Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of L’Oreal. L’Oréal, founded in 1909 by Eugène Schueller in Paris, is a world-renowned cosmetics and beauty company. Here’s an overview of L’Oréal’s business:
- Product Segments: L’Oréal’s product offerings span across various segments of the beauty industry, including:
- Skincare
- Haircare
- Make-up
- Fragrances
- Sun protection
- Hair Color
- Major Brands: L’Oréal’s brand portfolio includes both luxury and mass-market brands. Some of the most notable ones include:
- L’Oréal Paris
- Lancôme
- Giorgio Armani Beauty
- Kiehl’s
- Yves Saint Laurent Beauté
- Garnier
- Maybelline New York
- Urban Decay
- Essie
- CeraVe, and many more.
- Research and Innovation: The company strongly emphasizes research and development. With numerous research centers worldwide, L’Oréal is a leader in cosmetics innovation, developing safer and more efficient products in response to global beauty trends.
- Global Presence: L’Oréal has a vast international footprint, selling products in around 150 countries. The company’s operations are typically divided into Western Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Eastern Europe, and other regions.
- Sales Channels: Products are marketed through various channels, such as department stores, drugstores, e-commerce platforms, travel retail, branded retail, professional salons, and more.
- Acquisitions and Partnerships: Over the years, L’Oréal has grown its portfolio through strategic acquisitions, including NYX Cosmetics and IT Cosmetics. Such moves have enabled the company to tap into new customer segments and broaden its product range.
- Digital and E-commerce: With the rise of digital platforms and e-commerce, L’Oréal has invested significantly in its digital transformation, focusing on data analytics, personalized consumer experiences, and online sales.
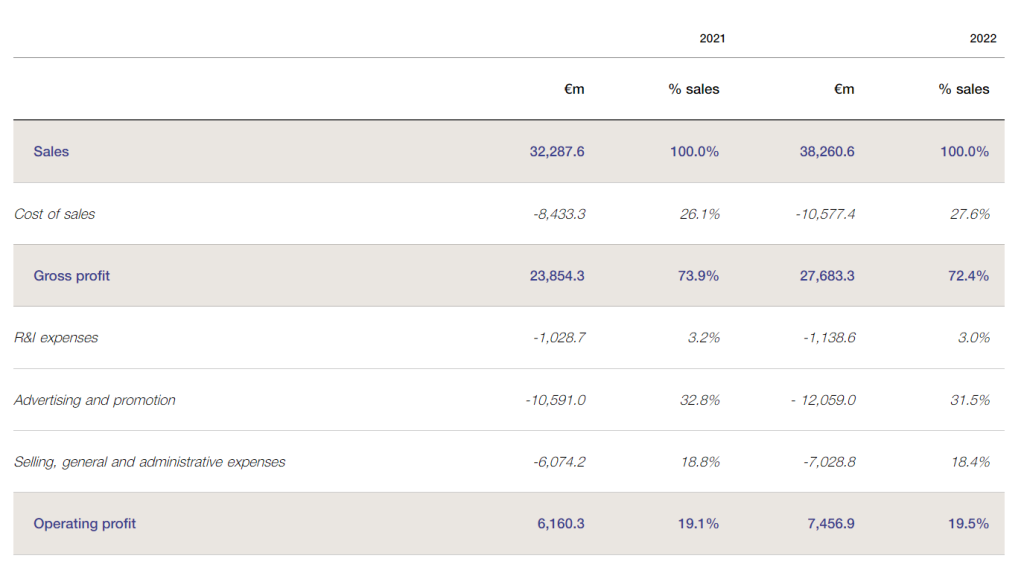
Financial Performance 2022: Refer to the table below:
What strategies make L’Oreal an unbeatable beauty company?
Here is the PESTEL analysis of L’Oreal
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of L’Oreal.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Regulation and Compliance: Cosmetic and personal care product industries are highly regulated in many countries. For instance, strict rules about product safety, ingredient disclosures, animal testing, and more exist. L’Oréal must ensure compliance with these regulations wherever it operates.
- International Trade Policies: L’Oréal operates in around 150 countries, making it susceptible to international trade policies. Tariffs, trade wars, or restrictions can affect its supply chain, cost structures, and market access.
- Stability of Political Environment: Political stability in countries where L’Oréal operates can directly impact its operations. For instance, political unrest or regime changes can lead to disrupted supply chains, market uncertainties, or even asset seizures.
- Animal Testing Bans: Several countries and regions, like the European Union, have banned or restricted animal testing for cosmetics. L’Oréal must adapt its R&D practices according to these political decisions. It’s worth noting that L’Oréal stopped animal testing in 1989 and has been developing alternative methods since then.
- Government Initiatives: Governments might introduce initiatives promoting sustainable or local products, which could impact L’Oréal’s positioning in these markets. Conversely, there may be incentives for foreign companies or specific industries that L’Oréal could benefit from.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Tensions between countries where L’Oréal has significant operations or sources of materials can affect its business, from supply chain disruptions to market access issues.
- Public Health Policies: In situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, governments’ responses and regulations related to public health (lockdowns, store closures, etc.) can directly impact L’Oréal’s sales and operations.
Economic
- Economic Growth: Economic growth in a country or region can increase disposable income for consumers, positively impacting sales of beauty and personal care products. Conversely, an economic downturn might lead to reduced consumer spending.
- Exchange Rates: Being a global company, L’Oréal’s revenues and profits are susceptible to fluctuations in exchange rates. For instance, a strong Euro might affect the competitiveness of its products outside the Eurozone.
- Inflation and Interest Rates: Inflation can impact the cost of raw materials, production, and distribution for L’Oréal. Similarly, interest rates can influence the company’s borrowing costs. High-interest rates might make borrowing expensive, while low rates could offer opportunities for cheap financing.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment can reduce consumer spending, affecting L’Oréal’s sales. On the flip side, it can also affect labor costs and availability for the company.
- Raw Material Prices: The cost of raw materials used in cosmetics and beauty products (like oils, chemicals, and natural ingredients) can fluctuate due to various economic factors, impacting L’Oréal’s production costs.
- Global Supply Chain Factors: Economic disruptions, like trade wars or regional economic crises, can impact the availability and cost of products and raw materials, affecting L’Oréal’s supply chain.
- Retail and E-commerce Dynamics: Economic shifts can influence consumer buying patterns. Economic downturns might lead to more price-sensitive shopping or a shift towards e-commerce platforms offering deals and discounts.
Sociocultural
- Changing Beauty Standards: Beauty perceptions vary across cultures and evolve. What’s considered attractive or desirable in one decade or region might change in the next. L’Oréal must stay attuned to these shifts to develop products that resonate with consumers.
- Diversity and Inclusion: As awareness and demand for inclusivity grow, consumers seek products that cater to a wide range of skin tones, hair types, and more. L’Oréal has made strides in offering products for diverse demographics, but it’s an ongoing effort.
- Aging Populations: In many developed countries, the population is aging. This demographic shift leads to a growing market for anti-aging products and other cosmetics tailored for older consumers.
- Sustainability and Ethical Consumption: Modern consumers, especially younger generations, are increasingly concerned about the environment and ethical production. They prefer sustainable, cruelty-free, and ethically produced products. L’Oréal’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices can influence its brand image and consumer trust.
- Gender Roles and Expressions: With changing views on gender norms and increasing acceptance of diverse gender expressions, there’s a growing market for gender-neutral beauty products. L’Oréal may need to adapt its product lines and marketing strategies accordingly.
- Cultural Traditions: Different regions have distinct beauty rituals and traditions. Understanding and respecting these traditions and possibly offering products tailored to them can benefit L’Oréal.
- Health and Wellness Trends: Consumers increasingly link beauty with overall health and wellness. There’s a growing demand for products that are not just cosmetic but also beneficial for skin health, hair health, etc.
- Economic Mobility and Middle-Class Growth: In many emerging markets, the growth of the middle class means more consumers can afford beauty and personal care products, influencing L’Oréal’s market potential and product pricing strategies.
Technological
- Digital Transformation: The rise of e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, and augmented reality (AR) experiences has transformed how consumers shop for beauty products. L’Oréal has been leveraging these technologies to offer virtual try-ons, personalized recommendations, and more seamless online shopping experiences.
- Research & Development: Advancements in biotechnology, chemistry, and materials science drive the development of new cosmetic formulations, product types, and applications. L’Oréal invests significantly in R&D to ensure it remains at the forefront of beauty innovation.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics: AI and data analytics enable better consumer insights, tailored marketing strategies, and personalized consumer experiences. By analyzing customer data, L’Oréal can anticipate trends, refine its product offerings, and optimize its marketing efforts.
- Supply Chain Management: Advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain can improve the supply chain’s traceability, efficiency, and sustainability. These tools can also help ensure raw materials’ authenticity and quality.
- Sustainable Technologies: As sustainability becomes a crucial aspect of business, technological advancements in green chemistry, eco-friendly packaging, and waste reduction methods become paramount. L’Oréal can leverage these to enhance its environmental credentials.
- Production Automation: Automated and robotic systems in manufacturing can lead to increased production efficiency, consistency in product quality, and cost savings. These systems can also quickly adapt to changes in product demand or design.
- Interactive Marketing: Technologies like AR and virtual reality (VR) provide new avenues for interactive and immersive marketing campaigns, allowing L’Oréal to engage consumers in novel ways.
Environmental
- Sustainable Sourcing: As one of the world’s leading cosmetics companies, L’Oréal sources various raw materials. Ensuring that these are sourced sustainably and ethically is crucial. This involves monitoring supply chains, collaborating with suppliers, and sometimes rethinking product formulations.
- Waste Management: Waste, especially plastic waste from beauty products, can have a significant environmental impact. L’Oréal must consider packaging innovations, recycling initiatives, and waste reduction strategies to minimize its ecological footprint.
- Water Usage: The cosmetics industry relies heavily on water as an ingredient and in manufacturing. Efficient water use and wastewater treatment are essential for L’Oréal to reduce its environmental impact and ensure it can sustainably source water, especially in water-scarce regions.
- Carbon Footprint: The company’s operations generate carbon emissions from manufacturing to transportation. L’Oréal has actively reduced its carbon footprint through renewable energy use, energy efficiency measures, and other sustainable practices.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Some ingredients used in cosmetics come from specific ecosystems. L’Oréal must ensure that its sourcing practices do not endanger these ecosystems or the species that inhabit them.
- Consumer Demand for Green Products: Modern consumers are increasingly eco-conscious, seeking out products that are not just effective but also environmentally friendly. This drives the need for L’Oréal to offer eco-friendly products, from formulations to packaging.
- Animal Testing and Cruelty-Free Products: There’s a growing global movement against animal testing in the cosmetics industry. While L’Oréal stopped animal testing many years ago, it’s essential to maintain and communicate its commitment to cruelty-free practices.
- Natural and Organic Trend: There’s a rising trend for natural and organic beauty products. While these terms can be ambiguous, L’Oréal might benefit from offering product lines that cater to consumers seeking “natural” or organic ingredients, provided they align with the company’s standards for efficacy and safety.
Legal
- Regulations on Ingredients: Different countries have different regulations regarding the ingredients used in cosmetics and personal care products. L’Oréal must ensure its products comply with each market’s ingredient lists and restrictions.
- Animal Testing Laws: Several countries have banned animal testing for cosmetics, while others still require it for certain products. L’Oréal must navigate these regulations, especially when launching new products or entering new markets.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Protecting patents, trademarks, and copyrights is vital for L’Oréal, especially given its investment in research and development. The company must ensure its intellectual properties are registered and protected against infringements.
- Advertising and Marketing Regulations: Different regions have varying regulations about what can be claimed in advertisements. L’Oréal must ensure its marketing campaigns do not make false or misleading claims and adhere to local advertising standards.
- Environmental and Sustainability Laws: As environmental concerns grow globally, many countries are introducing stricter regulations about sustainability, waste management, and emissions. L’Oréal must ensure its operations, products, and supply chain align with these legal mandates.
- Labor and Employment Laws: With operations worldwide, L’Oréal must adhere to local labor laws, including those related to minimum wages, working conditions, workers’ rights, and more.
- Health and Safety Regulations: L’Oréal’s products must meet health and safety standards set by various countries. This can involve specific testing, quality checks, and certifications.
- Taxation and Tariffs: As trade dynamics shift globally, L’Oréal needs to stay updated with taxation policies and tariffs in its countries. This impacts the company’s pricing strategies, profitability, and supply chain decisions.
- Antitrust and Competition Laws: L’Oréal must ensure its business practices do not violate antitrust and competition laws, especially given its significant market share in many regions.











