Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Singapore Airlines. Singapore Airlines (SIA) is the flag carrier airline of Singapore and is known globally for its high service and operational excellence standards. Established in 1947 as Malayan Airways, it has grown to become one of the most respected travel brands worldwide. Here’s a brief overview of the airline:
- Branding and Reputation: Singapore Airlines is often cited as one of the world’s top airlines, mainly known for its customer service, quality of in-flight amenities, and overall passenger experience. As per CNN, Singapore Airlines was named the best airline in the world in 2023.
- Fleet and Network: SIA operates a modern Airbus and Boeing aircraft fleet. It serves numerous destinations across all inhabited continents, providing passenger and cargo services.
- Subsidiaries and Associated Companies: The Singapore Airlines Group includes several subsidiaries, such as SilkAir (regional flights), Scoot (low-cost carrier), and SIA Cargo (freight and logistics).
- In-flight Services: The airline is renowned for its in-flight services, from its luxurious first-class suites to the specially trained flight attendants known as the Singapore Girl. The in-flight entertainment system, KrisWorld, offers various movies, music, and other entertainment options.
- Headquarters and Training Facilities: SIA is headquartered at the Airline House in Singapore and has its primary hub at Singapore Changi Airport, consistently ranked among the best airports in the world. The airline also invests heavily in training, with facilities like the Singapore Airlines Training Centre providing comprehensive training for its crew and staff.
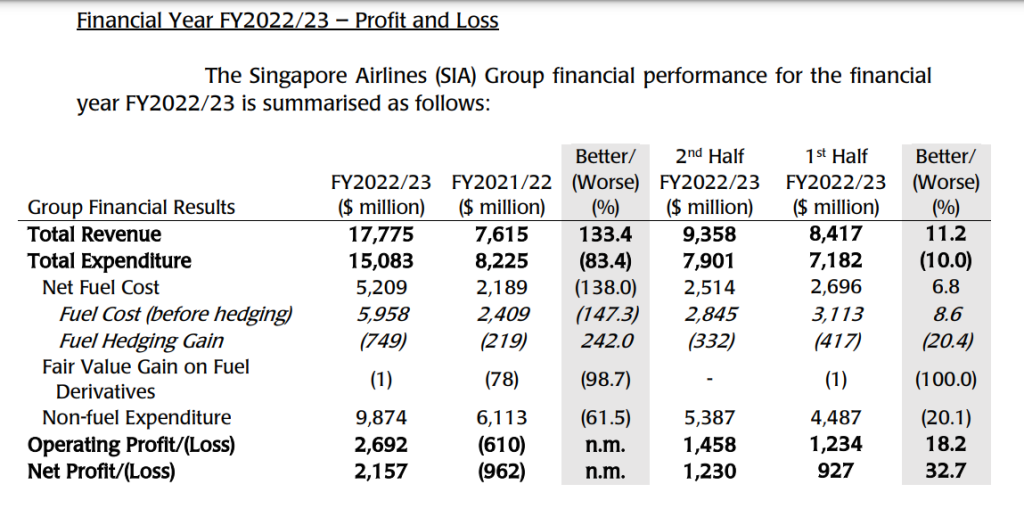
- Financial Performance 2022: Group revenue increased by $10,160 million (+133.4%) year-on-year to a record $17,775 million. Passenger-flown revenue rose $10,560 million (+376.3%) to $13,366 million as traffic grew 449.9%, outpacing the capacity expansion of 94.0%.
Here is the SWOT analysis for Singapore Airlines
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Singapore Airlines.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong Brand Reputation: SIA is consistently ranked as one of the world’s best airlines, known for its high levels of customer service and in-flight experience. This reputation is a powerful asset that encourages brand loyalty and is a significant differentiator in the competitive airline market.
- Strategic Hub Location: Singapore’s geographic location is a strategic hub for international travel, especially for routes between the East and the West, facilitating SIA’s extensive route network and connectivity.
- Premium Service Offering: SIA offers a superior product focusing on quality, including state-of-the-art in-flight entertainment, fine dining, and renowned service by its cabin crew, often referred to as the “Singapore Girl.”
- Modern Fleet: The airline frequently updates its fleet with the latest aircraft models, which are more fuel-efficient and offer enhanced passenger comfort. This also helps in maintaining a high level of operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: Alongside passenger transport, SIA has a profitable cargo division and a strong portfolio of subsidiary businesses, including ground handling and engineering.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: The airline’s loyalty program, KrisFlyer, is comprehensive and offers significant incentives for frequent flyers, helping to encourage repeat business and customer retention.
- Alliances and Partnerships: SIA is a part of the Star Alliance, the world’s largest airline alliance, and has codeshare agreements with multiple airlines, expanding its global reach.
- Operational Excellence: Singapore Airlines has a strong track record of operational reliability, punctuality, and safety, which enhances customer trust and satisfaction.
- Award-Winning In-Flight Service: The in-flight service of SIA is award-winning and often sets the standard for luxury travel, adding to its allure as a premium airline carrier.
Weaknesses
- High Operational Costs: The commitment to high service standards and the operation of a young fleet of aircraft contribute to higher operational costs compared to some competitors, particularly budget airlines.
- Dependence on International Travel: SIA relies heavily on international travel demand, which can be vulnerable to global events such as economic downturns, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions that reduce international travel frequency.
- Limited Domestic Market: Unlike many carriers that have a domestic market to fall back on, SIA is dependent on the Singapore hub, which lacks a domestic market to serve as a buffer against international volatility.
- Premium Pricing: The focus on premium service limits the ability to compete on price with low-cost carriers, which could be a challenge in price-sensitive markets.
- Complexity of Fleet: While SIA has a modern fleet, it also has various aircraft types, which can lead to higher maintenance and training costs compared to a more standardized fleet.
- Fuel Costs: As a long-haul carrier with many international flights, fuel costs are a significant expense. Fluctuating oil prices can heavily impact profitability.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Being an international carrier, SIA is subject to the aviation policies and regulations of every country it operates in, which can limit its operational flexibility and increase costs.
- Stiff Competition: The airline faces stiff competition from other full-service carriers and particularly aggressive competition from budget airlines in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Evolving Consumer Behavior: High expectations and changing preferences among travelers may pressure SIA to invest in service upgrades, which can be costly continually.
- Labor Costs: The commitment to high-quality service also means that labor costs can be high, as staff require intensive training and are generally compensated at a higher level to maintain service excellence.
Opportunities
- Expansion of Route Network: With the global aviation market growing, particularly in Asia, there are opportunities to expand to new destinations, increasing the airline’s global footprint and revenue.
- Strategic Alliances and Partnerships: Forming new partnerships or strengthening existing alliances can provide Singapore Airlines access to new markets and customer bases and potentially reduce operational costs through shared services.
- Investment in Technology: Advancements in aviation technology could offer Singapore Airlines opportunities to improve operational efficiency and customer service, such as through AI and big data analytics.
- Growth in Air Travel: As economic development continues, especially in emerging markets, there is likely to be an increase in demand for air travel, from which SIA can benefit.
- Sustainable Aviation: Investing in sustainable aviation practices and technologies can present new business opportunities and improve the airline’s environmental footprint, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
- Cargo Services: Expanding e-commerce globally can increase demand for cargo services, an area where SIA can leverage its expertise and fleet capabilities.
- Premium Economy and Leisure Market: There is growing demand for a middle ground between business and economy class, providing an opportunity to capture the segment that seeks affordable luxury.
- Diversification: Diversifying into related services like aircraft maintenance, training, or travel insurance can provide additional revenue streams.
- Enhanced Travel Experience: Opportunities exist to improve the travel experience through investments in customer service, in-flight amenities, and airport services.
- Ancillary Revenue Growth: SIA can explore additional ancillary revenue streams, such as in-flight connectivity, shopping, and innovative loyalty programs.
- Digital Transformation: Implementing digital transformation initiatives to streamline the customer journey, from booking to post-flight, can improve customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The airline industry is highly competitive, with both full-service and low-cost carriers competing for market share. SIA faces competition from global airlines on international routes and regional airlines within Asia.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns and fluctuations can significantly impact consumer spending and business travel budgets, leading to reduced demand for air travel.
- Fuel Price Volatility: As a major operational cost for airlines, fluctuations in fuel prices can adversely affect profitability.
- Geopolitical Instabilities: Political tensions and conflicts in regions where SIA operates can disrupt travel patterns and decrease passenger volumes.
- Exchange Rate Risks: As an international carrier, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact revenues and costs significantly when the Singapore dollar strengthens against other currencies.
- Regulatory Challenges: Changes in aviation regulations, both in Singapore and internationally, can impose additional operational restrictions or costs.
- Environmental Concerns: Increasing environmental regulations and the growing social movement towards sustainable travel can pressure airlines to invest in eco-friendly technologies, which may increase costs.
- Health Pandemics and Crises: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted how vulnerable the airline industry is to health crises, which can lead to widespread travel restrictions and a significant drop in passenger traffic.
- Technological Disruptions: Technological advancements such as high-speed rail or video conferencing could replace air travel.
- Security Threats: Acts of terrorism or security breaches can lead to tighter security measures, higher operating costs, and a potential decrease in travel due to safety concerns.
- Price-Sensitive Consumers: The rise of budget-conscious travelers could lead to a preference for low-cost carriers over full-service airlines like SIA.
- Air Traffic Control Challenges: Increased air traffic can lead to congestion and delays, impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.











