Before we dive deep into the PESTEL analysis, let’s get the business overview of Ford. Ford Motor Company is one of the oldest automobile companies in the world. Henry Ford founded it on June 16, 1903. The company introduced revolutionary methods of mass production, such as the assembly line, which played a crucial role in the industrialization of many countries.
The core business of Ford revolves around the design, manufacture, marketing, and servicing of a full line of cars, trucks, SUVs, and electrified vehicles.
Ford operates globally with a significant presence in North America, Europe, South America, Asia Pacific, and Africa. Its headquarters is located in Dearborn, Michigan, USA.
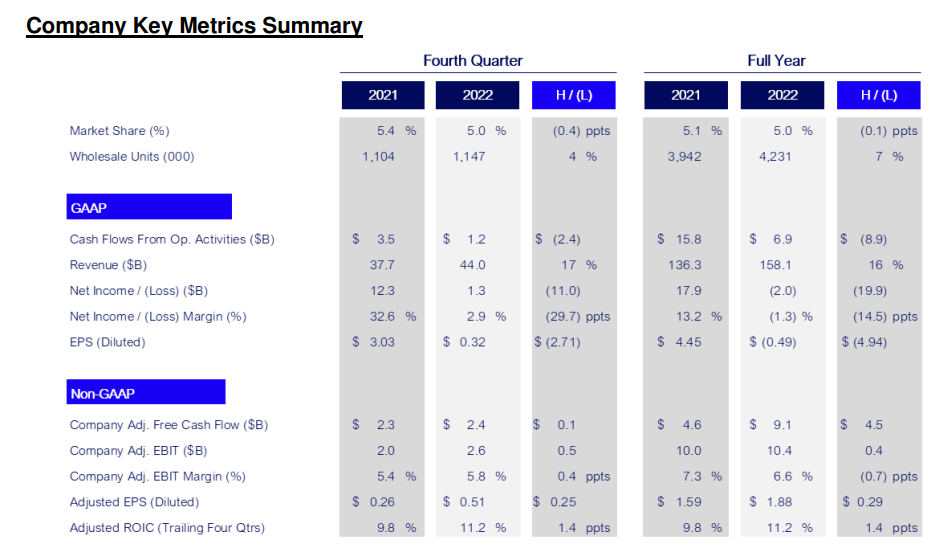
Financial Performance 2022: Ford generated $158 bn in revenue in 2022 at a loss of $2 bn. Details are as follows:
Here is the PESTEL analysis of Ford
A PESTEL analysis is a strategic management framework used to examine the external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization or industry. The acronym PESTEL stands for:
- Political factors: Relate to government policies, regulations, political stability, and other political forces that may impact the business environment.
- Economic factors: Deal with economic conditions and trends affecting an organization’s operations, profitability, and growth.
- Sociocultural factors: Relate to social and cultural aspects that may influence consumer preferences, lifestyles, demographics, and market trends.
- Technological factors: Deal with developing and applying new technologies, innovations, and trends that can impact an industry or organization.
- Environmental factors: Relate to ecological and environmental concerns that may affect an organization’s operations and decision-making.
- Legal factors: Refer to the laws and regulations that govern businesses and industries.
In this article, we will do a PESTEL Analysis of Ford.
PESTEL Analysis Framework: Explained with Examples
Political
- Government Stability: The stability of governments in countries where Ford operates can influence its business. Stable governments often mean consistent policies, which are preferable for long-term investments. On the other hand, political instability can lead to unpredictable regulation changes or even pose risks to company assets and employees.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs, trade barriers, and trade agreements can significantly affect Ford’s operations. For example, tariffs on steel or other essential materials would increase manufacturing costs. At the same time, favorable trade agreements can open up new markets or make producing cars in specific regions more cost-effective.
- Environmental Regulations: Political decisions about environmental standards can influence the production processes. Ford, like other automakers, needs to adhere to emission standards, which differ across countries. These regulations can dictate the type of vehicles that can be sold in certain regions (e.g., favoring electric vehicles over traditional combustion engines).
- Tax Policies: Corporate tax rates and incentives can influence where Ford might choose to invest or set up manufacturing plants.
- Safety Regulations: Governments regularly update safety regulations for vehicles. Companies like Ford must ensure that their vehicles comply with these standards, which might require design and feature updates.
- Foreign Policy and Diplomatic Relations: The relations between countries can impact Ford’s business. For instance, strained diplomatic ties might affect the ease of business or lead to boycotts in certain regions.
- Political Support for Innovation and Infrastructure: Governments may offer incentives for research and development or for building infrastructure like charging stations for electric vehicles. Such incentives can benefit companies like Ford in their push toward electrification.
- Public Transport Policies: If a government invests heavily in public transport, this could reduce the demand for private cars, which could, in turn, impact Ford’s sales.
Economic
- Economic Growth/Recession: The economy’s overall health can influence consumer purchasing power. In a growing economy, consumers are more likely to buy new vehicles, while car sales typically decline in a recession.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates set by central banks affect consumer financing for automobile purchases. Low-interest rates can encourage consumers to take out car loans, potentially boosting sales. Conversely, high rates might discourage buying.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Ford deals with multiple currencies as a global company. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the cost of production in one country or the relative price of cars in another. For instance, if the U.S. dollar strengthens against other currencies, Ford vehicles might become more expensive for foreign customers, potentially reducing sales abroad.
- Inflation Rates: Inflation affects both production costs and consumer purchasing power. High inflation can erode consumers’ buying capacity and increase production costs, impacting profitability.
- Unemployment Rates: High unemployment can decrease car demand as fewer people have the financial stability to make significant purchases.
- Fuel Prices: The price of fuel can influence consumer preferences. High fuel prices might push consumers towards more fuel-efficient or alternative energy vehicles, like hybrids or electric cars.
- Availability of Credit: The ease with which consumers can access credit impacts vehicle sales. If banks are willing to lend, it becomes easier for consumers to finance vehicle purchases.
- Raw Material Prices: The cost of raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, rubber, etc., can impact the manufacturing cost of vehicles. A spike in raw material prices can squeeze margins unless the company can pass these costs onto the consumer.
Sociocultural
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Societies evolve, and so do the preferences of their people. As urbanization increases and cities become more congested, there might be a preference shift from large vehicles to smaller, more maneuverable ones, or even towards car-sharing services.
- Environmental Consciousness: As awareness of environmental issues grows, there is a stronger push towards sustainable and eco-friendly vehicles. This can impact Ford’s production emphasis, pushing them towards electric vehicles (EVs), hybrids, and other eco-friendly models.
- Cultural Attitudes towards Cars: In some cultures, owning a car is a status symbol, while in others, especially some European cities, there’s a growing trend of living car-free due to environmental concerns or the availability of efficient public transportation.
- Demographic Changes: Aging populations in many developed countries might prioritize safety and comfort over speed or aesthetics. Conversely, younger populations might prioritize technological integration, connectivity, or unique designs.
- Lifestyle Changes: A rise in remote work might reduce the need for daily commuting, potentially impacting vehicle demand. Conversely, increased suburban or rural living might increase the demand for personal vehicles.
- Health and Wellness Trends: For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many people preferred personal vehicles over public transport due to health concerns. Societal emphasis on physical health might also increase demand for vehicles that can transport recreational equipment, like bicycles or kayaks.
- Gender Dynamics: As gender roles evolve, so do purchasing patterns. Women have become significant decision-makers in car purchases, influencing car design and marketing strategies.
- Attitudes Toward Technology: Societies that are more receptive to technological advancements might be more open to autonomous vehicles, sophisticated in-car tech features, and EVs.
Technological
- Electrification of Vehicles: The move towards electric vehicles (EVs) represents a significant technological shift in the automobile industry. Like other automakers, Ford has been investing heavily in EV technology to produce efficient and environmentally friendly cars.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving or autonomous vehicles are at the forefront of automotive technological advancements. Ford has been involved in research and development for autonomous driving technologies to remain at the cutting edge.
- Connectivity and Infotainment: Modern consumers demand vehicles that can seamlessly integrate with their digital lives. Features like advanced infotainment systems, smartphone integration, and onboard internet connectivity are becoming standard expectations.
- Advanced Manufacturing Technologies: Innovations like 3D printing, robotics, and AI-driven quality checks can optimize production processes, reduce costs, and enhance precision.
- Vehicle Safety Technologies: Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), like lane-keeping assistance, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking, leverage technology to improve vehicle safety.
- Shared Mobility Platforms: The rise of ride-sharing platforms like Uber and Lyft has influenced how vehicles are designed and utilized. Ford has explored partnerships and technologies in this domain, considering it a new business avenue.
- Battery Technology: EVs’ efficiency, cost, and performance largely depend on battery technology. Advancements in this area, such as solid-state batteries, can significantly improve the range, reduce costs, and increase the adoption rate of EVs.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies can enhance various aspects of the automotive experience, from predictive maintenance and personalizing driving experiences to optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: This refers to the communication of a vehicle with any entity it may come in contact with, such as other vehicles (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), or pedestrians (V2P). Such technologies can improve road safety and streamline traffic flow.
Environmental
- Emissions Regulations: Governments worldwide enforce stricter emissions standards to combat air pollution and climate change. Like all automakers, Ford needs to comply by producing vehicles that meet these standards, which often requires investment in cleaner technologies.
- Push for Electrification: With the global emphasis on reducing carbon footprints, there’s a push toward electric vehicles (EVs). Ford has been adapting to this trend by increasing its lineup of EVs and hybrids.
- Resource Scarcity: The availability and prices of certain raw materials, such as rare metals used in batteries, can impact production costs and strategies. Sustainable sourcing and recycling initiatives can become more crucial.
- Environmental Disasters: Natural disasters, potentially exacerbated by climate change, can disrupt production and supply chains. For instance, floods or hurricanes can affect manufacturing plants or the availability of components.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Regulations and societal expectations around waste reduction mean Ford must consider sustainable production practices, from reducing waste in manufacturing processes to developing more easily recyclable vehicles at the end of their lifecycle.
- Water Usage: Manufacturing vehicles require significant amounts of water. In areas where water scarcity is an issue, Ford might face challenges or be compelled to invest in water-saving technologies.
- Consumer Awareness and Preferences: An increasingly environmentally conscious consumer base might prefer vehicles that are seen as eco-friendly. This preference can shape Ford’s vehicle lineup and marketing strategies.
- Alternative Fuels: Beyond electrification, there’s research and interest in alternative fuels like hydrogen fuel cells. The viability and adoption of these technologies can influence the direction of Ford’s R&D.
- Sustainable Supply Chain: There’s a growing emphasis on producing eco-friendly products and ensuring the entire supply chain is sustainable. Ford might need to assess and ensure that its suppliers also adhere to sustainable practices.
- Biodiversity Concerns: The location and operation of manufacturing plants can impact local biodiversity. Ensuring operations don’t negatively affect local ecosystems can be vital for regulatory compliance and corporate social responsibility.
Legal
- Safety Standards: Automotive industries are subject to stringent safety regulations. These standards dictate various design, manufacturing, and operational aspects of vehicles to ensure the safety of the users and the public.
- Emissions and Environmental Laws: As mentioned in the environmental factors, regulations around vehicle emissions, pollution, and other environmental impacts can dictate the kinds of vehicles Ford can produce and sell in certain markets.
- Labor and Employment Laws: These laws vary by country and can impact hiring practices, wage determinations, worker safety, and union relations.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Protecting innovations through patents, trademarks, and copyrights is vital in a technology-driven industry. Conversely, Ford must also ensure it doesn’t infringe on others’ intellectual properties.
- Trade and Tariff Regulations: These dictate the terms under which Ford can import or export vehicles and parts. Changes in trade agreements or tariffs can significantly affect Ford’s global supply chain and pricing strategies.
- Antitrust and Competition Laws: These laws prevent companies from engaging in anti-competitive practices. Given the competitive nature of the automotive industry, Ford must ensure its practices align with these regulations.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These regulations protect consumers from fraudulent business practices and ensure that companies provide accurate product information. This could relate to advertising claims, warranty provisions, and vehicle recall procedures for Ford.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws: With modern vehicles collecting and transmitting various types of data, automakers like Ford must ensure they comply with global data protection standards, like the GDPR in Europe.
- Tax Laws and Regulations: Operating in multiple countries, Ford has to navigate diverse tax systems, ensuring compliance while strategically leveraging tax incentives where available.
- Import and Export Restrictions: Beyond just tariffs, certain countries may have restrictions on importing or exporting specific goods or technologies. This can impact how Ford sources materials or where it can sell certain vehicles.











