Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of Bosch. The Bosch Group is a leading global supplier of technology and services, with its operations spanning across four major business sectors: Mobility Solutions, Industrial Technology, Consumer Goods, and Energy and Building Technology. The company’s extensive global presence is supported by around 468 subsidiaries and regional companies across 60 countries, emphasizing its vast international footprint and influence in various industries.
Bosch is known for its commitment to innovation and sustainability, employing around 90,100 associates in research and development across 136 locations globally. This innovative strength is crucial for the company’s future growth and is evident in its efforts to become carbon neutral since 2020 at over 400 locations worldwide. Bosch’s dedication to sustainability is also reflected in its use of green electricity and offsetting residual emissions through carbon credits.
The company’s rich history dates back to its founding by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886. Over the years, Bosch has grown to become not only the most prominent automotive supplier in terms of revenue but also a significant player in various other sectors, including household appliances, power tools, security systems, engineering, electronics, cloud computing, and IoT.
Bosch’s ownership structure is unique, with 94% of its share capital held by Robert Bosch Stiftung, a charitable foundation, ensuring the company’s ability to plan for the long term and make significant investments in its future.
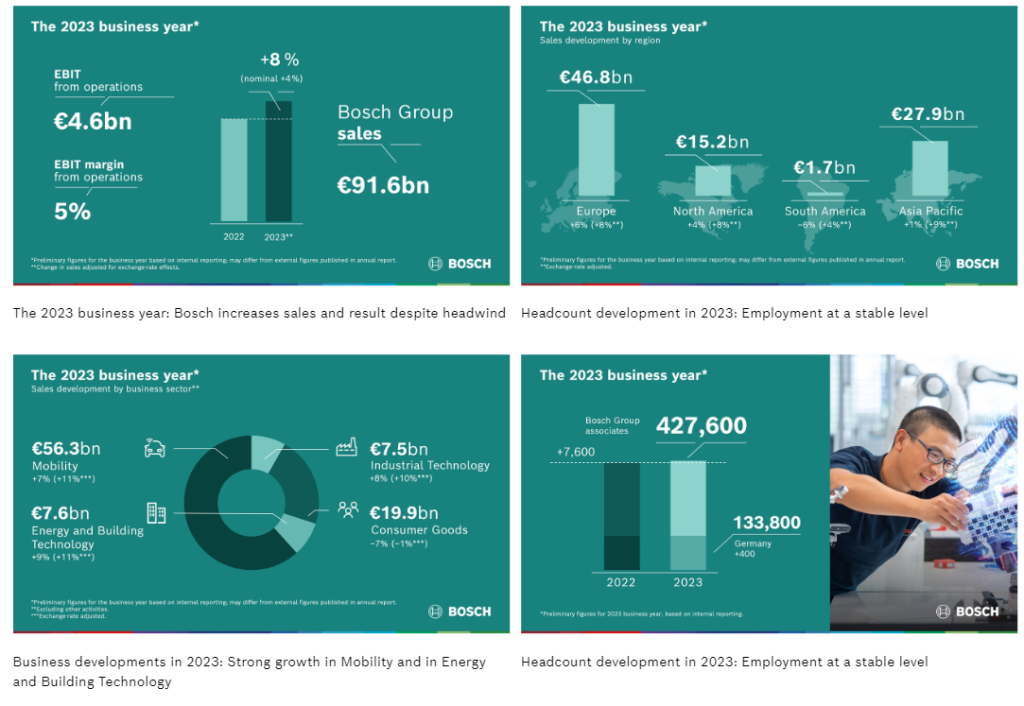
Financial Performance: In 2023, Bosch generated significant sales revenue of 91.6 billion euros and employed approximately 428,000 associates worldwide.
Here is the SWOT analysis for Bosch
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Bosch.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Diverse Product Portfolio: Bosch operates across multiple sectors, including Mobility Solutions, Industrial Technology, Consumer Goods, and Energy and Building Technology, allowing it to serve a wide range of customer needs and stabilize its market position across different industries.
- Global Presence: With operations in around 60 countries and a workforce of approximately 428,000 associates, Bosch’s extensive global footprint enables it to capitalize on market opportunities worldwide and mitigate regional market fluctuations.
- Strong Focus on Innovation and R&D: Bosch’s significant investment in research and development, with around 90,100 associates dedicated to R&D across 136 locations, underscores its commitment to innovation, driving future growth and maintaining technological leadership.
- Commitment to Sustainability: Bosch’s achievement of carbon neutrality across its more than 400 locations worldwide reflects its commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility, enhancing its brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers and partners.
- Robust Financial Performance: The company’s substantial revenue growth and strong financials provide it with the resources needed to invest in new technologies, expand into new markets, and navigate economic challenges.
- Ownership Structure and Foundation: Bosch’s unique ownership structure, with the majority owned by the Robert Bosch Stiftung, a charitable foundation, ensures long-term planning and investment capabilities, distinguishing it from competitors.
Weaknesses
- Complexity and Diversification: Bosch’s involvement in a wide range of sectors, from automotive to consumer goods and industrial technology, could lead to operational complexities and challenges in maintaining focus and efficiency across diverse business units.
- Dependence on the Automotive Sector: Despite its diversification, Bosch is heavily reliant on the automotive industry, which is subject to cyclical demand, regulatory changes, and technological disruptions. This dependence could make Bosch vulnerable to industry-specific downturns and shifts towards electric and autonomous vehicles.
- High R&D Costs: Bosch’s strong commitment to innovation and research and development is crucial for its technology leadership. However, this also results in significant R&D expenses, impacting profit margins, especially if not all investments lead to commercially successful products.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Bosch’s extensive global operations and supply chain are susceptible to disruptions from geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and global events like pandemics, which can affect production and lead to increased costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Operating in multiple countries and sectors exposes Bosch to a complex web of regulations, including environmental, safety, and data protection laws, which can entail substantial compliance costs and operational challenges.
- Competition and Market Pressure: Bosch faces intense competition in several of its key markets, including from other global conglomerates, specialized companies, and emerging startups, especially in rapidly evolving areas like IoT, AI, and electric mobility.
Opportunities
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Bosch can further tap into emerging markets, where rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing consumer spending present significant growth opportunities, especially in the Mobility Solutions and Consumer Goods sectors.
- Electrification and Sustainable Technologies: With the automotive industry’s shift towards electric vehicles (EVs), Bosch has the opportunity to expand its offerings in electric mobility, battery technology, and related services, reinforcing its position as a leader in sustainable transportation solutions.
- Digitalization and IoT Solutions: As a leading IoT provider, Bosch can capitalize on the growing demand for smart homes, Industry 4.0, and connected mobility solutions by offering innovative, connected, and cross-domain solutions from a single source, enhancing its competitiveness in the digital era.
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: The healthcare sector presents new growth avenues for Bosch, particularly in diagnostics, patient monitoring, and digital health services, leveraging its expertise in sensor technology, software, and services.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Strategic partnerships with tech companies, research institutions, and startups can accelerate Bosch’s innovation efforts, access new technologies, and enter new markets, particularly in fast-evolving fields like AI, robotics, and sustainable energy.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Bosch’s commitment to sustainability and carbon neutrality can be leveraged to develop eco-friendly products and solutions, meeting the increasing demand from consumers and businesses for sustainable and responsible practices.
Threats
- Intense Global Competition: Bosch operates in highly competitive markets, facing challenges from both established industry giants and innovative startups. This competition can pressure pricing, margins, and market shares across its diverse business sectors.
- Technological Disruption: Rapid advancements in technology, especially in the automotive sector with the rise of electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and alternative mobility solutions, pose a threat to Bosch’s traditional business models and necessitate continuous innovation and adaptation.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events such as pandemics, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions can disrupt Bosch’s complex global supply chain, affecting production capabilities and leading to increased operational costs.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: Bosch’s operations across multiple countries and industries subject it to a wide array of regulations, including environmental standards, data protection laws, and trade regulations. Compliance with these evolving regulations can be costly and impact business operations.
- Economic Fluctuations: Economic downturns in critical markets can lead to reduced consumer spending and investment in industrial technologies, potentially affecting Bosch’s sales and revenue across its various business sectors.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As Bosch expands its digital offerings and IoT solutions, the risk of cyber threats increases. Protecting against these threats is crucial to safeguard customer data and maintain trust in Bosch’s digital and connected services.











