Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of AstraZeneca. AstraZeneca is a global, science-led biopharmaceutical company focusing on discovering, developing, and commercializing prescription medicines. Founded in 1999 through the merger of Astra AB of Sweden and Zeneca Group PLC of the UK, it has since become one of the world’s foremost pharmaceutical companies.
Therapeutic Areas: AstraZeneca operates in a variety of therapeutic areas, including:
- Oncology
- Cardiovascular, Renal & Metabolism (CVRM)
- Respiratory & Immunology
- Other areas like neuroscience and infection
COVID-19 Vaccine: AstraZeneca has been in the global spotlight due to its development of a COVID-19 vaccine in collaboration with the University of Oxford. This vaccine has been distributed to numerous countries and is vital in global vaccination campaigns.
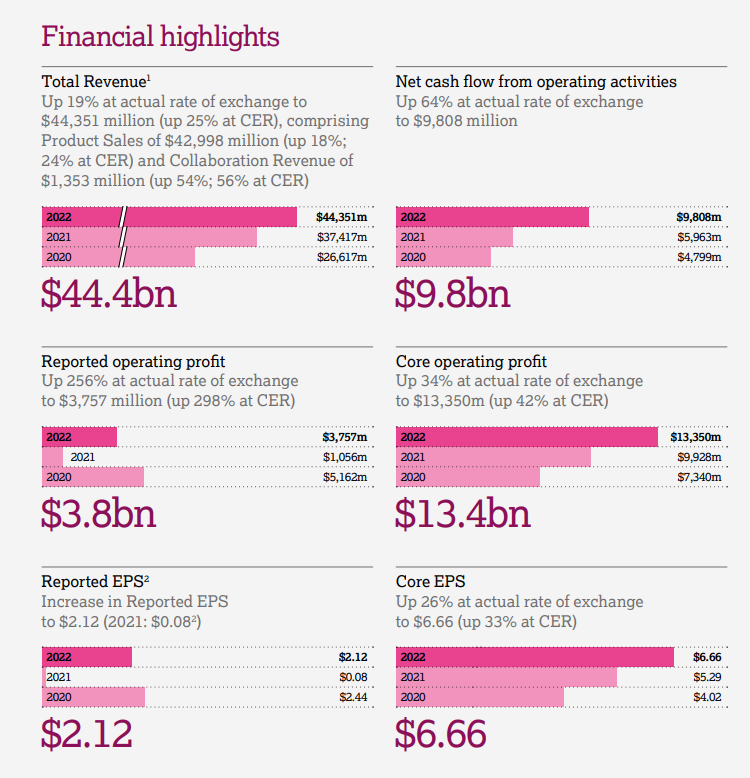
Here is the PESTEL analysis of AstraZeneca
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of AstraZeneca.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Regulation and Approval: Pharmaceutical companies like AstraZeneca operate under strict regulatory environments. Obtaining approvals for new drugs from agencies like the FDA (U.S.), EMA (Europe), and MHRA (UK) can take time and effort.
- Pricing and Reimbursement: Governments and public health bodies influence drug pricing, especially in countries with nationalized healthcare systems. These entities may negotiate drug prices, which can impact AstraZeneca’s profitability.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Political decisions around patent laws can affect AstraZeneca’s revenue. Extensions or restrictions on patents directly impact the duration of time a drug remains exclusive to the company before generics can enter the market.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs, trade barriers, and international trade agreements can influence AstraZeneca’s operations, especially considering they operate globally and source raw materials and distribute products across borders.
- Government Healthcare Policies: Changes in healthcare policy can impact pharmaceutical companies. For instance, healthcare reforms aiming to cut costs might pressure drug prices.
- Global Diplomacy and Relations: As a global company, AstraZeneca can be affected by diplomatic relations between countries. Strained relations might hinder its ability to operate in certain markets.
- Vaccination Campaigns and Public Health Initiatives: Government-driven vaccination or health campaigns, such as the widespread COVID-19 vaccination drive, can offer opportunities or challenges based on how governments decide to procure and distribute vaccines.
Economic
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic downturns or recessions can impact consumers’ ability to afford medications, especially in countries without comprehensive health insurance. Conversely, economic booms can enhance purchasing power.
- Currency Exchange Rates: AstraZeneca deals in multiple currencies as an international company. Fluctuations in exchange rates can influence profitability, especially when repatriating profits or sourcing materials.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can influence AstraZeneca’s cost of capital, especially if it has significant debt. It can also influence investment decisions.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can increase the cost of raw materials, production, and research, affecting profit margins. It also impacts the purchasing power of consumers.
- Healthcare Spending: The allocation of funds by governments or private entities towards healthcare can impact AstraZeneca. An increase in healthcare budgets may lead to more purchases of their drugs, while cuts or austerity measures might result in pressures to reduce drug prices.
- Economic Policies: Policies related to foreign direct investment, subsidies for the pharmaceutical sector, or economic protectionism can influence AstraZeneca’s operations in different countries.
- Cost of Research & Development: Economic factors like the availability of skilled labor, the cost of equipment, and the infrastructure for research can influence the economic feasibility of R&D projects.
- Supply Chain Costs: Economic situations, like fuel price volatility, can influence the cost of transporting goods, raw materials, and finished products. Additionally, the economic stability of suppliers can impact the supply chain’s reliability.
Sociocultural
- Health Awareness: A society’s focus on health and wellness can influence pharmaceutical demand. Societies with heightened health awareness might be more proactive in seeking medical treatments and preventive measures.
- Demographics: Aging populations, especially in developed countries, might require more medications and treatments for age-related ailments, creating a higher demand for AstraZeneca’s products.
- Cultural Attitudes Towards Medication: Some cultures might prefer traditional or alternative medicines over pharmaceutical drugs, affecting market demand.
- Public Opinion on Pharmaceuticals: Trust in the pharmaceutical industry and perceptions of pharmaceutical companies, whether positive or negative, can affect sales. Scandals, perceived price gouging, or perceived altruism can all sway public opinion.
- Lifestyle Diseases: Sociocultural changes leading to sedentary lifestyles, dietary habits, and stress can lead to a rise in lifestyle-related diseases, influencing demand for related treatments.
- Education and Information Availability: With more people gaining access to the Internet, patients are becoming increasingly informed about health issues and treatment options. This empowerment can influence their choices and demands.
- Cultural Perception of Vaccination: Societal views on vaccination can hugely impact pharmaceutical companies like AstraZeneca, especially given their role in the COVID-19 vaccination drive. Vaccine hesitancy or acceptance in different cultures and communities can affect sales and distribution strategies.
- Epidemiological Patterns: Societal behaviors and norms can influence the spread of diseases, impacting the need for specific treatments or preventive measures.
- Stigma Associated with Diseases: Some diseases carry a stigma, which might deter individuals from seeking treatments. Understanding and addressing these sociocultural sensitivities can be crucial for pharmaceutical companies.
Technological
- R&D Innovations: The pharmaceutical industry thrives on innovation. Advances in biotechnology, genomics, and personalized medicine can lead to the discovery of new drugs and treatments. AstraZeneca needs to be at the forefront of these innovations to remain competitive.
- Data Analytics and AI: With the rise of big data and artificial intelligence, pharmaceutical companies can analyze vast datasets for drug discovery patient outcomes and optimize clinical trials, making the R&D process more efficient and targeted.
- Telemedicine and Digital Health: The increasing acceptance of telemedicine and digital health platforms can impact how patients access treatment and medications, offering new channels for engagement and distribution.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Innovations in manufacturing can lead to more efficient, scalable, and flexible production processes, impacting cost, quality, and supply chain dynamics.
- Blockchain: This technology has potential applications in ensuring drug traceability, securing clinical trial data, and preventing counterfeit drugs, enhancing transparency and trust.
- Wearable Health Devices: Integrating health monitoring devices can provide real-time patient data, enabling more proactive healthcare interventions and personalized treatments.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: These technologies can be used in patient education, physician training, and even designing drug molecules or visualizing cellular interactions.
- Clinical Trial Innovations: Technology can streamline and optimize clinical trial processes, from patient recruitment to real-time data monitoring, reducing the time and cost of drug development.
- E-Pharmacy and Online Distribution: The rise of online pharmacies and digital platforms for drug distribution can change the way AstraZeneca reaches its end consumers.
- Regenerative Medicine: Technological advances in stem cell research and regenerative medicine can open new avenues for treatments, potentially changing the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry.
- Collaboration Platforms: Digital platforms facilitate collaboration between researchers, institutions, and companies globally, accelerating drug discovery and development.
Environmental
- Sustainability Initiatives: With a growing focus on environmental sustainability, AstraZeneca might be expected to adopt greener practices in its operations, from drug production to supply chain management.
- Waste Management: The pharmaceutical industry often produces hazardous waste. Proper disposal and management, aligned with environmental regulations, are vital to reduce environmental impact and potential legal issues.
- Energy Consumption: Reducing energy consumption in research labs, manufacturing units, and other facilities can lead to both cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint, reflecting positively on the company’s environmental commitment.
- Packaging: Sustainable packaging options that are biodegradable or recyclable can help in reducing the environmental impact of the company’s products.
- Environmental Regulations: Different countries have diverse regulations related to environmental protection. Compliance is crucial to avoid legal issues and potential reputational damage.
- Supply Chain Integrity: Ensuring suppliers and partners adhere to environmentally friendly practices is vital. The environmental lapses of suppliers can negatively impact AstraZeneca’s reputation.
- Transparency: Stakeholders expect transparency in environmental practices. Regular reporting on sustainability initiatives, carbon emissions, and other environmental metrics can enhance trust.
Legal
- Regulatory Approvals: One of the most significant legal factors for pharmaceutical companies is obtaining approval for their drugs from regulatory bodies like the FDA (U.S.), MHRA (U.K.), EMA (EU), etc. This process ensures that the drugs are safe and effective for use.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Rights: Pharmaceutical companies must protect patents, trademarks, and other IP rights. Patents allow companies like AstraZeneca to maintain exclusivity over their drug formulations, ensuring profitability.
- Clinical Trial Regulations: Adherence to legal norms during clinical trials, including patient consent, data protection, and trial transparency, is essential. Violations can lead to legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Pricing and Marketing: Various jurisdictions have laws regulating the pricing of medicines, especially for essential drugs. Additionally, there are rules governing how medicines can be advertised and marketed to both doctors and the public.
- Data Protection and Privacy: Pharmaceutical companies hold vast amounts of patient data from clinical trials and research. They must comply with data protection laws, such as the GDPR in Europe, to ensure the privacy and security of this data.
- Product Liability: Pharmaceutical companies can face legal claims if a drug or treatment causes harm or unforeseen side effects. Ensuring comprehensive testing and transparent communication about potential risks is critical.
- Competition and Antitrust Laws: These laws prevent companies from engaging in practices that might stifle competition, like price-fixing or monopolistic behavior.
- Import and Export Regulations: As a global company, AstraZeneca must navigate the complexities of international trade laws, including regulations about importing raw materials and exporting finished products.