Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of EasyJet. EasyJet is a British low-cost airline carrier based at London Luton Airport. It is one of the largest airlines in Europe by the number of passengers flown, and along with competitors Ryanair, Wizz Air, and Eurowings, EasyJet has a predominant presence in the European low-cost air travel market.
Founded by Sir Stelios Haji-Ioannou in 1995, EasyJet has been characterized by its rapid expansion, fueled by the deregulation of the aviation industry in Europe in 1997 and the increasing consumer demand for low-cost air travel.
Key features of EasyJet’s business include:
- Point-to-Point Model: EasyJet operates on a point-to-point model rather than the traditional hub-and-spoke model used by many airlines. This means they operate non-stop flights between two cities, resulting in shorter travel times and lower costs.
- Cost Efficiency: A key part of EasyJet’s business strategy is keeping costs low. They achieve this through measures such as operating a single type of aircraft to reduce maintenance costs, maximizing aircraft utilization, using secondary airports with lower fees, and offering no-frills services with additional options available for purchase.
- Online Sales and Distribution: EasyJet was one of the first airlines to embrace the Internet for booking tickets. This has allowed them to keep costs low by cutting out intermediaries and has provided a convenient platform for customers to manage their bookings.
- Fleet: As of 2021, EasyJet operates a fleet of Airbus A319 and A320 aircraft. They have chosen to operate a single type of aircraft to simplify operations and reduce costs.
- Network: EasyJet serves numerous destinations across Europe and some outside of Europe in North Africa and the Middle East. This extensive network, combined with high-frequency flights, makes the airline popular for leisure and business travelers.
- Ancillary Revenue: In addition to revenue from ticket sales, EasyJet also earns income from ancillary services such as baggage fees, seat selection fees, in-flight sales, and car rental partnerships.
- Customer Segmentation: While initially focusing on leisure travelers, EasyJet has also attracted business travelers by offering flexible fares, fast-track security, and other services.
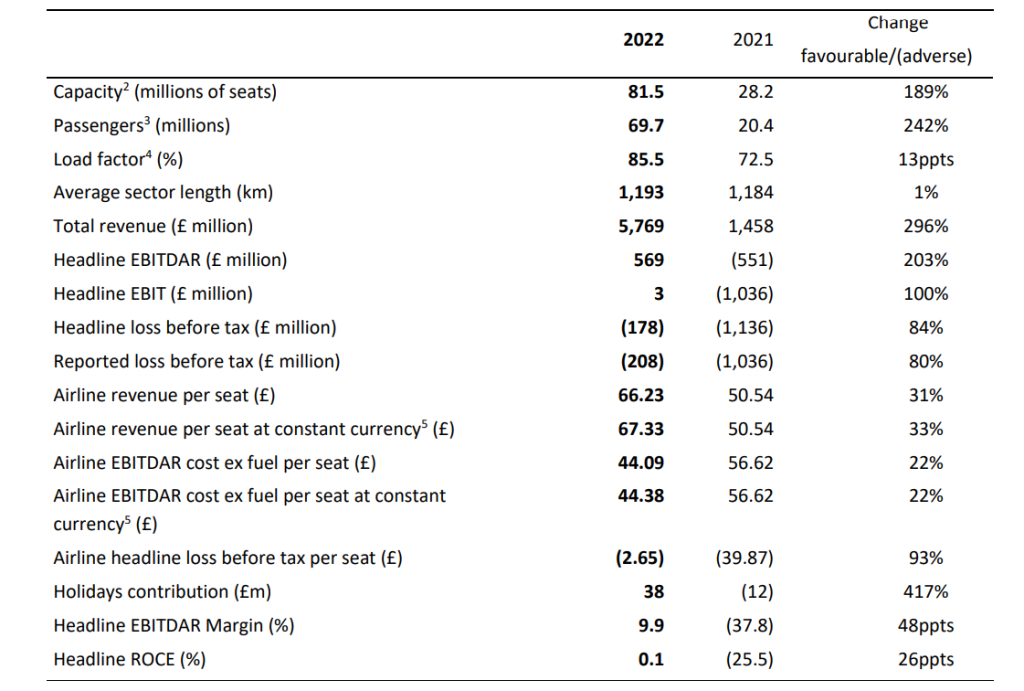
- Headline loss before tax of £178 million (2021: £1,136 million loss)
- Total revenue increased by 296% to £5,769 million (2021: £1,458 million), predominantly due to increased capacity flown and ancillary products continuing to deliver incremental revenue.
- Group headline costs increased by 129% to £5,947 million (2021: £2,594 million), primarily due to the increase in flow capacity.
Here is the PESTEL analysis of EasyJet
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of EasyJet.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Government Stability: Political instability, such as changes in government, can lead to changes in policy or regulations that can affect EasyJet’s operations. For instance, changes in aviation regulations or taxation policies can impact their profitability.
- International Relations: EasyJet operates in various countries across Europe. The relations between these countries can impact EasyJet’s operations. For instance, political tensions or conflicts could disrupt flight schedules or lead to bans on flights to certain destinations.
- Brexit: The UK’s exit from the European Union (Brexit) has significant political implications for EasyJet. Brexit has led to regulation changes, such as those concerning flight rights and operations within the EU. This could potentially limit EasyJet’s ability to operate freely across EU countries, impacting its business model.
- Regulatory Environment: EasyJet is subject to numerous regulations, such as safety standards, environmental regulations, and labor laws. Changes in these regulations can impact EasyJet’s costs and operational efficiency. For example, stricter environmental regulations could require EasyJet to invest in newer, more environmentally-friendly aircraft.
- Terrorism and Security: Political factors such as terrorism threats or security issues can also impact EasyJet. This can increase security measures, increase costs, and impact passenger experience. It could also lead to decreased demand for air travel in certain regions.
- Government Support and Subsidies: Any changes in government support or subsidies in the aviation sector can also affect EasyJet. For instance, if a government decides to support its national carrier more aggressively, it could result in an uneven playing field for EasyJet.
Economic
- Economic Cycles: The demand for EasyJet’s services is closely tied to economic conditions. In times of economic prosperity, people are more likely to travel for business and leisure, increasing demand for flights. Conversely, in times of economic downturn, people are likely to cut back on travel, which could reduce demand for EasyJet’s services.
- Exchange Rates: As a company that operates across different countries, EasyJet is exposed to fluctuations in currency exchange rates. These rates can affect the company’s costs (for example, fuel is often priced in dollars) and revenues (for example, tickets sold in a different currency).
- Fuel Prices: One of the most significant operating costs for any airline is fuel. Therefore, fluctuations in oil prices can significantly impact EasyJet’s profitability.
- Inflation and Interest Rates: Inflation and interest rates can impact EasyJet’s costs. For example, higher interest rates can increase the cost of borrowing for capital expenditures, such as purchasing new aircraft.
- Consumer Confidence and Spending Power: Consumers’ financial health directly impacts the travel industry. If consumer confidence is high and people feel financially secure, they are more likely to spend money on travel, benefiting EasyJet. On the other hand, if consumer confidence is low, discretionary spending on things like travel may decrease.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment rates can decrease demand for air travel, as people have less disposable income to spend on trips. Conversely, low unemployment rates could result in increased demand for air travel.
Sociocultural
- Changing Travel Habits: Sociocultural changes can affect people’s travel habits. For instance, increased interest in eco-tourism or adventure tourism could impact the destinations EasyJet serves. Similarly, a growing trend of remote work and digital nomadism might lead to increased demand for travel, as people are not tied to a specific location for work.
- Environmental Awareness: As environmental concerns become more prominent, there is increased scrutiny of the aviation industry’s environmental impact. Customers are becoming more conscious about their carbon footprint, and some may choose other forms of transportation over flying to reduce their impact. This could affect the demand for EasyJet’s services.
- Demographic Changes: Changes in the population’s age, gender, income, and educational level can also impact EasyJet. For example, an aging population might increase demand for specific destinations or services.
- Cultural Differences: EasyJet operates in various countries and must be mindful of cultural differences. This can affect everything from marketing strategies to customer service practices.
- Health and Wellness Trends: Increasing focus on health and wellness could impact the travel demand, especially during pandemics. Concerns about health risks associated with travel could decrease demand for air travel.
- Shifts in Consumer Behavior Post-Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic has led to significant changes in travel behavior. Even after the pandemic, some changes may persist, such as a preference for less crowded destinations or increased concern about hygiene standards.
Technological
- Online Booking Systems and E-commerce: The rise of online booking systems has revolutionized the travel industry. EasyJet, like many airlines, has an online booking system that allows customers to book flights, check-in, and manage their bookings. Any advances in this technology or changes in how customers use it could impact EasyJet.
- Mobile Technology: With the increase in smartphone usage, airlines are increasingly expected to offer mobile services, such as mobile boarding passes and flight updates via mobile notifications. EasyJet needs to keep up with these technological trends to meet customer expectations.
- In-flight Entertainment and Connectivity: Technology advances have increased expectations for in-flight entertainment and connectivity options. In contrast, this is more relevant to long-haul flights. As a budget airline, EasyJet needs to consider the cost-benefit analysis of implementing such technologies.
- Fuel Efficiency and Aircraft Technology: Technological improvements in aircraft design and fuel efficiency can significantly impact EasyJet’s operations. More fuel-efficient aircraft can reduce costs and also help meet environmental targets.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation: AI and automation can be used in various ways in the airline industry, from automated customer service bots to predictive maintenance for aircraft. Implementing these technologies could help EasyJet improve efficiency and customer service.
- Cybersecurity: As more services move online and the use of technology increases, cybersecurity becomes increasingly important. Data breaches or cyber threats could harm EasyJet’s reputation and result in significant costs.
- Sustainable Technology: There’s increasing pressure for airlines to adopt more sustainable practices. Technological developments in areas like biofuels or even electric aircraft could become significant.
Environmental
- Climate Change: Climate change can lead to more extreme and unpredictable weather patterns, disrupting flight schedules and increasing operating costs for EasyJet. Furthermore, climate changes can also affect travel patterns and the attractiveness of certain destinations.
- Carbon Emissions and Environmental Regulations: The aviation industry is a significant contributor to carbon emissions, which are a leading cause of climate change. There is increasing regulatory pressure on airlines to reduce carbon emissions, which could require significant investment from EasyJet. For example, the European Union’s Emissions Trading System (ETS) requires airlines to buy carbon credits, which can increase operating costs.
- Sustainable Aviation Fuels: There is a growing interest in sustainable aviation fuels to reduce the environmental impact of air travel. These fuels can be more expensive than conventional jet fuel, but they could become more important if regulations around carbon emissions become stricter.
- Noise Pollution: Noise pollution is a significant issue for communities living near airports, and there are strict regulations around noise levels. This could impact EasyJet’s operations, especially at airports near residential areas.
- Waste Management: Airlines generate significant waste, from food waste to disposable items like plastic cutlery and cups. Airlines are increasingly pressured to reduce their waste and improve recycling efforts.
- Biodiversity: The construction and expansion of airports can significantly impact local ecosystems and biodiversity. There is increasing attention on the need to minimize this impact, which could affect EasyJet’s ability to expand or develop new routes.
Legal
- Aviation Regulations: EasyJet is subject to a range of aviation-specific regulations as an airline. These include safety standards, flight regulations, and issues like overbooking and passenger compensation for delayed or canceled flights. Changes in these regulations can significantly impact EasyJet’s operations and costs.
- Employment Laws: Employment laws can affect a range of areas in EasyJet’s operations, from hiring practices to employee benefits and working conditions. For example, changes in minimum wage laws could impact EasyJet’s labor costs.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws: With the increasing use of online booking systems and other digital technologies, data protection, and privacy laws are becoming increasingly important. EasyJet must comply with regulations like the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Environmental Laws: As mentioned in the environmental factors, a range of environmental laws and regulations can affect EasyJet. These can include regulations around carbon emissions, noise pollution, and waste management.
- Brexit-Related Legal Changes: As a UK-based airline, the legal implications of Brexit can impact EasyJet. For example, it may affect their ability to operate freely across EU countries or lead to changes in regulations around things like customer compensation.
- Health and Safety Regulations: Airlines are subject to strict health and safety regulations to ensure the safety of passengers and crew. These regulations can cover a range of areas, from aircraft maintenance to onboard safety procedures.











