Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of Singapore Airlines. Singapore Airlines (SIA) is the flag carrier airline of Singapore and is known globally for its high service and operational excellence standards. Established in 1947 as Malayan Airways, it has grown to become one of the most respected travel brands worldwide. Here’s a brief overview of the airline:
- Branding and Reputation: Singapore Airlines is often cited as one of the world’s top airlines, mainly known for its customer service, quality of in-flight amenities, and overall passenger experience. As per CNN, Singapore Airlines was named the best airline in the world in 2023.
- Fleet and Network: SIA operates a modern Airbus and Boeing aircraft fleet. It serves numerous destinations across all inhabited continents, providing passenger and cargo services.
- Subsidiaries and Associated Companies: The Singapore Airlines Group includes several subsidiaries, such as SilkAir (regional flights), Scoot (low-cost carrier), and SIA Cargo (freight and logistics).
- In-flight Services: The airline is renowned for its in-flight services, from its luxurious first-class suites to the specially trained flight attendants known as the Singapore Girl. The in-flight entertainment system, KrisWorld, offers various movies, music, and other entertainment options.
- Headquarters and Training Facilities: SIA is headquartered at the Airline House in Singapore and has its primary hub at Singapore Changi Airport, consistently ranked among the best airports in the world. The airline also invests heavily in training, with facilities like the Singapore Airlines Training Centre providing comprehensive training for its crew and staff.
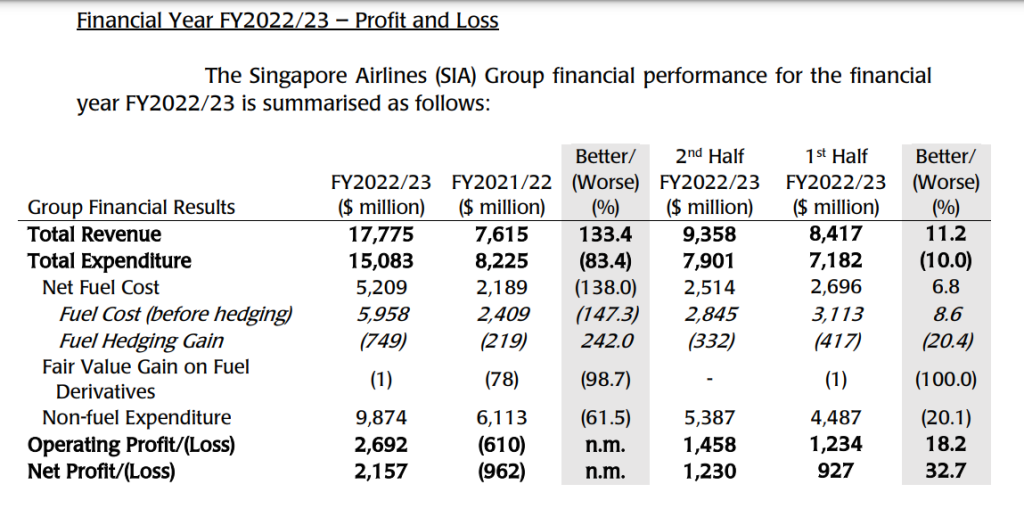
- Financial Performance 2022: Group revenue increased by $10,160 million (+133.4%) year-on-year to a record $17,775 million. Passenger-flown revenue rose $10,560 million (+376.3%) to $13,366 million as traffic grew 449.9%, outpacing the capacity expansion of 94.0%.
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Singapore Airlines
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Singapore Airlines.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Government Stability: Singapore’s political environment is one of the most stable in Asia. This stability provides a predictable business environment for Singapore Airlines to operate in.
- Bilateral Aviation Agreements: Aviation agreements and treaties between countries can either hinder or facilitate Singapore Airlines’ expansion into new markets or continuation in existing ones. The airline benefits from Singapore’s proactive approach to securing open skies agreements and expanding bilateral ties with other nations.
- Regulations and Policies: Stringent regulations imposed by the Civil Aviation Authority of Singapore (CAAS) ensure high safety and service standards, bolstering Singapore Airlines’ global reputation.
- Geopolitical Risks: In an interconnected world, airlines, including Singapore Airlines, must be vigilant about geopolitical tensions. Issues such as territorial disputes, wars, or diplomatic tensions can impact flight routes, demand, and operational costs.
- Government Support: Historically, the Singapore government has supported its flagship carrier, recognizing its importance for the country’s reputation, tourism, and business. This support can be in the form of strategic decisions, infrastructure investments, or even financial aid during crises.
- Regulatory Scrutiny on Alliances: Singapore Airlines’ membership in the Star Alliance and its other partnerships can be subject to regulatory scrutiny, affecting its ability to collaborate on routes, pricing, or services.
Economic
- Economic Growth and Recession: The general economic health of the countries Singapore Airlines operates in affects consumer and business travel spending. During economic upswings, there’s typically more demand for air travel, especially in business and first-class sectors. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to reduced spending on travel.
- Exchange Rate Volatility: Currency exchange rate fluctuations can impact Singapore Airlines in several ways, from influencing the cost of aircraft purchases (usually priced in USD) to affecting the competitiveness of ticket prices in foreign markets.
- Fuel Costs: One of the significant expenses for any airline is fuel. Fluctuations in global oil prices can significantly impact Singapore Airlines’ operational costs. While hedging can provide some protection, long-term trends in fuel prices are vital to strategic planning.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation can increase operational costs, including labor, maintenance, and catering. High inflation in Singapore or key markets could impact the airline’s profitability.
- Tourism Trends: Economic health also affects tourism. A thriving global or regional economy often sees increased tourists, benefiting airlines serving popular tourist destinations.
- Corporate Travel: Business travel, a lucrative airline sector, depends on the economic health of key industries. For instance, a booming tech sector or a significant international event in Singapore can increase demand for business travel.
Sociocultural
- Cultural Diversity: Singapore is a melting pot of cultures, and Singapore Airlines often highlights this diversity in its service, branding, and advertising.
- Travel Culture: The increasing interest in travel and tourism, especially among the middle class in Asia, has benefited airlines like Singapore Airlines. Social media has also fueled travel as a lifestyle choice.
- Demand for Quality and Service: Singapore Airlines is known for its world-class service. The value placed on premium service in many Asian cultures works in the airline’s favor.
- Language and Communication: Operating globally, Singapore Airlines has to cater to various languages and cultural nuances. Its commitment to understanding and adapting to local cultures can enhance the passenger experience.
- Religious and Cultural Sensitivities: Catering to passengers’ religious and dietary needs, like offering Halal food, is important. Recognizing and respecting major holidays in various cultures can also impact flight scheduling and promotions.
- Changing Family Dynamics: The increase in solo travelers, changing family structures, or trends like “bleisure” (blending business with leisure travel) can influence airline services and packages.
Technological
- In-flight Entertainment and Connectivity: Singapore Airlines has consistently updated its in-flight entertainment system, KrisWorld, offering a wide range of movies, TV shows, music, and games. Additionally, providing in-flight Wi-Fi has become an expected service for many passengers.
- E-ticketing and Mobile Apps: Digital ticketing and check-in processes, facilitated through the airline’s mobile app, provide convenience and efficiency for travelers. These systems have also reduced operational costs and increased customer data collection opportunities.
- Aircraft Technology: Investing in new, more efficient aircraft models can reduce fuel consumption and emissions. For instance, Singapore Airlines was the launch customer for the Airbus A350-900, known for its advanced aerodynamics and materials.
- Operational Efficiency Technologies: The use of advanced data analytics and AI can help optimize flight routes, predict maintenance needs, manage crew rosters, and improve fuel efficiency.
- Robotics and Automation: To enhance operational efficiency, robotics and automated systems can be deployed in areas like baggage handling, check-in kiosks, and customer service chatbots.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Advanced CRM systems enable the airline to understand customer preferences better, personalize offers, and enhance loyalty programs.
- Safety and Security Technologies: Advanced security screening technologies, biometric systems for passenger identification, and aircraft safety technologies are paramount in ensuring the safety of operations and building trust with passengers.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: These technologies can be used for training purposes, virtual aircraft tours for prospective customers, or even as a part of the in-flight entertainment system.
- Blockchain: While still emerging in the aviation sector, blockchain can be used for ticketing, loyalty programs, and maintenance tracking, ensuring transparency and security.
Environmental
- Fuel Emissions and Efficiency: Aircraft emissions contribute to greenhouse gas accumulations and global warming. Like other major carriers, Singapore Airlines faces pressures to enhance fuel efficiency and adopt technologies or practices that reduce emissions.
- Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF): The airline industry has been exploring using SAF to reduce carbon emissions. Singapore Airlines has taken initiatives in testing and integrating SAF into its operations as a step towards more sustainable flying.
- Waste Management: The amount of waste generated on flights, especially single-use plastics in in-flight meals, is a concern. Efforts to reduce, reuse, or recycle waste can positively affect the airline’s environmental footprint.
- Conservation Initiatives: Singapore Airlines has been involved in various environmental and conservation initiatives in Singapore and internationally to offset its environmental impact and boost its corporate social responsibility profile.
- Adaptation to Climate Change: The effects of climate change, such as more frequent extreme weather events, can disrupt flight schedules and safety. Airlines, including Singapore Airlines, need strategies to mitigate and adapt to these challenges.
- Regulations and Treaties: International agreements like the Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) aim to cap and reduce the aviation industry’s CO2 emissions. Singapore Airlines has to align its operations with such regulations.
- Eco-friendly Ground Operations: Beyond flying, ground operations, including vehicle emissions, building energy consumption, and more, contribute to the airline’s overall environmental footprint. Greening these operations can further reduce their impact.
Legal
- Aviation Regulations: The aviation industry is heavily regulated globally. Singapore Airlines must comply with the air traffic regulations of every country it operates in, which affects its routes, schedules, and operational practices.
- Safety Standards: Regulatory authorities, such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), have stringent safety standards. Singapore Airlines must regularly update its safety protocols and ensure staff training to comply with these standards.
- Labor Laws: As a global employer, Singapore Airlines has to adhere to labor laws in multiple jurisdictions, affecting hiring practices, working hours, employee rights, and more.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws pertain to passengers’ rights, including compensation for flight delays, cancellations, lost baggage, and other inconveniences. Singapore Airlines must have policies in place to handle such incidents in line with international and local regulations.
- Anti-Trust and Competition Laws: With mergers, partnerships, and alliances common in the aviation industry, airlines must ensure they don’t violate antitrust laws or create monopolistic conditions in any market.
- Data Protection and Privacy: With the advent of digital ticketing, loyalty programs, and online check-ins, airlines accumulate vast amounts of personal data. They must adhere to data protection laws, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, to ensure the privacy of their passengers.
- Licensing and Certification: Airline operations require various licenses and certifications, including aircraft operation certificates, airport slots, and pilot certifications. Regular renewals and audits ensure that Singapore Airlines meets the necessary legal standards.











