Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of SAP. SAP, which stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, is a multinational software corporation specializing in enterprise software to manage business operations and customer relations. The company was founded in Germany in 1972 and has since grown to become one of the world’s largest software providers.
SAP’s software solutions are used by companies of all sizes and industries, focusing on helping organizations streamline their business processes, increase efficiency, and gain real-time insights into their operations. Some of the key products offered by SAP include:
- SAP S/4HANA – a suite of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software that helps organizations manage financials, procurement, inventory, and more.
- SAP SuccessFactors – a cloud-based human capital management (HCM) software that helps organizations manage employee performance, goals, and development.
- SAP Ariba – a procurement software that allows businesses to connect with suppliers, manage contracts, and streamline purchasing processes.
- SAP Customer Experience – a software solution suite that enables businesses to engage with customers across multiple channels, including sales, marketing, and service.
In addition to its core software offerings, SAP also provides consulting services, support, and training to help customers get the most out of its software solutions. With a global presence and a focus on innovation, SAP continues to be a leading provider of enterprise software for businesses worldwide.
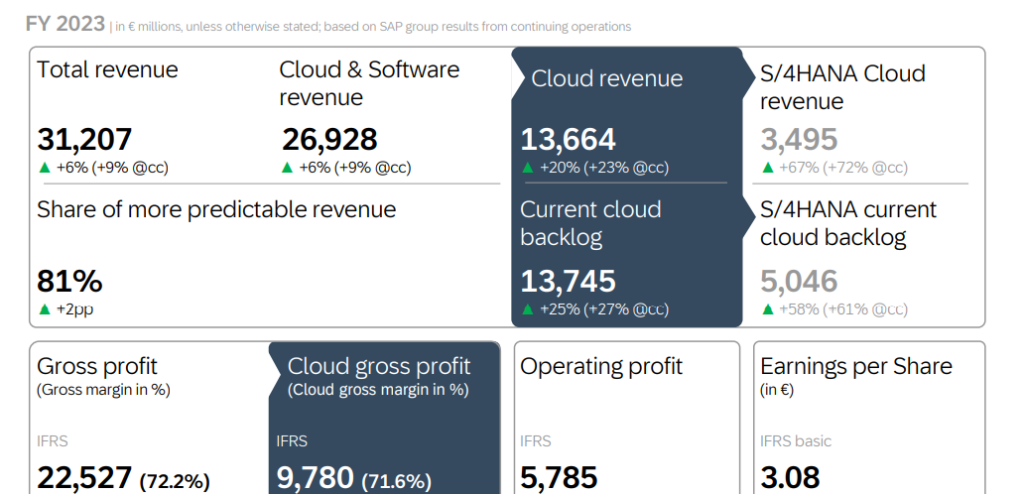
Financial Performance 2023: Total revenue was up 6% to €31.21 billion.
Here is the SWOT analysis for SAP
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of SAP.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- The breadth of offerings: SAP offers a wide range of software solutions that cover many areas of business operations, from finance and procurement to human resources and customer experience. This breadth of offerings allows SAP to provide end-to-end solutions for businesses, which can be more convenient and cost-effective than using multiple software vendors.
- Scalability: SAP’s software solutions are designed to be scalable, making them suitable for businesses of all sizes, from small startups to large multinational corporations. This scalability allows SAP to serve a broad range of customers and adapt to changing customer needs.
- Global presence: SAP has a global presence, with offices in over 130 countries and customers in nearly every industry. This global reach allows SAP to understand and meet the needs of businesses across different regions and markets.
- Innovation: SAP invests heavily in research and development to stay at the forefront of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and blockchain. This commitment to innovation helps SAP to provide its customers with cutting-edge software solutions that can help them stay ahead of their competition.
- Industry expertise: SAP has a deep understanding of the industries it serves, with specialized software solutions for industries such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing. This industry expertise allows SAP to provide tailored solutions that meet each industry’s specific needs and requirements.
Weaknesses
- Complexity: SAP’s software solutions can be complex and challenging to implement and use, especially for smaller businesses without dedicated IT departments. This complexity can make it more difficult for businesses to get the full value of SAP’s software solutions.
- Cost: SAP’s software solutions can be expensive, especially for smaller businesses. The cost of licensing, implementation and ongoing maintenance can be a significant investment for many businesses, which may deter them from using SAP’s software solutions.
- Customization: SAP’s software solutions can be highly customizable, which can be a strength for some businesses. However, this customization can also lead to complexity and additional costs if businesses need to make significant changes to the software to meet their needs.
- Integration: SAP’s software solutions may not integrate easily with other software solutions businesses already use. This can create additional challenges for businesses that need to integrate SAP’s solutions into their existing workflows.
- Perception: SAP has had some high-profile customer complaints in the past regarding software performance and pricing, which may create a negative perception of the company for some potential customers. However, SAP has taken steps to address these issues and improve its reputation over time.
Opportunities
- Cloud computing: Cloud-based software solutions are becoming increasingly popular among businesses, offering greater flexibility and scalability than traditional on-premise software solutions. SAP has been investing heavily in cloud computing, which presents a significant opportunity for the company to expand its customer base and grow its revenue.
- Digital transformation: Many businesses are undergoing digital transformation initiatives, which involve using technology to streamline operations, improve customer experience, and gain new insights. SAP’s software solutions can help businesses achieve these goals, making it well-positioned to benefit from the growing digital transformation trend.
- Emerging technologies: SAP has invested in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technologies. These technologies can transform business operations and create new opportunities for SAP to develop innovative software solutions.
- Industry-specific solutions: SAP has a strong track record of developing industry-specific software solutions, such as its software for the healthcare and manufacturing industries. As businesses become more specialized, there is an opportunity for SAP to create more targeted software solutions that meet the specific needs of different industries.
- Partnerships: SAP has formed partnerships with other technology companies, such as Microsoft and Google, to provide integrated solutions that offer more excellent value to customers. These partnerships allow SAP to expand its offerings and reach new customers through collaboration with other industry leaders.
Threats
- Competition: SAP faces intense competition from other enterprise software vendors, such as Oracle, Microsoft, and Salesforce, who offer similar software solutions. This competition could lead to price pressures and reduced market share for SAP.
- Economic uncertainty: SAP’s revenue is highly dependent on global economic conditions, as businesses may delay or cancel software investments during periods of economic uncertainty. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the risks of economic uncertainty and could impact SAP’s revenue in the short term.
- Security threats: As a provider of enterprise software solutions, SAP is a prime target for cyber attacks. A major security breach could damage SAP’s reputation and lead to a loss of customer trust.
- Technological disruption: Emerging technologies like cloud computing and artificial intelligence could disrupt SAP’s business model and software solutions. If SAP adapts slowly to these technological changes, it could lose market share to more innovative competitors.
- Data privacy regulations: SAP’s software solutions often involve processing sensitive personal and business data, subject to increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide. Compliance with data privacy regulations could be costly for SAP, and non-compliance could result in fines or legal action.











