Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Kia. Kia Motors Corporation, commonly known as Kia, is a South Korean multinational automotive manufacturer. It’s the second-largest automobile manufacturer in South Korea after Hyundai Motor Company. Here’s a brief overview of Kia Motors:
- History: Kia was founded in 1944 as Kyungsung Precision Industry. Initially, the company produced steel tubing and bicycle parts. By the 1950s, it had started building complete bicycles, and by the 1970s, it had transitioned to producing automobiles.
- Product Line: Kia offers a comprehensive range of vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, MPVs, and even hybrid/electric models. Some popular models include the Kia Seltos, Kia Telluride, Kia Soul, Kia Niro, and Kia Sportage.
- Innovation & Technology: Kia has actively developed electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids. They have also invested in autonomous driving technology and other innovative transportation solutions.
- Rebranding: In 2021, Kia underwent a significant rebranding. They dropped “Motors” from their name, becoming just “Kia” and introduced a new logo. This rebranding is part of their strategy to emphasize their move towards a broader mobility solutions provider, not just a car manufacturer.
- Partnership with Hyundai: Kia is a subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group, one of the largest automotive groups in the world. The partnership allows both companies to share research, development costs, and technologies, enabling them to remain competitive in the global market.
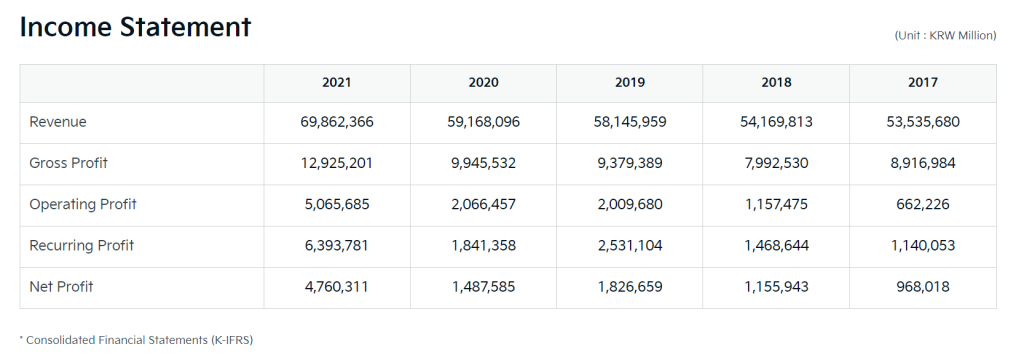
- Financial Performance: Kia has historically shown steady sales growth, driven by its ability to offer quality vehicles at competitive prices. The brand has gained a reputation for its warranty offers, design, and value for money. Refer to the image below for more details.
Here is the SWOT analysis of Kia
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Kia.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong Brand Value: Kia has built a strong brand over the years, known for its quality, durability, and design. Numerous awards and recognitions have reinforced this.
- Global Presence: With operations in many countries worldwide, Kia has a strong global presence, allowing it to diversify risks and capitalize on opportunities in various markets.
- Diverse Product Portfolio: Kia offers various vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, and hybrids, catering to a broad spectrum of customers with different needs and preferences.
- Innovation and Technology: Kia invests significantly in research and development, which leads to innovative features in its vehicles, including advanced safety technology, eco-friendly powertrains, and user-friendly infotainment systems.
- Strategic Alliances: Kia has benefitted from its alliance with Hyundai Motor Company, gaining access to shared technology, research, and development resources, which enhances its competitive edge.
- Design Excellence: Kia has received acclaim for its vehicle design, making it stand out in the crowded auto market. The company has also hired notable designers to enhance its vehicle aesthetics.
- Aggressive Marketing: Kia employs aggressive and innovative marketing strategies, including high-profile sponsorships and advertising campaigns, to boost its brand visibility and appeal.
- Manufacturing Efficiency: Kia has state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities that use advanced production techniques to ensure high efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Warranty and Services: Kia offers competitive vehicle warranties, which can be a compelling selling point for customers looking for reliability and assurance.
- Sustainable Focus: Kia increasingly focuses on sustainable mobility solutions, including electric and hybrid vehicles, which positions it well for future trends.
Weaknesses
- Perception Issues: Despite improvements in quality and design, Kia may still battle against consumer perceptions of being a budget brand compared to more established competitors, particularly in the luxury car segment.
- Limited Premium Segment Presence: Kia has traditionally been more successful in the economy and mid-price range markets. Their presence in the premium segment is not as strong, potentially limiting profitability and brand prestige.
- Recalls and Quality Concerns: Any automaker is vulnerable to recalls, but for Kia, past recalls can contribute to ongoing consumer concerns about vehicle reliability and safety.
- Dependence on External Markets: A significant portion of Kia’s revenue comes from outside its home country, South Korea, making it vulnerable to economic fluctuations and political tensions in its export markets.
- Heavy Reliance on Hyundai: Kia’s alliance with Hyundai provides many benefits but also ties Kia’s fortunes closely to Hyundai. Should Hyundai face difficulties, Kia could be negatively impacted.
- Competition with Hyundai: While the alliance with Hyundai Motor Group has advantages, it also means that Kia competes directly with Hyundai for market share, which could lead to internal competition issues.
- R&D Costs: Keeping up with technological advances and consumer expectations requires significant and ongoing investment in research and development, which can strain financial resources.
- Lower Profit Margins: Competing primarily in the economy and mid-tier segments often results in lower profit margins than companies with a substantial presence in the luxury or specialty segments.
- Product Recalls: Like many auto manufacturers, Kia has had to initiate vehicle recalls. Recalls can lead to direct financial costs and indirect costs in terms of brand image and customer trust.
Opportunities
- Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Market: The global shift towards environmentally friendly vehicles is a significant opportunity for Kia to expand its line of electric (EV) and hybrid vehicles.
- Emerging Markets: Kia can continue to expand in emerging markets, where the demand for affordable, reliable transportation is growing.
- Technological Advancements: Investing in new technologies such as autonomous driving features, advanced safety systems, and connected car technologies can provide Kia with a competitive edge.
- Sustainable Practices: As the focus on sustainability increases, Kia can lead in eco-friendly manufacturing practices and develop vehicles that are less harmful to the environment.
- Market Diversification: Diversifying its market base can reduce Kia’s dependency on specific regional markets and spread its risk.
- Strategic Partnerships: Forming new strategic partnerships or deepening existing ones, especially in technology and innovation, can lead to shared growth and development opportunities.
- New Model Launches: Kia can capture more market share by regularly updating its model range with fresh and refreshed vehicles that meet current consumer trends and preferences.
- Lifestyle Branding: Positioning itself as a lifestyle brand rather than just an automotive brand can open new avenues for marketing and customer engagement.
- Mobility Services: There’s an opportunity to expand into mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms, offering services like car-sharing, ride-hailing, or subscription-based vehicle access.
- Aftermarket Services: Strengthening the aftermarket services, including parts, accessories, and servicing, can enhance customer loyalty and create additional revenue streams.
- Customer Experience: Improving the overall customer experience, both online and at dealerships, can differentiate Kia from competitors and build brand loyalty.
- Expand in Luxury Segment: With the right strategy, Kia can expand its presence in the luxury car segment, which could lead to higher margins.
- Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning in operations, from supply chain management to personalized customer experiences, could improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Threats
- Intense Competition: The automotive industry is highly competitive, with many well-established players and new entrants, especially in the electric vehicle market, putting pressure on market share and margins.
- Global Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns, currency volatility, and trade disputes can lead to decreased consumer spending and disruptions in global supply chains.
- Rising Material Costs: Increases in the cost of raw materials, such as steel and precious metals used in vehicle manufacturing, can erode profit margins.
- Regulatory Challenges: Stricter environmental and safety regulations can increase costs for car manufacturers, necessitate redesigns, and impact the competitiveness of existing models.
- Technological Disruption: Rapid technological advancements, such as autonomous driving and alternative mobility solutions, may outpace Kia’s ability to adapt, leading to a potential loss of market relevance.
- Environmental Policies: Increasingly stringent global environmental policies and the push toward zero-emission vehicles could require significant investments from Kia to keep up with the industry transformation.
- Shift in Consumer Preferences: Changes in consumer preferences, such as the shift towards shared mobility or service-based transportation options, could reduce demand for personal vehicles.
- Market Saturation: In some regions, the vehicle market may be reaching saturation, making it more difficult for Kia to grow without taking market share from competitors.
- Reliance on Specific Markets: Heavy reliance on particular markets makes Kia vulnerable to region-specific economic and political risks.
- Fuel Price Volatility: Fluctuating fuel prices can shift consumer demand away from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles to more fuel-efficient or electric alternatives.
- Quality Control Issues: Any lapses in quality control can lead to recalls and damage the brand’s reputation.











