Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of Alibaba. Alibaba Group is a Chinese multinational conglomerate specializing in e-commerce, technology, and other sectors. The company was founded by a group of 18 people led by Jack Ma in 1999, and it has grown exponentially since then. Here’s an overview of its primary businesses:
- Alibaba.com: This is the company’s original business. It’s a business-to-business (B2B) marketplace that connects manufacturers and wholesale sellers in China to businesses worldwide.
- Taobao: Launched in 2003, Taobao is a consumer-to-consumer (C2C) online marketplace similar to eBay in the United States. Individuals can buy and sell a broad range of goods.
- Tmall: Tmall is a platform for businesses to sell brand-name goods to consumers in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. It was introduced as a business-to-consumer (B2C) platform in 2008.
- AliExpress: AliExpress is a retail marketplace targeting consumers worldwide. It allows small businesses in China to sell to customers worldwide.
- Alipay: Alipay is a popular digital payment platform in China, similar to PayPal. It was launched by Alibaba but was spun off as a part of Ant Financial (later rebranded as Ant Group), which is an affiliate of the Alibaba Group.
- Alibaba Cloud: Alibaba Cloud provides a comprehensive suite of global cloud computing services to power international customers and Alibaba Group’s e-commerce ecosystem.
- Ant Group: Ant Group is a financial technology company that operates Alipay, the world’s largest mobile and online payments platform, and Yu’e Bao, the world’s largest money-market fund. It also provides financial services for small businesses. Although Ant Group is affiliated with Alibaba, it’s a separate entity.
- Cainiao Network: Cainiao is a logistics company launched by Alibaba. It operates a logistics information platform that provides real-time information access for buyers and sellers.
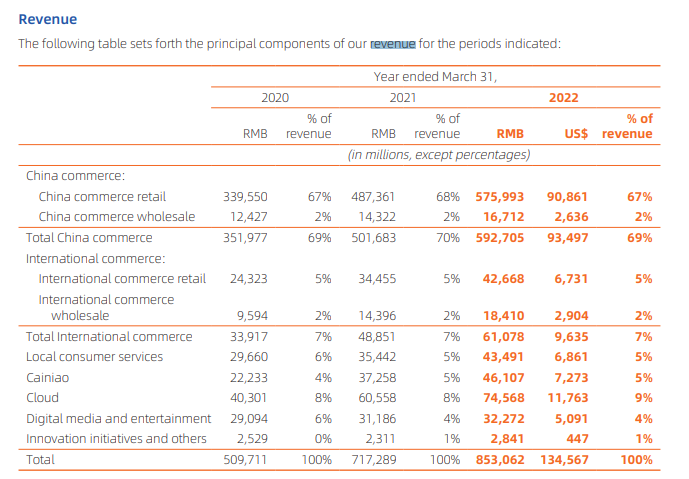
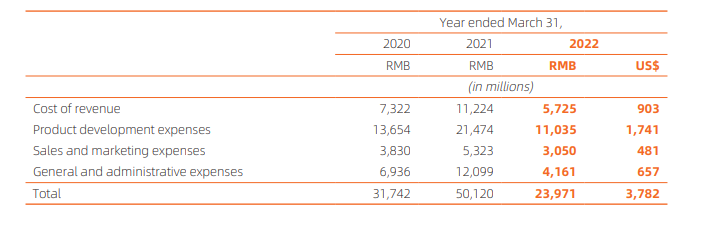
Financial Performance: Check the table below from its FY22 Annual Report.
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Alibaba
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Alibaba.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Chinese Government Policies: Alibaba operates primarily in China, and thus the company’s operations are significantly affected by the Chinese government’s policies. The Chinese government controls Internet access and content, affecting Alibaba’s operations. For instance, strict data privacy and cyber security regulations directly affect Alibaba’s business model.
- International Trade Policies: Alibaba has a global presence, so international trade policies can significantly impact its business. Import/export regulations, tariffs, trade agreements, or sanctions can influence Alibaba’s operational costs and market access. For instance, the US-China trade war had significant implications for Chinese companies, including Alibaba.
- Political Stability: Political stability in China and in countries where Alibaba operates is crucial. Political instability can disrupt business operations and affect consumer confidence, decreasing sales.
- Regulatory Changes: Any changes in regulations related to e-commerce, cross-border trade, data protection, etc., can affect Alibaba. For instance, in 2020, Chinese regulators suspended the IPO of Ant Group, an affiliate of Alibaba, leading to significant financial and reputational repercussions.
- Geopolitical Tensions: As Alibaba expands globally, geopolitical tensions between China and other nations can affect its business. Tensions can lead to stricter regulations, barriers to market entry, and other challenges.
Economic
- China’s Economic Growth: Alibaba’s success is closely tied to the economic growth of China, as the majority of its customers are based in the country. When the Chinese economy is doing well, consumers tend to have more disposable income, which can boost Alibaba’s revenues.
- Global Economic Conditions: As Alibaba expands its operations globally, the company becomes more exposed to global economic conditions. Economic downturns or uncertainty in key markets could negatively impact Alibaba’s revenues.
- Exchange Rates: Given Alibaba’s global presence, currency exchange rate fluctuations can significantly impact its profits. For example, a weaker Chinese Yuan against the US Dollar can make Alibaba’s goods more expensive for international customers, potentially affecting sales.
- Inflation and Interest Rates: High inflation rates can erode purchasing power and decrease consumer spending, impacting Alibaba’s sales. Similarly, changes in interest rates can affect Alibaba’s cost of capital, influencing investment decisions.
- E-commerce Market Growth: The overall economic health of the e-commerce industry is vital to Alibaba’s success. Factors such as increased internet penetration and growth in online shopping due to lifestyle changes or the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic can boost Alibaba’s revenues.
- Consumer Spending Patterns: Economic factors that influence consumer behavior, such as changes in income levels, employment rates, and consumer confidence, can affect Alibaba’s sales.
Sociocultural
- Changing Consumer Behaviors: With the digital revolution and the increased use of smartphones and the internet, consumer behaviors have significantly shifted towards online shopping. This change has dramatically benefitted Alibaba, increasing demand for its e-commerce platforms.
- Digital Literacy and Trust: The success of Alibaba depends on the level of digital literacy and the trust consumers have in online transactions. In markets where consumers have low digital literacy or lack trust in online transactions, Alibaba might face challenges in expanding its user base.
- Population Demographics: China’s population is rapidly aging. An aging population might impact the demand for certain products on Alibaba’s platforms. At the same time, the rising middle class in China represents a significant opportunity for Alibaba, as they typically have more disposable income and are more likely to shop online.
- Cultural Preferences: Consumers’ preferences in different cultures can affect the demand for Alibaba’s products. For instance, the success of Alibaba’s expansion into other countries depends on its ability to cater to the tastes and preferences of those markets.
- Social Trends: Sustainability and environmental consciousness can influence consumer preferences. For example, suppose consumers prefer to purchase from companies that demonstrate environmental responsibility. In that case, Alibaba might need to ensure that its operations and the products sold on its platforms align with these values.
Technological
- E-commerce Technologies: Alibaba’s business model is highly dependent on advancements in e-commerce technologies. This includes improvements in user interface design, mobile technology, payment systems, data analytics, and logistics technologies, which can help improve user experience, streamline operations, and enhance the efficiency of Alibaba’s platforms.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Alibaba uses AI and ML technologies for various purposes, such as personalized product recommendations, customer service (with AI chatbots), and fraud detection. The advancement and adoption of these technologies can significantly influence Alibaba’s competitiveness and effectiveness.
- Data Analytics: Alibaba collects vast amounts of data from its users. Advanced data analytics technologies can help Alibaba derive valuable insights from this data to understand customer behaviors and preferences better, optimize its operations, and make more informed business decisions.
- Blockchain Technologies: Blockchain technology can offer improved security and trust in online transactions, which could benefit Alibaba. For instance, it can track the provenance of goods and combat counterfeit products on Alibaba’s platforms.
- 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G technology can improve the speed and reliability of internet connections, which could enhance user experience on Alibaba’s platforms and boost the demand for its services.
- Cybersecurity: As an online platform, Alibaba faces significant cybersecurity risks. Advances in cybersecurity technologies are crucial for protecting Alibaba’s systems and user data from cyber threats.
- Cloud Computing: Alibaba Cloud is one of Asia’s leading cloud service providers. Technological advancements in cloud computing can present significant growth opportunities for Alibaba.
Environmental
- Carbon Footprint: As an e-commerce and logistics company, Alibaba contributes to carbon emissions through its delivery and logistics operations. There’s increasing pressure from consumers, governments, and society for companies to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Waste Management: E-commerce contributes to packaging waste. As one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies, Alibaba needs to reduce packaging waste and promote recycling.
- Energy Efficiency: The operation of data centers (like those used by Alibaba Cloud) consumes significant energy. Thus, improving energy efficiency and using renewable energy sources are important for reducing Alibaba’s environmental impact.
- Sustainable Products: There’s a growing trend among consumers to prefer products that are ethically sourced and environmentally friendly. Alibaba could benefit by ensuring that such products are available on its platforms.
- Regulations: Alibaba must also navigate environmental regulations both domestically in China and internationally. These could pertain to emissions, waste management, renewable energy, and more. Non-compliance can lead to legal ramifications and damage to reputation.
- Climate Change: Global climate change can have indirect effects on Alibaba. For example, extreme weather events could disrupt logistics and delivery services, impacting business operations.
Legal
- E-commerce Regulations: As an e-commerce company, Alibaba must adhere to laws governing online sales, consumer protection, data privacy, and cybersecurity in all markets where it operates. Any changes in these laws can have significant implications for Alibaba’s operations.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Alibaba has faced criticism and legal issues over counterfeit goods sold on its platforms. Compliance with intellectual property laws is essential to avoid legal problems and maintain trust with customers and brands.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws: As a digital platform, Alibaba collects and processes large amounts of user data. Compliance with data protection and privacy laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), is critical.
- Antitrust Laws: Like many large tech companies, Alibaba has faced scrutiny from antitrust regulators. In 2020, China started tightening regulations on monopolistic practices in the internet industry, which led to Alibaba being fined in 2021.
- Cross-Border Trade Laws: Since Alibaba operates globally, it needs to comply with laws and regulations related to cross-border trade, including customs regulations, tax laws, and export and import controls.
- Employment Laws: As a global employer, Alibaba must comply with employment laws in all countries. This includes laws related to working conditions, wages, diversity and inclusion, and labor rights.
- Environmental Laws: Alibaba must also comply with environmental laws and regulations affecting its business, from logistics operations to data centers.











