Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Tinder. Tinder, a leading player in the online dating industry, was founded by Sean Rad and Justin Mateen. The app is known for its user-friendly interface and the innovative “swipe” feature, which has significantly contributed to its popularity, especially among younger demographics.
Tinder’s business model primarily operates on a freemium basis, offering essential services for free while charging for advanced features through subscription plans like Tinder Plus and Tinder Gold.
Tinder’s revenue generation strategy includes subscription tiers and premium features such as boosts and super likes. The subscription plans vary in price and features offered, with options including Tinder Plus, Tinder Gold, and Tinder Platinum. The dynamic pricing model can vary based on age, geographic location, and market demand.
Financial performance 2023: For the full year 2023, Tinder delivered $1.9 billion of Direct Revenue, an increase of 7% Y/Y.
Here is the SWOT analysis for Tinder
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Tinder.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Vast User Base: Tinder has a large and growing user base, which has been a critical factor in its success. The app’s popularity, particularly among younger demographics, has helped it establish a strong market presence. In 2022, Tinder had 10.9 million subscribers and 75 million monthly active users.
- Innovative User Interface: The app’s simple and intuitive “swipe” feature has revolutionized how people interact with dating platforms, making it easy and fun for users to engage with the service.
- Strong Brand Recognition: Tinder has become a well-known online dating brand synonymous with mobile dating and social discovery. This recognition has helped it to attract new users and retain existing ones.
- Effective Monetization Strategy: Through its freemium business model and various subscription tiers such as Tinder Plus, Tinder Gold, and Tinder Platinum, Tinder has successfully monetized its user base. The app offers premium features like unlimited likes, rewind swipes, and the ability to see who likes you, contributing to its revenue.
- Location-Based Matching System: Tinder’s use of geographical proximity for matching users adds convenience and immediacy to the dating process, allowing users to quickly find and connect with potential matches in their area.
- Data-Driven Matchmaking: By leveraging data analytics, Tinder can provide personalized matchmaking recommendations, which enhances the user experience and increases the likelihood of successful matches.
- User Network Effect: As more people join Tinder, the platform’s value increases for all users due to a larger pool of potential matches. This network effect has helped Tinder remain a leading dating app.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: Besides subscriptions, Tinder generates revenue through in-app advertising and premium features like Boosts and Super Likes, providing multiple income streams.
Weaknesses
- Limited Revenue Model: Tinder’s revenue heavily relies on subscription fees and in-app purchases. While effective, this model may limit revenue diversification and make the business vulnerable to fluctuations in user spending habits.
- User Safety and Privacy Concerns: The platform has faced criticism regarding user safety and data privacy. Vulnerabilities in protecting user information can expose users to security risks, such as identity theft or other malicious activities. These issues could potentially damage the company’s reputation and user trust.
- Perception as a Hook-Up App: Tinder has gained a reputation as a “hook-up app,” which might deter users looking for serious relationships. This perception can limit the app’s appeal to a broader audience seeking long-term connections.
- User Experience Issues: The anonymous nature of the platform can lead to exploitative or unpleasant behavior among users. Such experiences can harm the overall user experience and may lead to legal challenges or further reputational damage.
- Dependence on Network Effects: While a large user base is a strength, it also presents a weakness. The value of the service is highly dependent on network effects, meaning that any decrease in user activity or engagement could significantly impact the platform’s attractiveness to new and existing users.
- Competition and Market Saturation: Online dating is highly competitive, with new apps continually emerging. Tinder faces the challenge of maintaining its user base and market share amidst growing competition and the potential for user fatigue.
- Dynamic Pricing Controversy: Tinder’s practice of offering dynamic pricing, where subscription costs can vary based on factors like age and location, has led to controversy and dissatisfaction among users who may feel unfairly charged.
Opportunities
- Market Expansion: Tinder has the opportunity to expand into new geographic markets, especially in regions where online dating is still gaining popularity. This can increase its global user base and revenue.
- Diversification of Services: Tinder could attract a wider audience and increase user engagement by broadening its services beyond dating to include social networking or professional networking.
- Enhanced User Experience: Implementing advanced features and algorithms to improve match quality and user experience could increase user satisfaction and retention rates.
- Safety and Privacy Enhancements: Investing in more robust safety features and privacy protections can address user concerns, improve trust in the platform, and potentially attract a more diverse user base.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with other companies for events and promotions or integrating complementary services could provide new user experiences and revenue streams.
- Leveraging Data for Personalization: Utilizing vast user data for more personalized experiences and recommendations can enhance user satisfaction and engagement on the platform.
- Technological Innovations: Adopting new technologies like AI and AR for features like improved matchmaking and virtual dates could differentiate Tinder from competitors and enhance the user experience.
- Content and Community Building: Creating platform-specific content and fostering a sense of community among users can increase engagement and loyalty, turning the app into more than just a tool for finding dates.
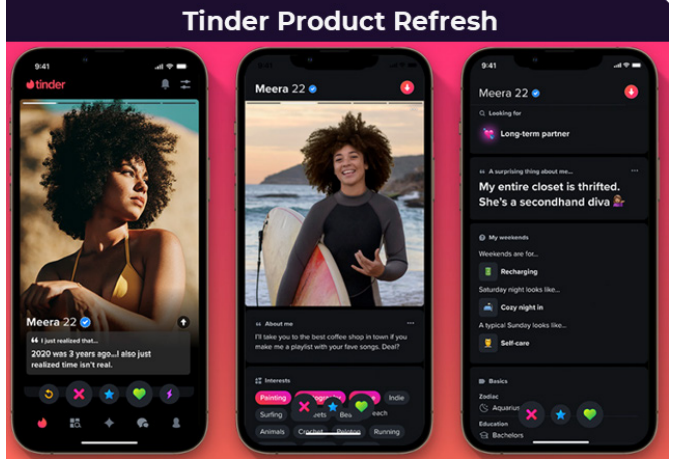
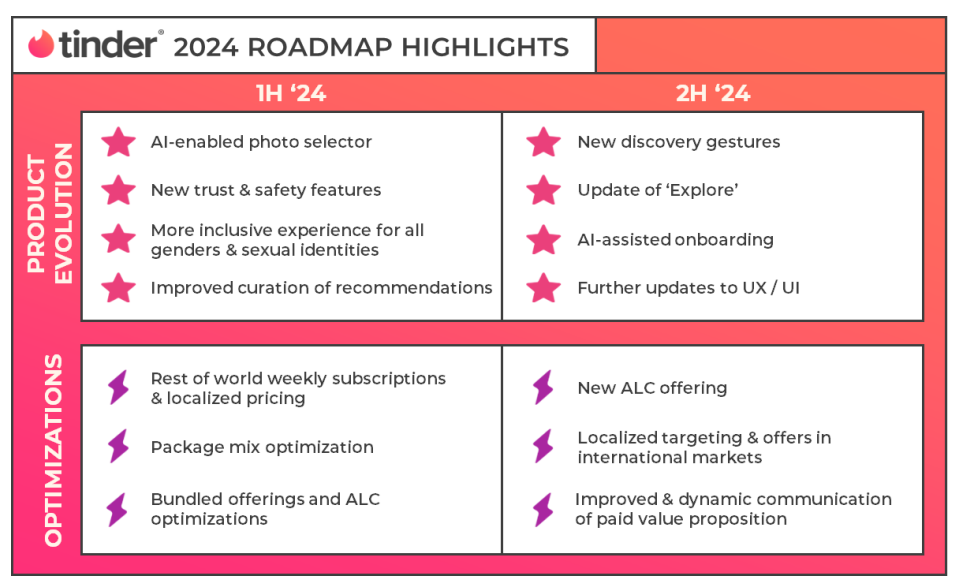
- New suite of features: Tinder introduced a new profile and discovery features suite in Q4 of 2023 to reflect better how the latest generation of daters connect, marking the first step in Tinder’s broader product evolution. In addition to a fresh look and feel, Tinder introduced profile prompts and quizzes to help users stand out more authentically. On the marketing front, Tinder continued progressing with its award-winning global brand campaign.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The online dating industry is highly competitive, with new platforms constantly emerging. Apps like Bumble, Hinge, and others offer unique features that can attract users away from Tinder. This competition can lead to user attrition and decreased market share.
- Changing User Preferences: Users’ preferences and expectations from dating platforms continuously evolve. A shift towards more meaningful connections or different interaction models could make Tinder’s swipe-based mechanism less appealing.
- Technological Advancements: The rapid pace of technological change threatens Tinder. New entrants using advanced technologies like AI, VR, or better algorithms could offer superior matchmaking and user experiences, making it challenging for Tinder to keep up.
- Regulatory Challenges: Increasing data privacy and user safety scrutiny, especially in regions like the European Union with GDPR, can pose regulatory challenges. Compliance issues or legal challenges could lead to financial penalties or operation restrictions.
- Reputation Risks: Incidents related to user safety, data breaches, or privacy concerns can significantly damage Tinder’s reputation, leading to a loss of trust among current and potential users.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns can impact Tinder’s revenue, primarily from discretionary spending on subscriptions and in-app purchases. Users may prioritize essential spending during tough economic times, reducing their expenditure on dating platforms.
- Technological Disruptions: The emergence of disruptive technologies or innovative platforms that offer a new approach to online dating could threaten Tinder’s current business model and user base.