets, consumers may prefer larger, family-size vehicles, while in others, compact cars may be favored due to crowded cities or high fuel costs. Understanding these cultural nuances can help Volkswagen better tailor its product offerings.
- Demographics: Changes in population demographics, like aging populations in developed countries, could shift demand for different types of vehicles. For example, an aging population might demand more comfortable and safer cars, while younger consumers may look for more technologically advanced, stylish, or environmentally-friendly vehicles.
- Lifestyle Trends: Changes in lifestyle trends can influence the types of vehicles in demand. For example, increased remote working due to the COVID-19 pandemic could decrease the demand for commuter vehicles. Rising interest in outdoor activities might boost the demand for SUVs or off-road vehicles.
- Health and Safety Concerns: Health and safety have recently become paramount for consumers. Consumers now demand vehicles with advanced safety features, which Volkswagen must incorporate into its vehicle designs to stay competitive.
Technological
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Technologies: The world is transitioning towards more sustainable means of transportation. Volkswagen must invest in and prioritize electric vehicle technology, hybrid cars, and innovative fuel alternatives like hydrogen fuel cells to stay competitive.
- Autonomous Driving: The development of self-driving vehicles is accelerating, with many of Volkswagen’s competitors investing heavily in this technology. The success of autonomous driving technology will significantly affect Volkswagen’s competitive standing.
- Connected Cars and Internet of Things (IoT): As cars become more integrated with digital technologies, consumers increasingly demand vehicles with advanced features like remote diagnostics, infotainment systems, and connectivity. Investing in these technologies can give Volkswagen a competitive edge.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML technologies have significant implications for vehicle safety, predictive maintenance, and personalized driving experiences. Volkswagen should capitalize on these technologies to enhance its product offerings.
- Manufacturing Technology: Advancements in manufacturing technology such as automation, robotics, and 3D printing can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the quality of Volkswagen’s products.
- Cybersecurity: With the rise of connected cars and digitization, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. Protecting customers’ data and ensuring the safety of connected and autonomous vehicles are crucial for maintaining consumer trust.
- Battery Technology: Advancements in battery technology are key to the viability and success of electric vehicles. Investing in or securing access to the most efficient, cost-effective, and long-lasting battery technology is crucial for Volkswagen’s electric vehicle strategy.
Environmental
- Emissions Standards and Regulations: After the Dieselgate scandal, Volkswagen faces significant pressure to adhere to strict emission standards set by governments worldwide. The company must ensure its vehicles meet or exceed these standards to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
- Climate Change: Increasing concerns about climate change are driving consumers and governments towards eco-friendly alternatives, including electric and hybrid vehicles. Given its substantial investments in electric vehicle technology, Volkswagen has the opportunity to establish itself as a leader in this area.
- Resource Scarcity: As raw materials like metals become scarcer and potentially more expensive, Volkswagen may need to find new materials or more efficient production methods.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Regulations and societal expectations around waste management and recycling are tightening. Volkswagen should minimize its waste and increase the recyclability of its products to improve its environmental footprint and conform to regulatory requirements.
- Sustainable Supply Chain: Consumers and governments increasingly expect companies to ensure their sustainable and ethically sound supply chains. Volkswagen may need to assess and address any environmental issues in its supply chain.
- Energy Use: The amount and type of energy used in Volkswagen’s production processes can impact its environmental footprint. Transitioning to renewable energy sources can help the company reduce its environmental impact and save on energy costs.
- Biodiversity: Volkswagen’s operations, particularly in manufacturing and resource extraction, can have implications for local biodiversity. The company needs to ensure that it minimizes its impact on local ecosystems.
Legal
- Emissions Standards and Regulations: After the “Dieselgate” scandal, where Volkswagen was found to have cheated emissions tests, the company has faced substantial legal scrutiny and penalties. Compliance with emissions standards worldwide is a critical legal issue for Volkswagen.
- Safety Standards: Automobile manufacturers like Volkswagen must adhere to stringent safety standards in every market they operate in. These regulations pertain to features like airbags, brakes, stability controls, seat belts, and more.
- Labor Laws: Volkswagen operates in many different countries, each with its own set of labor laws regarding wages, working conditions, overtime, and worker rights. Non-compliance can result in legal issues and damage to the company’s reputation.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws: With the rise of connected cars, data protection, and privacy have become important legal considerations. Volkswagen must ensure compliance with regulations like the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and similar laws in other countries.
- International Trade Laws: As a global corporation, Volkswagen must navigate complex international trade laws, including import/export regulations, tariffs, and trade agreements. The changing landscape of trade laws, such as the impact of Brexit, also poses legal challenges.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Volkswagen must protect its innovations and designs through patents, copyrights, and trademarks. Conversely, it must also avoid infringing on the intellectual property rights of others.
- Corporate Governance Laws: Volkswagen, as a publicly traded company, is subject to laws and regulations concerning financial reporting, transparency, and corporate governance. Volkswagen must comply with these laws to maintain investor trust and avoid legal penalties.











