Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of LEGO. The LEGO Group, founded in 1932, is a Danish family-owned company known for its globally popular plastic construction toys, LEGO bricks.
The company’s name is derived from the Danish words “leg godt,” meaning “play well.” Since its inception, LEGO has expanded its product range to include various themes and sets, catering to different age groups, interests, and skill levels.
Key Product Segments:
- LEGO System: These are the traditional LEGO bricks and sets featuring various themes such as LEGO City, LEGO Technic, LEGO Ninjago, LEGO Friends, and LEGO Star Wars. These sets cater to a wide range of age groups, from toddlers to adults.
- LEGO DUPLO: Designed for younger children aged 1.5 to 5, DUPLO sets are larger, more colorful, and easier to handle than traditional LEGO bricks. They help to develop creativity, fine motor skills, and problem-solving abilities in young children.
- LEGO Education: This division provides learning solutions for schools and educational institutions. LEGO Education products integrate STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) concepts into engaging, hands-on learning experiences using LEGO bricks and digital tools.
- LEGO Architecture: This product line targets adult fans of LEGO and architecture enthusiasts. The sets replicate famous landmarks and buildings worldwide, such as the Eiffel Tower, the White House, and the Sydney Opera House.
- LEGO Ideas: This platform allows LEGO fans to submit designs for future LEGO sets. If a design receives enough support from the community, it may be produced and sold as an official LEGO set.
- Licensed Themes: LEGO collaborates with various intellectual properties (IPs) to create sets based on popular franchises such as Marvel, DC Comics, Disney, Harry Potter, and many more.
Other Business Areas:
- Digital Experiences: The LEGO Group offers various digital experiences like video games, mobile apps, and online platforms, which provide a complementary experience to their physical products.
- LEGO Stores: The company operates LEGO-branded retail stores worldwide, offering a unique shopping experience, exclusive sets, and engaging in-store activities.
- LEGOLAND: Owned by Merlin Entertainments, LEGOLAND is a chain of family-friendly theme parks and resorts centered around the LEGO brand. These parks feature rides, attractions, and life-sized LEGO models for visitors to enjoy.
- Media and Content: LEGO produces animated movies, TV shows, and web content based on their popular themes, further expanding its brand reach and creating a broader entertainment ecosystem.
- Revenue was DKK 65.9 billion up 2 percent despite declining toymarket.
- Consumer sales* grew 4 percent.
- Outperformed the toy market and significantly grew market share globally.
- Operating profit was DKK 17.1 billion against DKK 17.9 billion in 2022 as the company accelerated spending on strategic initiatives to support growth. Operating profit grew 7 percent in H2 vs. H2 2022.
- Cash flow from operating activities increased 1 percent to DKK 15.4 billion.
- 60 percent increase in spending on environmental initiatives in 2023.
Here’s a SWOT analysis for LEGO:
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of LEGO.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Brand Recognition: LEGO is one of the world’s most recognizable and beloved brands. Its iconic, interlocking brick system has been a staple of children’s playrooms for decades, and the company has successfully cultivated a loyal customer base that spans generations. In 2021, the LEGO brand was valued at approximately 9.1 billion U.S.
- Product Quality and Innovation: LEGO is known for its high-quality products that are built to last. The company continually invests in research and development, introducing innovative new themes, sets, and building techniques that cater to a wide range of interests and age groups.
- Diverse Product Portfolio: LEGO offers diverse products, from the traditional LEGO System and DUPLO sets to licensed themes and niche offerings like LEGO Architecture. This variety ensures the brand remains relevant and appealing to a broad audience.
- Licensing Agreements: LEGO’s partnerships with popular intellectual properties (IPs), such as Marvel, Disney, Star Wars, and Harry Potter, allow the company to create highly sought-after sets that capitalize on the success of these franchises. These licensing agreements help to drive sales and maintain consumer interest.
- Community Engagement: The LEGO Ideas platform and the Adult Fans of LEGO (AFOL) community demonstrate the company’s commitment to fostering a strong connection with its customers. These platforms enable fans to share their creations, collaborate on projects, and contribute to developing new products.
- Digital Presence: LEGO has successfully integrated digital experiences with its physical products, offering video games, mobile apps, and online platforms that enhance and complement the traditional brick-building experience. This digital expansion allows LEGO to engage with consumers in new and innovative ways.
- Retail Experience: LEGO Stores provide a unique and immersive retail experience, featuring exclusive products, in-store activities, and life-sized models made from LEGO bricks. These stores help reinforce the brand image and create memorable customer experiences.
- Global Presence: With a strong presence in international markets, LEGO can cater to consumers’ needs and preferences worldwide, fueling global growth and expansion.
- Collaboration with Educational Institutions: LEGO Education focuses on providing learning solutions that integrate STEAM concepts into engaging, hands-on experiences using LEGO bricks and digital tools. These partnerships with schools and educational institutions enhance the brand’s credibility and support its mission to inspire and develop the builders of tomorrow.
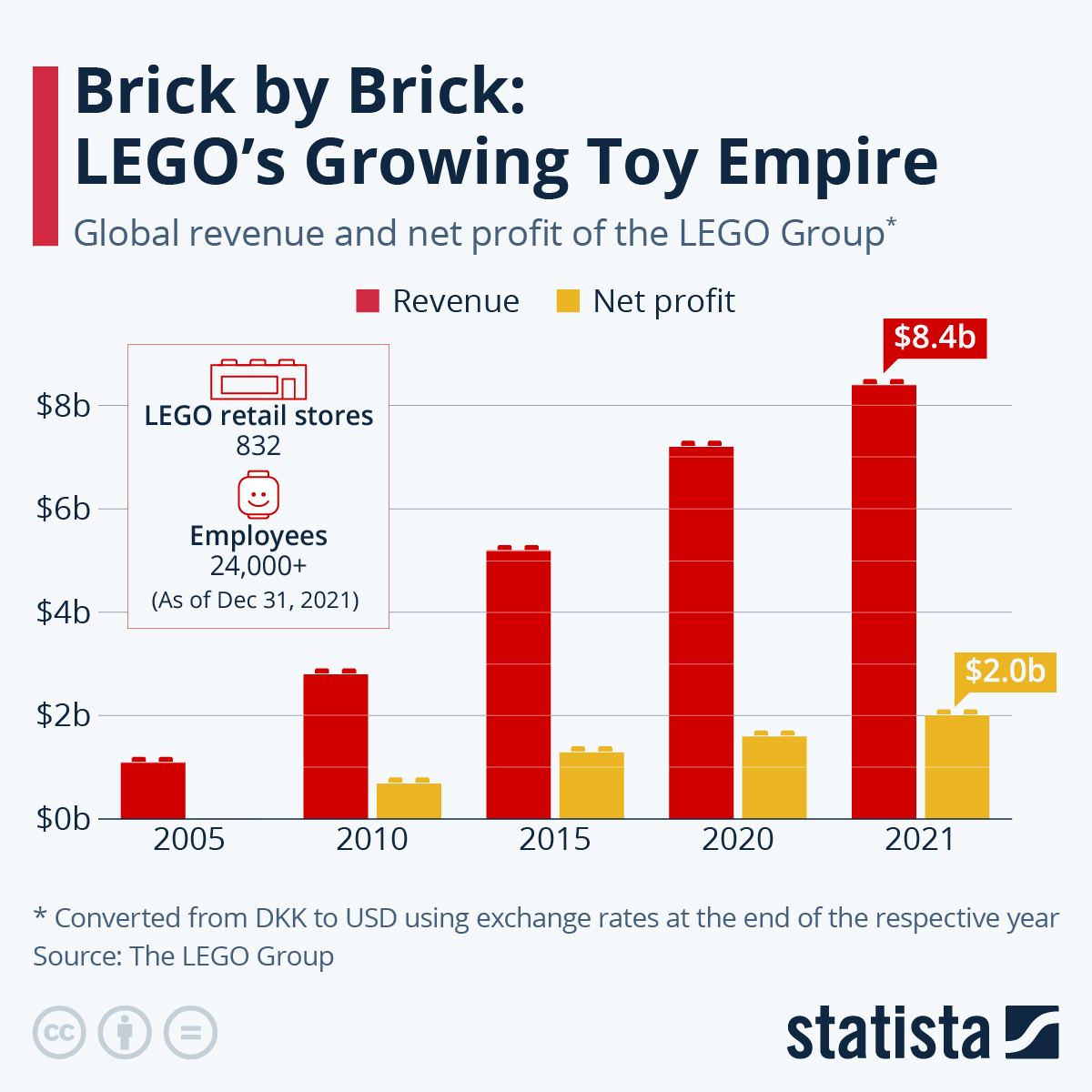 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
Weaknesses
- High Prices: LEGO products are often perceived as more expensive than other construction toys. This price premium may discourage price-sensitive customers and limit the brand’s ability to attract a broader consumer base.
- Dependence on Plastic: LEGO’s core products are primarily made from plastic, which faces increasing scrutiny due to environmental concerns. While the company is working towards using sustainable materials by 2030, it must address the environmental impact of its products in the meantime.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Dependency: LEGO’s collaborations with popular IPs have significantly driven its success. However, reliance on these partnerships also poses risks, as the company must continuously secure new agreements and adapt to the changing popularity of various franchises.
- Competition in Digital Space: The digital entertainment market is highly competitive, and LEGO faces challenges from numerous well-established players in the gaming and streaming industries. To succeed in this area, LEGO must continuously innovate and develop compelling digital content to retain and attract users.
- Product Complexity: Some LEGO sets have become increasingly complex and time-consuming to build, which may deter some consumers who prefer more straightforward, more accessible toys. Balancing the needs of advanced builders and casual fans can be challenging for the company.
- Counterfeits and Imitations: The LEGO brand faces competition from counterfeit and imitation products, often sold at lower prices. These products can undermine LEGO’s brand reputation, and the company must invest in legal and marketing efforts to protect its intellectual property and maintain consumer trust.
- Scalability of LEGO Education: While LEGO Education has the potential to impact learning, scaling this segment significantly may prove challenging. The company must navigate the complexities of educational systems and regulations across different countries to expand its offerings.
- Economic Conditions: The toy industry is sensitive to economic fluctuations, as consumer spending on non-essential items tends to decrease during economic downturns. Adverse economic conditions or shifts in consumer preferences may impact LEGO’s business.
Opportunities
- Sustainable Materials: As LEGO works towards its goal of using sustainable materials in its core products and packaging by 2030, it can strengthen its brand image as an environmentally responsible business and attract eco-conscious consumers.
- Emerging Markets: Expanding into emerging markets, such as Asia, Africa, and South America, can help LEGO tap into new consumer bases and achieve long-term growth.
- Personalization and Customization: Offering customized LEGO sets or bricks, such as personalized minifigures or unique designs, can create additional revenue streams and deepen customer engagement with the brand.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): LEGO can further explore opportunities in AR and VR, developing immersive experiences that combine physical and digital play, potentially revolutionizing how consumers interact with its products.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Establishing new collaborations with popular intellectual properties or partnering with other brands can help LEGO create innovative products and attract new audiences.
- Expanding LEGO Education: LEGO can continue to expand its presence in the education sector, working closely with schools, educators, and governments to develop and promote innovative learning solutions that integrate STEAM concepts.
- Adult Fan Base: Catering to the growing adult fan base (AFOLs) by offering more sophisticated and niche product lines, such as LEGO Architecture and LEGO Technic, can help the company capitalize on this loyal and engaged customer segment.
- Direct-to-Consumer Sales: Strengthening its e-commerce capabilities and offering exclusive products through its online store can help LEGO capture more value from direct-to-consumer sales, reducing dependency on third-party retailers.
- Subscription Services: Introducing subscription-based services, such as monthly LEGO sets or access to premium digital content, can create recurring revenue streams and strengthen customer loyalty.
- Media and Content Expansion: LEGO can continue to invest in its media and content division, producing more animated movies, TV shows, and web content based on popular themes, further expanding its entertainment ecosystem and brand reach.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The toy industry is highly competitive, with numerous established brands and new entrants vying for market share. LEGO faces competition from other construction toy makers and alternative forms of entertainment, such as video games and mobile apps.
- Changing Consumer Preferences: LEGO must adapt its product offerings and marketing strategies to remain relevant as consumer preferences evolve. The growing popularity of digital entertainment poses a challenge, as children may increasingly favor screen-based activities over traditional toys.
- Environmental Concerns: As concerns about plastic pollution and environmental sustainability grow, the demand for eco-friendly products increases. LEGO’s dependence on plastic materials may become a liability if it fails to develop and implement sustainable alternatives on time.
- Counterfeit Products: The prevalence of fake and imitation LEGO products in the market can erode consumer trust in the brand and result in lost sales. The company must invest in legal and marketing efforts to protect its intellectual property and maintain its brand reputation.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns can reduce consumer spending on non-essential items like toys. This may result in lower sales for LEGO, impacting its revenue and profitability.
- Intellectual Property Dependency: LEGO’s reliance on licensing agreements with popular franchises exposes the company to risks associated with the changing popularity of these IPs and the potential loss of partnerships due to contractual issues or disputes.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events, such as natural disasters, political instability, or pandemics, can disrupt LEGO’s complex supply chain, affecting its ability to produce and distribute products. The company must develop contingency plans and adopt flexible supply chain strategies to mitigate these risks.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations, such as safety standards, import/export restrictions, or environmental policies, can impact LEGO’s operations and require the company to adapt its products or manufacturing processes accordingly.
- Technological Disruption: Rapid technological advancements can render certain products or business models obsolete. LEGO must continually innovate and invest in research and development to stay ahead of technological trends and maintain its competitive edge.
- Data Security and Privacy: As LEGO expands its digital offerings, the company must ensure the security of its customers’ data and comply with increasingly strict data protection regulations. A data breach or failure to meet regulatory requirements could damage the brand’s reputation and result in financial penalties.











