Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of Kia. Kia Motors Corporation, commonly known as Kia, is a South Korean multinational automotive manufacturer. It’s the second-largest automobile manufacturer in South Korea after Hyundai Motor Company. Here’s a brief overview of Kia Motors as of my last training data in 2021:
- History: Kia was founded in 1944 as Kyungsung Precision Industry. Initially, the company produced steel tubing and bicycle parts. By the 1950s, it had started building complete bicycles, and by the 1970s, it had transitioned to producing automobiles.
- Product Line: Kia offers a comprehensive range of vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, MPVs, and even hybrid/electric models. Some popular models include the Kia Seltos, Kia Telluride, Kia Soul, Kia Niro, and Kia Sportage.
- Innovation & Technology: Kia has actively developed electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids. They have also invested in autonomous driving technology and other innovative transportation solutions.
- Rebranding: In 2021, Kia underwent a significant rebranding. They dropped “Motors” from their name, becoming just “Kia” and introduced a new logo. This rebranding is part of their strategy to emphasize their move towards a broader mobility solutions provider, not just a car manufacturer.
- Partnership with Hyundai: Kia is a subsidiary of Hyundai Motor Group, one of the largest automotive groups in the world. The partnership allows both companies to share research, development costs, and technologies, enabling them to remain competitive in the global market.
- Financial Performance: Kia has historically shown steady sales growth, driven by its ability to offer quality vehicles at competitive prices. The brand has gained a reputation for its warranty offers, design, and value for money. Refer to the image below for more details.
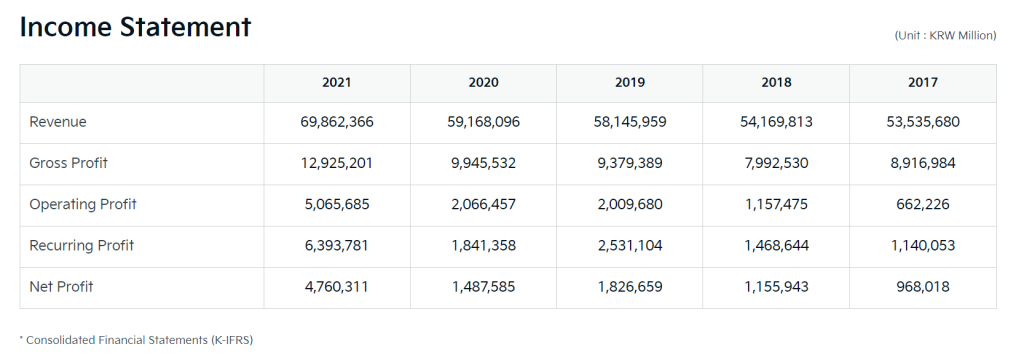
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Kia
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Kia.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Trade Policies and Tariffs: As a global brand, Kia is significantly affected by international trade policies. Tariffs and trade restrictions can influence where Kia establishes its manufacturing plants and how it exports and imports its vehicles.
- Regulatory Environment: Different countries have varying safety standards, emissions, and fuel efficiency regulations. Kia must ensure that its vehicles comply with these standards in all markets.
- Governmental Support & Incentives: Many governments are promoting using electric and hybrid vehicles to combat climate change. Incentives, tax breaks, or subsidies for manufacturing and purchasing green vehicles can benefit Kia, especially given its focus on EVs.
- Local Content Requirements: Some countries have local content requirements, which means a certain percentage of the product (vehicle) should be produced using local materials or labor. This can influence Kia’s manufacturing decisions and partnerships in those countries.
- Infrastructure Development: Government policies on developing transportation infrastructure (like EV charging stations) can support or hinder Kia’s growth, especially in electric vehicles.
- Taxation Policies: Changes in taxation policies, including import duties, VAT, and other taxes, can affect Kia’s pricing strategy and overall sales in specific markets.
Economic
- Global Economic Health: The overall health of the global economy significantly affects the automotive industry. In economic downturns, consumers may delay purchasing new cars or opt for cheaper alternatives. Conversely, higher demand for luxury or premium models might occur during economic booms.
- Exchange Rates: Kia Motors, a South Korean company, is impacted by the fluctuation of the South Korean Won against other major currencies. Exchange rate volatility can affect the profitability of overseas sales and the cost of imported components.
- Interest Rates: The cost of borrowing is crucial for both Kia (for capital investments or operations) and its consumers (for car loans). Higher interest rates can reduce consumer spending on big-ticket items like cars and increase the company’s operational costs.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation affects Kia’s cost structure and consumers’ purchasing power. Rising inflation can increase raw materials and components costs, potentially affecting profit margins.
- Fuel Prices: Fluctuations in fuel prices can influence consumer preferences. High fuel prices increase demand for fuel-efficient or alternative-energy vehicles, while lower prices boost sales of conventional gasoline models.
- Employment Levels: Employment rates in key markets affect consumers’ ability to purchase new vehicles. High unemployment can reduce car demand, while strong employment levels can boost consumer confidence and spending.
- Technological Investments: Economic growth and stability can influence the amount of money available for R&D. In a booming economy, Kia might have more resources to invest in developing new technologies or models.
- Supply Chain Costs: Economic factors like wage rates in manufacturing countries or raw material costs can influence vehicle production costs. These costs can affect Kia’s margins and its pricing strategy.
Sociocultural
- Consumer Lifestyle and Preferences: As urbanization grows, many city dwellers might prioritize compact, fuel-efficient cars that are easier to maneuver in congested areas. On the other hand, in regions with rough terrains or suburban areas, SUVs or larger vehicles might be more popular.
- Safety Concerns: Safety is a top priority for many car buyers. Cultures emphasizing family and security will likely prioritize vehicles known for their safety features and ratings.
- Status and Brand Perception: In many societies, a car is not just a mode of transportation but also a status symbol. The brand and model of a car can reflect one’s socioeconomic status, influencing buying decisions.
- Changing Family Dynamics: The structure and size of families can influence vehicle preferences. For instance, extended families might prefer multi-seater vehicles, while smaller nuclear families might opt for sedans or compact cars.
- Generational Shifts: Younger generations might have different preferences compared to older ones. For instance, millennials and Gen Z might be more tech-savvy and look for cars with advanced technological features or might be more inclined towards car-sharing than ownership.
- Cultural Attitudes towards Mobility: Some cultures may view car ownership as a rite of passage or a necessary milestone in adulthood, while others might see it as optional, especially with the rise of alternative transportation and ridesharing services.
Technological
- Electrification: The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly advancing, driven by environmental concerns and government incentives. Kia has invested in electric and hybrid vehicle technologies to remain competitive and meet stringent emissions regulations.
- Autonomous Driving: Advances in AI and machine learning are paving the way for autonomous or self-driving cars. While fully autonomous vehicles might still be in the future, many automakers, including Kia, are integrating semi-autonomous features such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking.
- Connectivity: Modern consumers expect vehicles to be an extension of their connected lives. Features like in-car Wi-Fi, smartphone integration, and advanced infotainment systems are now standard expectations. Kia has been working on enhancing its UVO connect system to offer a seamless connected car experience.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Innovations in manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and automation, can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enable more flexible production. Kia must ensure its manufacturing plants employ the latest technologies to remain cost-effective and adaptable.
- Lightweight Materials: With the push for better fuel efficiency and performance, there’s an industry-wide trend toward using lighter yet durable materials. This involves researching materials like aluminum, carbon fiber, and advanced plastics.
- Vehicle Safety Technologies: Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are becoming commonplace, with technologies like collision avoidance, pedestrian detection, and blind-spot monitoring. Like other automakers, Kia continually innovates in this space to improve vehicle safety.
- Battery Technology: Battery technology is a significant area of focus for electric and hybrid vehicles. Enhancements in battery efficiency, capacity, and charging times can significantly influence the adoption rate of EVs.
- Shared Mobility and Ride-Hailing: The rise of platforms like Uber and Lyft is changing how people think about car ownership and transportation. Kia needs to consider how its vehicles fit into this changing landscape, potentially partnering with such services or developing vehicles tailored to the needs of drivers on these platforms.
Environmental
- Emissions Standards: Governments worldwide are setting stringent emission standards to combat air pollution and climate change. Like all automakers, Kia must ensure its vehicles meet or exceed these regulations, pushing the company towards cleaner and more efficient technologies.
- Electrification Trend: There’s a global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) in response to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Kia has recognized this trend and is investing in EVs, planning to launch several new electric models in the coming years.
- Resource Depletion: Concerns about depleting natural resources emphasize the need for sustainable materials in car manufacturing. This means Kia has to consider alternative materials and sustainable sourcing for vehicle components.
- Recycling and Waste Management: Automakers are under pressure to ensure their vehicles are recyclable. Kia must ensure its cars are designed in a way that, at the end of their life cycle, most components can be recycled, reused, or responsibly disposed of.
- Green Manufacturing: The environmental impact of manufacturing operations is a significant concern. Kia has been taking measures to ensure its factories are energy-efficient, minimize waste, and reduce water consumption.
- Sustainable Supply Chain: The environmental impact isn’t just about Kia’s direct operations. The company must ensure its suppliers adhere to environmental standards, leading to a green and sustainable supply chain.
- Alternative Fuels: Besides electrification, there’s a push for alternative fuels like hydrogen fuel cells, biofuels, etc. Kia has been exploring these technologies as potential solutions for a more sustainable automotive future.
Legal
- Safety Standards: Governments worldwide have stringent safety standards that vehicles must meet before they can be sold. Kia Motors must ensure all its vehicles comply with these standards in every market.
- Emissions Regulations: As mentioned in the environmental section, emission standards are becoming stricter. Legal requirements around emissions can influence the design and technology used in Kia’s vehicles.
- Labor Laws: Kia operates in various countries, each with labor laws related to wages, working conditions, worker’s rights, and more. Kia must comply with these regulations to avoid legal disputes and protect its brand image.
- Intellectual Property Rights: In the automotive industry, innovation is rampant. Kia must protect its innovations, designs, and technologies through patents, trademarks, and copyrights. Conversely, they must ensure they don’t infringe on others’ intellectual property rights.
- Import and Export Regulations: Since Kia exports its vehicles to various countries, they must be familiar with and adhere to the import and export regulations of those countries, which might include tariffs, trade barriers, and quotas.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws protect consumers against fraudulent business practices. Kia has to ensure transparent marketing, genuine advertising claims, and provision of all necessary information to consumers.
- Recall Regulations: Automakers are legally obliged to recall affected vehicles in case of manufacturing defects that could compromise safety or performance. Compliance with such regulations is crucial to ensure customer safety and trust.
- Taxation and Corporate Laws: These laws differ from country to country and can impact Kia’s operations, profitability, and business strategies.











