Before we dive deep into the SWOT analysis, let’s get the business overview of AWS. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Inc. It offers a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services, enabling businesses and developers to build, deploy, and manage applications, infrastructure, and services. Launched in 2006, AWS has become one of the world’s largest and most popular cloud computing platforms.
Key components of AWS’s business model include:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): AWS provides virtual servers, storage, and networking resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. Some key services in this category include Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): AWS offers managed platforms for building and deploying applications, abstracting away the underlying infrastructure. Examples of PaaS offerings include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, AWS Lambda, and AWS App Runner.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): AWS offers ready-to-use software applications hosted on its infrastructure. These applications are accessible over the internet and are billed on a subscription basis. Amazon Connect, Amazon WorkSpaces, and Amazon Chime are examples of SaaS offerings.
- Database and Data Management: AWS provides a wide range of managed database services, such as Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Aurora, catering to different use cases like relational, NoSQL, and in-memory databases.
- Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: AWS offers a suite of AI and ML services, including Amazon SageMaker for building, training, and deploying machine learning models; Amazon Rekognition for image and video analysis; and Amazon Lex for building conversational interfaces.
- Analytics: AWS provides services for processing, storing, and analyzing large volumes of data. Examples include Amazon Redshift (data warehousing), Amazon Kinesis (real-time data streaming), and Amazon EMR (big data processing).
- Security and Compliance: AWS offers tools and services to help customers meet their security and compliance requirements. Some examples include Amazon GuardDuty, AWS Security Hub, and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Internet of Things (IoT): AWS provides a suite of services to support IoT applications, such as AWS IoT Core, AWS IoT Device Management, and AWS IoT Greengrass.
- Developer Tools: AWS offers a range of tools and services to help developers build, deploy, and manage applications, such as AWS CodeStar, AWS Cloud9, and AWS X-Ray.
AWS operates on a global scale, with data centers spread across multiple regions and availability zones, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. The platform is known for its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, which attracts businesses of all sizes, from startups to enterprises.
AWS has a vast ecosystem of partners, including independent software vendors (ISVs), system integrators (SIs), and managed service providers (MSPs), which contribute to its growth and adoption.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) currently generates the majority of Amazon’s operating profits and is growing at a robust pace. In 2023, Amazon Web Services (AWS) generated 90.8 billion US dollars with its cloud services.
Here’s a SWOT analysis for AWS:
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business, project, or individual. It involves identifying the internal and external factors that can affect a venture’s success or failure and analyzing them to develop a strategic plan. In this article, we do a SWOT Analysis of AWS.
SWOT Analysis: Meaning, Importance, and Examples
Strengths
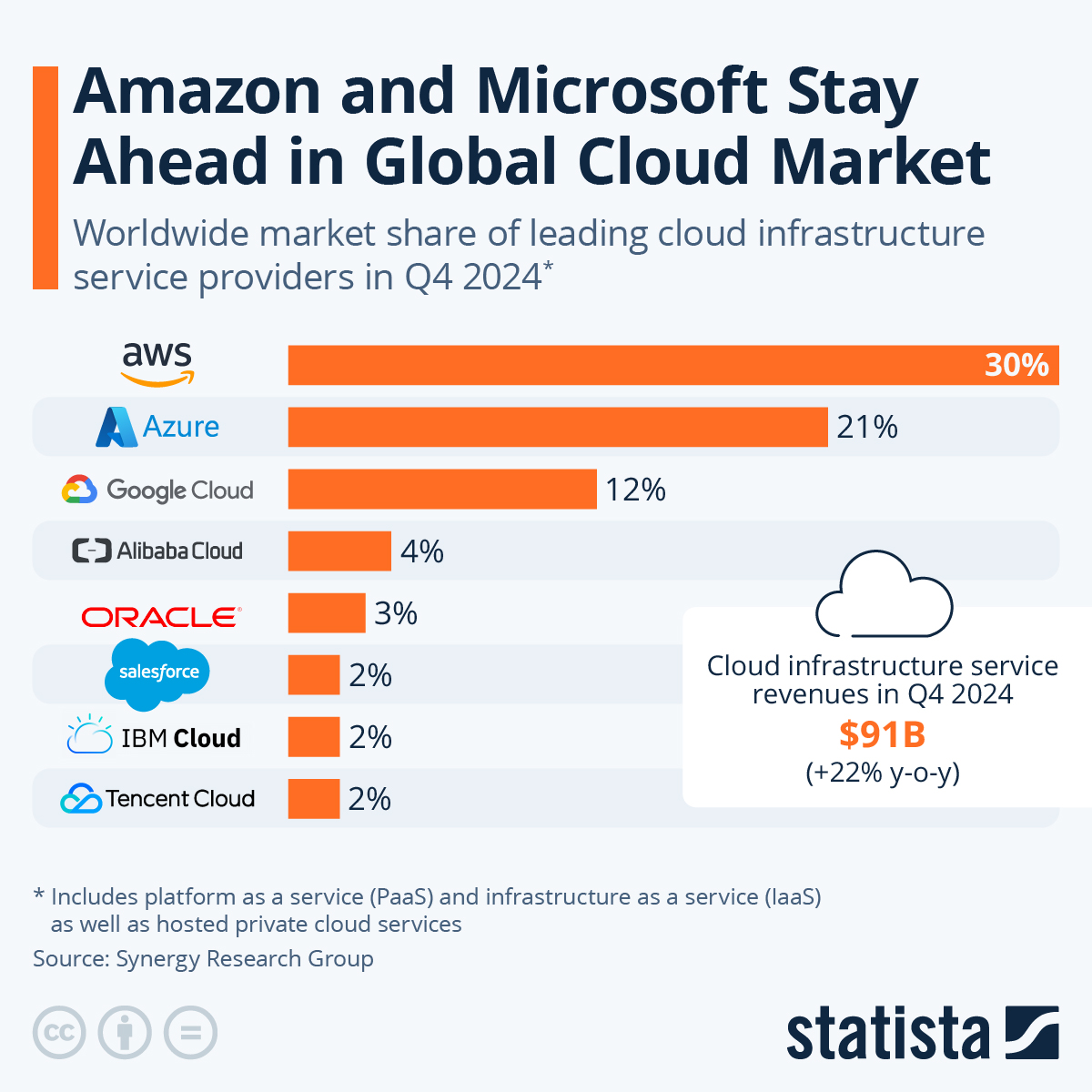
- Market Leadership: AWS is the leading cloud service provider, holding a significant market share and setting the pace for the industry regarding innovation, functionality, and scale.
- Comprehensive Service Offerings: AWS has an extensive and continually expanding portfolio of services, catering to various customer needs across IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. This broad range of offerings attracts diverse customers and use cases.
- Global Infrastructure: AWS has a vast network of data centers across multiple regions and availability zones worldwide. This global presence allows AWS to provide customers with worldwide low-latency access, high availability, and fault tolerance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: AWS enables customers to quickly scale their infrastructure up or down as per their requirements, providing a highly flexible and agile environment for businesses.
- Cost-Effectiveness: AWS follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which allows customers to pay only for the resources they use. This model and the platform’s scalability help businesses optimize their IT costs.
- Innovation and Continuous Improvement: AWS is known for its rapid pace of innovation, regularly introducing new services and features to address emerging customer needs and stay ahead of the competition.
- Strong Ecosystem: AWS has built a robust ecosystem of partners, including ISVs, SIs, and MSPs, which helps extend its reach and adds value to the platform through specialized expertise, complementary services, and support.
- Security and Compliance: AWS strongly focuses on security and compliance, offering various tools and services to help customers meet their requirements. The platform also adheres to industry-specific standards and certifications, building customer trust.
- Developer Support and Resources: AWS offers extensive documentation, tutorials, SDKs, and tools to support developers, making it easy to build, deploy, and manage applications on the platform.
- Brand Reputation: As a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Inc., AWS benefits from the strong reputation and credibility associated with the Amazon brand, which is known for its customer-centric approach and technological prowess.
 You will find more infographics at Statista
You will find more infographics at Statista
Weaknesses
- Complexity: AWS’s vast array of services and features can be overwhelming for new customers, leading to a steep learning curve. This complexity can make it challenging for businesses to adopt and optimize the platform effectively.
- Pricing: While AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, its pricing structure can be complicated, with many factors affecting the overall cost. Customers might find predicting and managing their cloud expenses difficult, leading to unexpected costs.
- Vendor Lock-in: As organizations increasingly rely on AWS services, they may become dependent on the platform, making it difficult to switch to alternative cloud providers without significant effort, time, and resources.
- Customer Support: AWS’s basic customer support is often considered limited, with users requiring higher levels of support needed to pay for premium support plans. This can result in dissatisfaction among customers seeking prompt and comprehensive assistance.
- Multi-cloud Strategy: Some customers want to adopt a multi-cloud strategy to distribute workloads and mitigate risks. AWS’s primary focus on its cloud platform can make it less appealing for organizations seeking a seamless multi-cloud experience.
- Competition: AWS faces intense competition from other major cloud service providers, such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform, continuously improving their offerings and investing in their cloud businesses. This competition can impact AWS’s growth and market share.
- Perception of Potential Conflicts of Interest: As a subsidiary of Amazon.com, Inc., AWS sometimes faces customer concerns that Amazon’s retail and e-commerce businesses may compete with their own. This perception of potential conflicts of interest might deter some customers from using AWS services.
- Outages: Although AWS is known for its high availability and fault tolerance, it is not immune to service outages. Any significant downtime can impact the platform’s reputation and affect customer trust.
Opportunities
- Growing Cloud Adoption: As more businesses and organizations of all sizes embrace cloud computing for their IT infrastructure, AWS can leverage its market leadership and comprehensive services to attract new customers.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: AWS can tap into the growth potential of emerging markets, such as Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia, by investing in local infrastructure and tailoring its offerings to meet regional demands.
- Vertical-specific Solutions: AWS can develop industry-specific solutions catering to the unique requirements of sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing. These tailored solutions can help AWS attract customers from these industries and deepen its penetration.
- Strengthening Hybrid Cloud and Multi-cloud Capabilities: To address the growing demand for hybrid and multi-cloud solutions, AWS can enhance its integration with on-premises and third-party cloud environments, making it easier for organizations to adopt and manage mixed cloud infrastructure.
- Edge Computing and IoT: AWS can expand its edge computing and IoT offerings to help businesses process and analyze data closer to the source, enabling faster decision-making and real-time insights.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies: By developing more blockchain and distributed ledger technology solutions, AWS can help customers implement secure, transparent, decentralized applications across various industries.
- Focus on Sustainability: As environmental concerns become increasingly important, AWS can invest in renewable energy and sustainable practices for its data centers, strengthening its commitment to environmental responsibility and attracting eco-conscious customers.
- Partnerships and Acquisitions: AWS can continue to forge strategic alliances and acquisitions to strengthen its ecosystem, broaden its service offerings, and expand its customer base.
- Training and Certification Programs: By expanding its training and certification programs, AWS can help businesses overcome the platform’s complexity and equip their workforce with the necessary skills to leverage AWS services effectively.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AWS can continue to invest in AI and ML capabilities to provide advanced analytics, automation, and personalization features, making its platform more valuable and attractive to customers.
Threats
- Competition: AWS faces fierce competition from other major cloud services providers, such as Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Alibaba Cloud. These competitors continuously improve their offerings, which may erode AWS’s market share or force it to lower prices.
- Market Saturation: As the cloud computing market matures, growth rates may slow down, making it increasingly challenging for AWS to maintain its current pace of revenue growth.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Data breaches, cyberattacks, and privacy violations can damage AWS’s reputation and customer trust. Regulatory changes related to data privacy, such as GDPR and CCPA, can also affect AWS’s operations and require additional investments in compliance.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: AWS may face increased regulatory scrutiny and legal challenges in various jurisdictions, affecting its ability to operate or expand its services. Regulations around data sovereignty, for example, may force AWS to invest in more localized data centers.
- Economic Uncertainty: Economic downturns or geopolitical instability can lead to reduced IT spending, impacting AWS’s revenues and growth prospects.
- Vendor Lock-in Concerns: As customers become more concerned about vendor lock-in, they may seek alternative solutions or multi-cloud strategies that enable them to avoid overdependence on a single provider, potentially reducing AWS’s market share.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: The rapidly evolving technology landscape requires skilled professionals, and AWS faces intense competition for talent. Attracting and retaining the right talent is crucial for the company’s ability to innovate and maintain its competitive edge.
- Technological Disruptions: Emerging technologies or disruptive innovations in the cloud computing landscape could challenge AWS’s dominance, requiring continuous investment in research and development to stay ahead of the competition.
- Environmental Impact: AWS’s data centers consume significant amounts of energy, which could lead to increased scrutiny regarding its environmental impact. The company may face pressure to adopt more sustainable practices and invest in renewable energy sources.
- Conflicts of Interest: AWS’s relationship with Amazon.com may raise concerns among some customers that the retail giant could access their data or compete with their businesses, making them hesitant to adopt AWS services.











