Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let us get the business overview of Boeing. The Boeing Company was founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing is in Seattle, Washington, and is one of the world’s leading aerospace and defense companies.
Boeing designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support services. Boeing operates through four major business segments:
- Commercial Airplanes (BCA): This segment designs, produces, and markets commercial jet aircraft for various passenger and cargo requirements. It includes the 737, 747, 767, 777, and 787 families of airplanes, as well as aviation services such as maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) solutions.
- Defense, Space & Security (BDS): This segment comprises three sub-segments: Boeing Defense, Space & Security (BDS), Boeing Global Services (BGS), and Boeing Capital (BCC). BDS is responsible for developing and producing military aircraft, weapons systems, satellites, and other defense and intelligence systems. Notable products include the F/A-18 Super Hornet, F-15 Eagle, KC-46 Pegasus, and P-8 Poseidon.
- Global Services (BGS): This segment provides a wide range of services and support to commercial and government customers. These services include supply chain and logistics management, engineering, modifications and maintenance, digital solutions, and training systems.
- Boeing Capital (BCC): This segment facilitates financing solutions for customers purchasing Boeing’s commercial aircraft and defense products. It primarily focuses on ensuring customers have access to the financing needed to buy and take delivery of their Boeing products.
- Generated $77.7 bn in revenue, a 17% YoY growth.
- Delivered 528 commercial airplanes and recorded 1,576 net orders
- Total company backlog grew to $520 billion, including over 5,600 commercial airplanes
- Generated $6.0 billion of operating cash flow and $4.4 billion of free cash flow (non-GAAP)
Here is a SWOT analysis for Boeing:
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of Boeing.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
- Strong brand and reputation: Boeing has a long history of innovation and excellence in the aerospace industry. Its brand is synonymous with quality, reliability, and advanced technology, which helps it attract and retain customers.
- Diversified product portfolio: Boeing’s wide range of products and services, from commercial airplanes to military aircraft, satellites, and other defense systems, allows the company to cater to a diverse customer base and reduce dependence on any single market segment.
- Global presence: Boeing has a strong global footprint, with customers in more than 150 countries. This geographical diversification helps the company mitigate regional economic downturns and political instability risks.
- Technological leadership: Boeing is known for its cutting-edge technology and research and development capabilities, which enable the company to develop advanced products that meet customer requirements and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
- Skilled workforce: Boeing’s experienced and skilled workforce is one of its most valuable assets. The company employs tens of thousands of engineers, technicians, and other professionals contributing to its success in designing, manufacturing, and supporting its products.
- Solid financial position: Boeing has a strong financial position, which allows it to invest in research and development, strategic acquisitions, and expanding its operations. This financial strength also enables the company to weather economic downturns and industry challenges.
- Strategic partnerships and collaborations: Boeing has established partnerships with various suppliers, governments, and other industry stakeholders. These relationships help the company access new markets, share risks and costs, and expand its expertise in different areas.
- Vertical integration: Boeing’s vertical integration strategy allows it to maintain better control over its supply chain and reduce production costs. By owning key suppliers and manufacturing components in-house, the company can achieve greater efficiency and responsiveness in its operations.
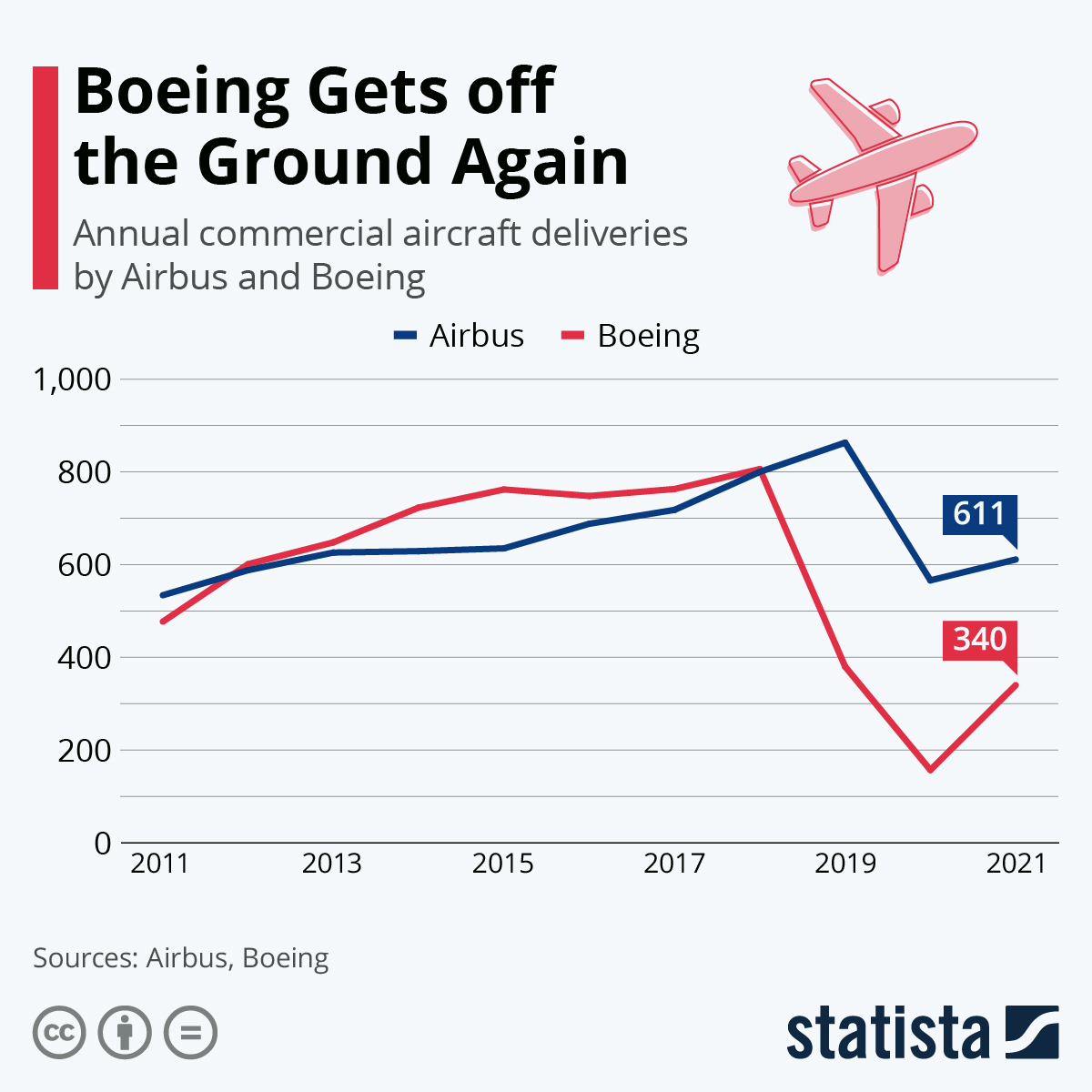 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
Weaknesses
- 737 MAX crisis: The two fatal crashes involving the 737 MAX and the subsequent worldwide grounding of the aircraft have significantly damaged Boeing’s reputation and market position. The crisis has raised questions about the company’s safety culture and regulatory oversight, which may affect customer trust and confidence in its products.
- Supply chain issues: Boeing has faced challenges in managing its supply chain, with delays and quality control issues occasionally affecting its production process. These issues can lead to cost overruns and delayed deliveries, impacting the company’s profitability and customer relationships.
- High dependence on the commercial aircraft segment: Boeing’s commercial aircraft segment is its largest revenue contributor, which makes the company vulnerable to fluctuations in demand for commercial airplanes. Economic downturns, geopolitical tensions, and other factors influencing commercial aviation can significantly impact Boeing’s financial performance.
- Intense competition: Boeing faces stiff competition from other aerospace and defense companies, particularly Airbus, in the commercial aircraft segment. Increased competition can pressure prices and market share, affecting the company’s profitability and growth prospects.
- Regulatory and political risks: Boeing’s operations are subject to various regulations and government policies in the United States and abroad. Regulation changes or political developments can significantly impact the company’s operations, contracts, and financial performance.
- Environmental concerns: The aviation industry is under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental footprint, particularly regarding greenhouse gas emissions. As a leading aircraft manufacturer, Boeing may face challenges in meeting stricter environmental regulations and customer demands for more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft.
- Workforce issues: Labor disputes and strikes have occasionally disrupted Boeing’s operations in the past. Maintaining positive labor relations and ensuring a skilled and motivated workforce is essential for the company’s success and competitiveness.
Opportunity
- Growing demand for commercial aircraft: Global air traffic is expected to continue growing in the long term, driven by economic growth, urbanization, and an expanding middle class, particularly in emerging markets. This growth in air travel is likely to drive demand for new commercial aircraft, providing Boeing with significant opportunities to increase its sales and market share.
- Demand for fuel-efficient aircraft: As concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability intensify, airlines increasingly seek fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly aircraft to reduce their carbon footprint and operating costs. Boeing can capitalize on this trend by investing in research and developing new technologies and materials to create more fuel-efficient and eco-friendly aircraft.
- Expansion in emerging markets: Emerging economies like China, India, and Southeast Asia present significant growth opportunities for Boeing, as these regions are expected to experience rapid growth in air travel and defense spending. By establishing a more substantial presence in these markets, Boeing can diversify its revenue sources and reduce its dependence on traditional markets.
- Growth in the services segment: There is a growing demand for aftermarket services like maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO), training, and digital solutions. By expanding its Global Services division, Boeing can tap into this market and generate additional revenue streams.
- Unmanned systems and autonomous technology: The development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and autonomous technology is a rapidly growing area in both commercial and military applications. Boeing can invest in these technologies to create innovative solutions and secure a competitive advantage in this emerging market.
- Space exploration and satellite business: With renewed interest in space exploration and the growth of satellite-based services, there are opportunities for Boeing to expand its presence in the space sector, leveraging its expertise in satellite manufacturing, launch services, and deep-space exploration.
- Strategic partnerships and acquisitions: Boeing can further strengthen its market position and access new technologies by forming strategic alliances and joint ventures and acquiring companies with complementary capabilities or expertise.
Threats
- Intense competition: Boeing faces strong competition from other aerospace and defense companies, particularly Airbus, in the commercial aircraft segment. Increased competition can pressure prices, market share, and margins, potentially affecting the company’s profitability and growth prospects.
- Economic downturns and geopolitical tensions: The demand for commercial aircraft is heavily influenced by global economic conditions and geopolitical factors. Economic downturns or geopolitical crises can result in reduced air travel demand, negatively impacting Boeing’s commercial aircraft business.
- Regulatory changes and political risks: Boeing’s operations are subject to various regulations and government policies in the United States and other countries where it operates. Changes in regulations, trade policies, or political developments can significantly impact the company’s operations, contracts, and financial performance.
- Environmental regulations and climate change concerns: The aviation industry is under increasing scrutiny due to its environmental impact, particularly regarding greenhouse gas emissions. Stricter environmental regulations and public pressure for sustainable aviation could challenge Boeing to develop and adopt more eco-friendly technologies and meet emissions targets.
- Technological disruption: Rapid advancements in technology and the emergence of new competitors, particularly in areas like electric aircraft, autonomous systems, and space exploration, can disrupt the traditional aerospace and defense market. Boeing must continually invest in research and development to stay ahead of these technological changes and maintain its competitive edge.
- Supply chain disruptions: Boeing’s complex global supply chain is susceptible to various risks, including natural disasters, political instability, and trade disputes. Disruptions in the supply chain can lead to delays in production, increased costs, and potential damage to customer relationships.
- Reputational risks: Boeing’s reputation has been impacted by the 737 MAX crisis, and regaining customer trust and confidence is crucial to its long-term success. Further safety incidents or quality control issues could further damage the company’s reputation and affect its market position.











