Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of L’Oreal. L’Oréal, founded in 1909 by Eugène Schueller in Paris, is a world-renowned cosmetics and beauty company. Here’s an overview of L’Oréal’s business:
- Product Segments: L’Oréal’s product offerings span across various segments of the beauty industry, including:
- Skincare
- Haircare
- Make-up
- Fragrances
- Sun protection
- Hair Color
- Major Brands: L’Oréal’s brand portfolio includes both luxury and mass-market brands. Some of the most notable ones include:
- L’Oréal Paris
- Lancôme
- Giorgio Armani Beauty
- Kiehl’s
- Yves Saint Laurent Beauté
- Garnier
- Maybelline New York
- Urban Decay
- Essie
- CeraVe, and many more.
- Research and Innovation: The company strongly emphasizes research and development. With numerous research centers worldwide, L’Oréal is a leader in cosmetics innovation, developing safer and more efficient products in response to global beauty trends.
- Global Presence: L’Oréal has a vast international footprint, selling products in around 150 countries. The company’s operations are typically divided into Western Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Eastern Europe, and other regions.
- Sales Channels: Products are marketed through various channels, such as department stores, drugstores, e-commerce platforms, travel retail, branded retail, professional salons, and more.
- Acquisitions and Partnerships: Over the years, L’Oréal has grown its portfolio through strategic acquisitions, including NYX Cosmetics and IT Cosmetics. Such moves have enabled the company to tap into new customer segments and broaden its product range.
- Digital and E-commerce: With the rise of digital platforms and e-commerce, L’Oréal has invested significantly in its digital transformation, focusing on data analytics, personalized consumer experiences, and online sales.
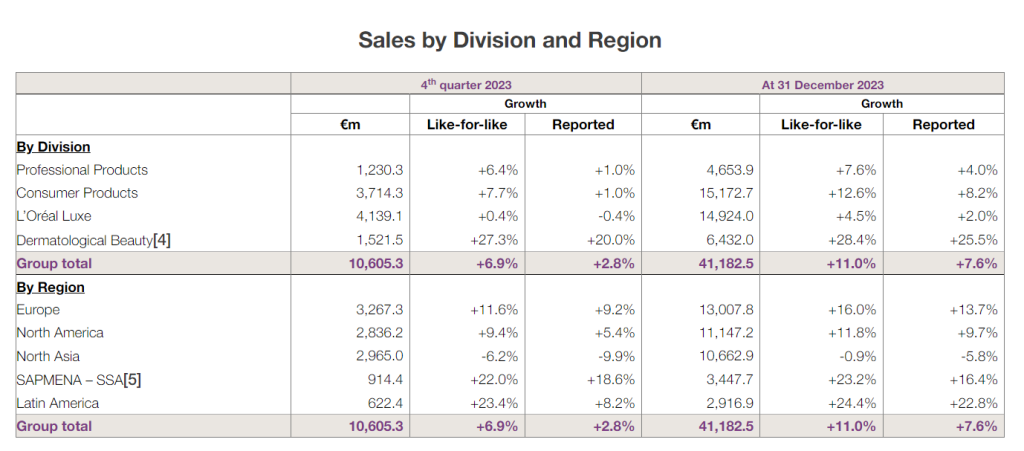
Financial Performance 2023: Refer to the table below:
What strategies make L’Oreal an unbeatable beauty company?
Here is the SWOT analysis for L’Oréal
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of L’Oréal.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
There are several strengths of L’Oréal as a company, including:
- Strong brand portfolio: L’Oréal has a strong portfolio of well-known and established beauty brands, which allows it to appeal to a wide range of customers across different segments and geographies.
- Innovation and R&D: L’Oréal invests heavily in research and development to develop new products, improve existing ones, and stay ahead of trends in the beauty industry.
- Global presence: L’Oréal has a strong global presence with operations in over 150 countries, which enables it to leverage economies of scale and reach a large customer base.
- Diversification: L’Oréal has a diversified product portfolio that includes makeup, skincare, hair care, and fragrance products, reducing the risk of overreliance on any one product category.
- Sustainability: L’Oréal is committed to sustainability and has set ambitious environmental and social goals. This focus on sustainability can attract environmentally-conscious consumers and improve the company’s reputation.
- Strong financial performance: L’Oréal has a robust financial performance, with consistently high revenue and profitability over the years. This gives the company the resources to invest in innovation, expand its product portfolio, and pursue strategic acquisitions.
Weaknesses
While L’Oréal has many strengths as a company, it also faces some weaknesses. These weaknesses include:
- Dependence on key markets: L’Oréal relies heavily on the European and North American markets for most of its revenue, making it vulnerable to economic downturns or political instability in these regions.
- Relatively high prices: L’Oréal’s premium brands are relatively expensive compared to competitors, which may make them less attractive to price-sensitive consumers.
- Limited online presence: While L’Oréal has made efforts to expand its e-commerce presence in recent years, its online sales still make up a relatively small portion of its overall revenue compared to some competitors.
- Limited geographical reach: While L’Oréal has a global presence, it is not as strong in some regions as in others. For example, it has a relatively low market share in some Asian countries compared to competitors.
- Product recalls: Like any company in the cosmetics industry, L’Oréal is subject to product recalls and other quality control issues, which can damage its reputation and lead to financial losses.
- Dependence on acquisitions: L’Oréal has grown partly through acquisitions, which can be risky if the acquired companies do not perform as expected or if integration is complex.
Opportunities
L’Oréal has several opportunities to grow and improve its business, including:
- Expanding its presence in emerging markets: L’Oréal can tap into the growing demand for beauty products in emerging markets, such as Asia and Latin America, by investing in marketing, distribution, and product development in these regions.
- Leveraging digital technologies: L’Oréal can use digital technologies to enhance customer engagement, personalize its products and services, and optimize its supply chain.
- Developing more sustainable products: L’Oréal can continue to invest in developing more environmentally friendly and sustainable products, which can appeal to eco-conscious consumers and improve its reputation.
- Diversifying into new product categories: L’Oréal can diversify into new product categories, such as wellness or personal care products, to expand its customer base and reduce its dependence on traditional beauty products.
- Acquiring new brands or technologies: L’Oréal can continue to acquire new brands or technologies that complement its existing product portfolio and help it stay ahead of competitors.
- Customizing products for diverse consumer needs: L’Oréal can further tailor its products to meet the unique needs of various consumer groups, such as aging populations or consumers with specific skin or hair types, to increase customer loyalty and drive sales.
Threats
There are several threats that L’Oréal faces as a company, including:
- Intense competition: The cosmetics industry is highly competitive, with many well-established global and local players. L’Oréal faces fierce competition from competitors that offer similar products at lower prices or with stronger brand recognition.
- Shifts in consumer preferences: Consumer preferences in the cosmetics industry can be highly unpredictable, and changes in trends or customer demands can quickly disrupt sales and revenue.
- Economic downturns: L’Oréal’s revenue is highly dependent on consumer spending, which can be impacted by economic downturns or other macroeconomic factors that affect disposable income.
- Counterfeit products: The cosmetics industry is susceptible to counterfeit products, which can damage L’Oréal’s brand reputation and lead to lost revenue.
- Regulations and compliance: L’Oréal operates in a highly regulated industry and must comply with strict product safety, labeling, and marketing regulations. Noncompliance can lead to legal and financial repercussions.
- Supply chain disruptions: L’Oréal relies on a complex global supply chain to manufacture and distribute its products, and disturbances in any part of the supply chain, such as raw material shortages or transportation delays, can lead to production delays and lost revenue.











